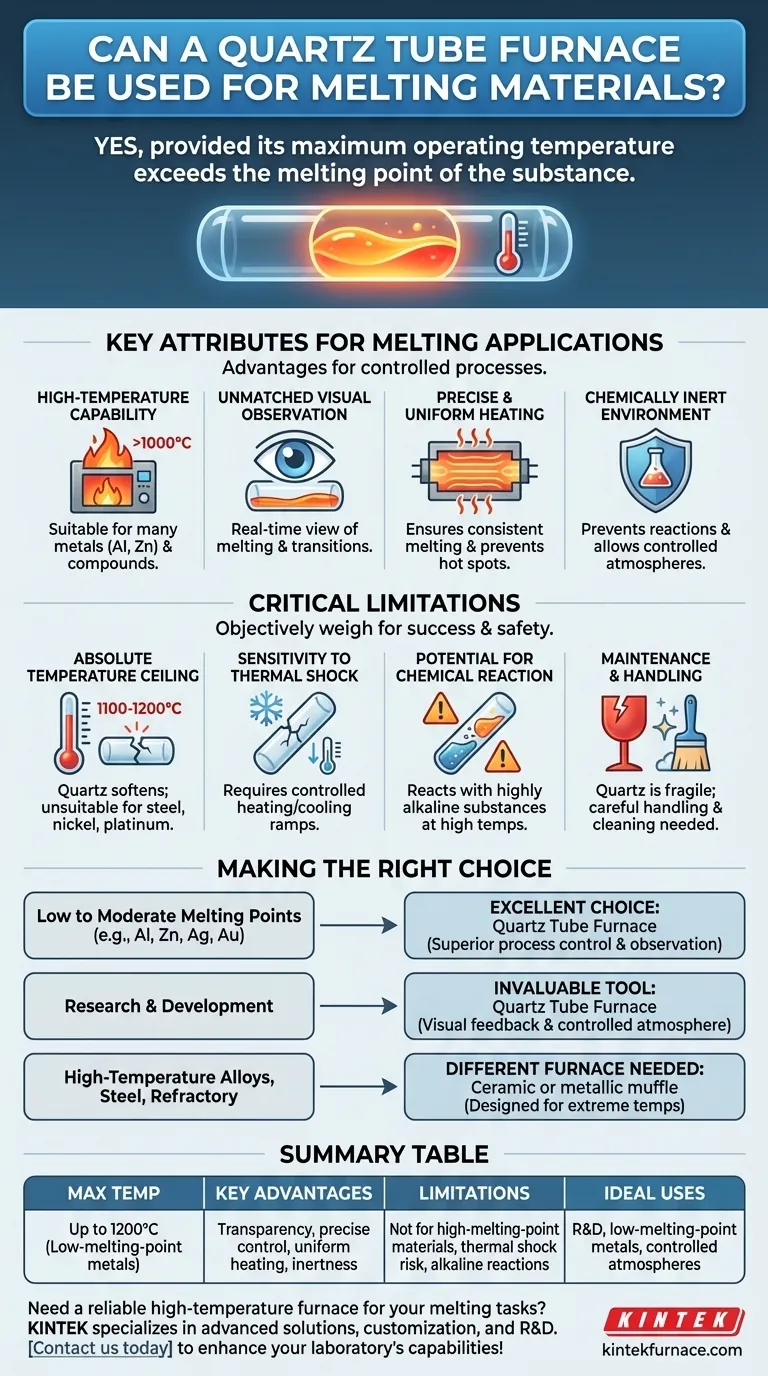
Yes, a quartz tube furnace can be used for melting materials, provided its maximum operating temperature exceeds the melting point of the substance you are working with. The suitability of the furnace is not a simple yes or no, but rather a function of matching the equipment's specifications to the physical properties of your material.
The decision to use a quartz tube furnace for melting hinges on a single critical factor: its temperature capability relative to your material's melting point. Its unique features, like transparency and chemical inertness, make it an exceptional tool for the right applications.
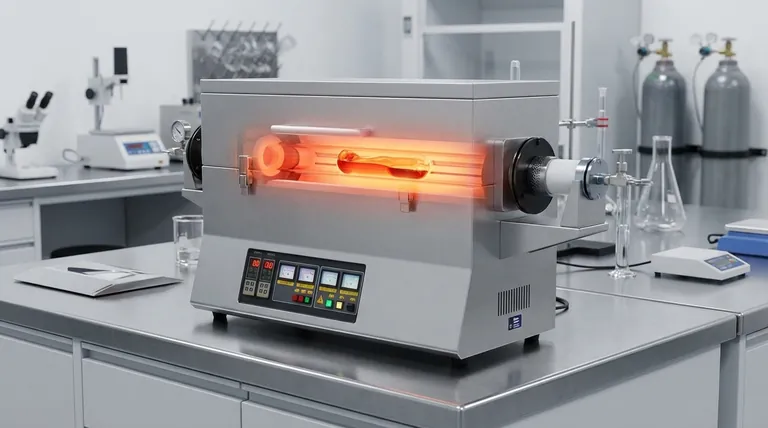

Key Attributes for Melting Applications
A quartz tube furnace is not just a simple heater; its design offers several distinct advantages for controlled melting processes. Understanding these features is key to leveraging the equipment effectively.
High-Temperature Capability
Most standard quartz tube furnaces are designed to operate at temperatures exceeding 1000°C. This makes them suitable for melting a wide range of materials, including many common metals (like aluminum or zinc) and various chemical compounds.
Unmatched Visual Observation
The most significant advantage of a quartz tube is its transparency. This allows for real-time, direct observation of the material as it heats, transitions to a liquid state, and cools. This visual feedback is invaluable for process control, research, and quality assurance.
Precise and Uniform Heating
These furnaces are engineered for precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution along the length of the tube. This prevents hot spots and ensures the entire sample melts consistently, which is critical for creating homogenous alloys or compounds.
A Chemically Inert Environment
Quartz is chemically inert to most substances, even at high temperatures. This prevents reactions between the furnace and the melt, ensuring the purity of your final material. The sealed tube design also allows for melting under a controlled atmosphere (e.g., inert gas) to prevent oxidation.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
While powerful, a quartz tube furnace is not a universal solution for all melting tasks. Objectively weighing its limitations against its benefits is crucial for success and safety.
The Absolute Temperature Ceiling
The primary limitation is the material of the tube itself. While high-purity quartz is robust, it begins to soften at temperatures around 1100-1200°C. Pushing the furnace beyond its rated maximum temperature risks catastrophic failure of the tube. It is unsuitable for melting high-temperature materials like steel, nickel, or platinum.
Sensitivity to Thermal Shock
Quartz can crack if subjected to rapid temperature changes. Heating and cooling cycles must be carefully controlled with programmed ramps. An accidental rapid cool-down, such as exposing a hot tube to cool air, can easily fracture it.
Potential for Chemical Reaction
Although generally inert, quartz (silicon dioxide) can react with highly alkaline substances (basic oxides) or certain reactive metals at very high temperatures. This can etch and weaken the tube over time, compromising both the equipment and the sample purity.
Maintenance and Handling
The quartz tube is the most fragile component. It requires careful handling and cleaning according to the manufacturer's instructions, typically with soft materials and appropriate solvents. Scratches or contamination can create stress points that lead to failure at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Melting Task
To determine if a quartz tube furnace is the correct tool, evaluate your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is melting metals with low to moderate melting points (e.g., aluminum, zinc, silver, gold): A quartz tube furnace is an excellent choice, offering superior process control and observation.
- If your primary focus is research and development of new materials: The visual feedback and controlled atmosphere capabilities make this furnace an invaluable tool for understanding material behavior.
- If your primary focus is melting high-temperature alloys, steel, or refractory materials: You must use a different type of furnace (such as one with a ceramic or metallic muffle) designed to safely handle those extreme temperatures.
By carefully aligning the furnace's specifications with your material's properties, you can effectively leverage its unique advantages for your melting application.
Summary Table:
| Attribute | Details for Melting Applications |
|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1200°C, suitable for low-melting-point metals (e.g., aluminum, zinc, gold) |
| Key Advantages | Transparency for visual observation, precise temperature control, uniform heating, chemical inertness |
| Limitations | Not for high-melting-point materials (e.g., steel), sensitive to thermal shock, potential reactions with alkaline substances |
| Ideal Uses | R&D, melting low-melting-point metals, processes requiring controlled atmospheres |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace for your melting tasks? KINTEK specializes in advanced solutions like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, backed by deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing for precise, efficient results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















