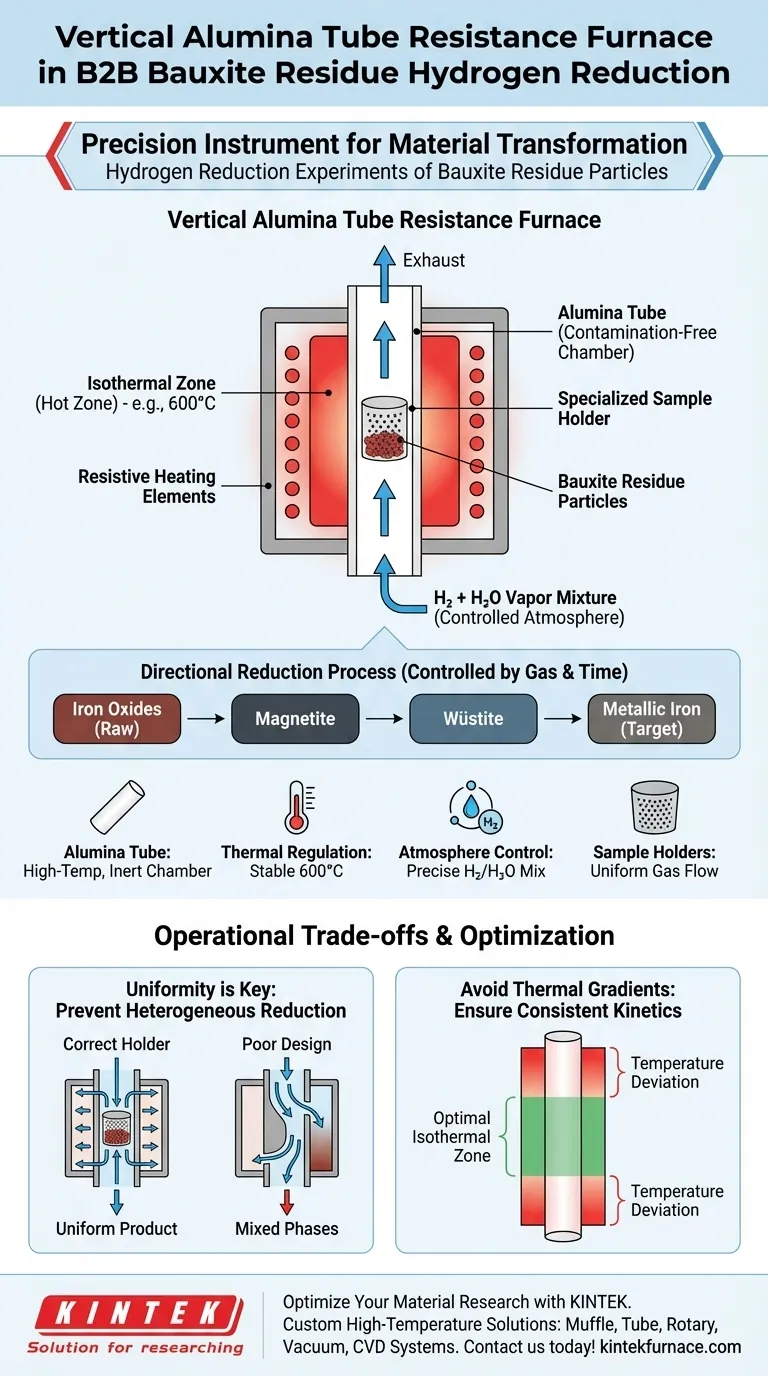
The vertical alumina tube resistance furnace serves as the central reaction vessel for hydrogen reduction experiments on bauxite residue. It functions by creating a strictly controlled environment where specific thermal conditions and chemical atmospheres converge to alter the material's composition.
By maintaining a constant temperature, such as 600 degrees Celsius, and utilizing specialized holders for uniform gas distribution, this apparatus drives the directional reduction of iron oxides found within the residue.
Core Takeaway: The furnace is not just a heat source; it is a precision instrument that synchronizes thermal stability with gas flow dynamics. This synchronization allows researchers to selectively target specific reduction phases—transforming iron oxides into magnetite, wüstite, or metallic iron—by manipulating the hydrogen-water vapor atmosphere.

Creating the Reaction Environment
Precise Thermal Regulation
The primary function of the resistance furnace is to establish a stable thermal field.
Through the use of resistive heating elements, the system achieves and maintains specific target temperatures.
The primary reference highlights 600 degrees Celsius as a standard operating temperature for these specific reduction experiments, ensuring the energy input is consistent throughout the process.
Atmosphere Control via Alumina
The core component is the alumina tube, which houses the reaction.
Alumina is selected for its ability to withstand high temperatures and maintain structural integrity without contaminating the chemical process.
This tube acts as the isolation chamber where the chemical atmosphere—specifically a mixture of hydrogen and water vapor—is introduced and regulated.
Mechanics of the Reduction Process
Uniform Gas Interaction
Success in these experiments relies on how the gas interacts with the solid particles.
The furnace employs specialized sample holders designed to optimize this interaction.
These holders ensure a uniform flow of the hydrogen-water vapor mixture around the bauxite residue particles, preventing "dead zones" where the reaction might stall.
Directional Reduction
The ultimate goal of applying this furnace is to achieve directional reduction.
This means the environment is tuned to strip oxygen from iron oxides in a predictable sequence.
Under these controlled conditions, iron oxides are systematically converted into magnetite, then wüstite, and finally into metallic iron, depending on the specific duration and gas composition used.
Operational Trade-offs
The Necessity of Uniformity
While this furnace setup is effective, it is highly sensitive to the distribution of gas flow.
If the specialized sample holders are not configured correctly, the hydrogen mixture may channel through the path of least resistance.
This results in heterogeneous reduction, where some particles achieve the metallic iron state while others remain as oxides due to a lack of contact with the reducing agent.
Thermal Gradients
Despite the goal of a constant temperature, vertical tube furnaces can experience thermal gradients along the tube length.
Users must ensure the sample is positioned exactly within the furnace's isothermal zone (the "hot zone").
Placing the sample too high or too low in the tube can lead to reaction temperatures significantly different from the setpoint, altering the final phase composition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a vertical alumina tube resistance furnace in your experiments, consider your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is Phase Selectivity (e.g., stopping at Magnetite): Prioritize precise temperature calibration and monitor the ratio of water vapor to hydrogen to halt the reduction at the desired stage.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Efficiency: Ensure your sample holder design maximizes surface area exposure to the gas flow to reduce processing time.
The vertical alumina tube furnace provides the requisite control to turn raw bauxite residue into valuable iron phases, provided the thermal and chemical variables are strictly managed.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Hydrogen Reduction Experiments |
|---|---|
| Alumina Tube | Provides a high-temperature, contamination-free isolation chamber for chemical reactions. |
| Thermal Regulation | Maintains stable temperatures (e.g., 600°C) to drive specific iron oxide phase changes. |
| Atmosphere Control | Enables precise mixing of hydrogen and water vapor for directional reduction. |
| Sample Holders | Designed to ensure uniform gas distribution and prevent heterogeneous reduction. |
| Isothermal Zone | The specific 'hot zone' location required to ensure consistent reaction kinetics. |
Optimize Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a successful reduction and a failed experiment. KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, specifically engineered for demanding lab environments.
Whether you are targeting phase selectivity in bauxite residue or scaling complex chemical vapor depositions, our expert R&D and manufacturing teams offer fully customizable furnaces to meet your unique thermal and atmospheric needs.
Ready to elevate your lab's performance? Contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Dali Hariswijaya, Jafar Safarian. Studying the Sintering Behavior of H2-Reduced Bauxite Residue Pellets Using High-Temperature Thermal Analysis. DOI: 10.3390/ma18102378
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab
- Why must air inlets be equipped with HEPA filters? Preventing Fiber Backflow in Split Tube Furnace Enclosures
- What is the function of a Tube Furnace in S-C3N4 preparation? Optimize Sulfur-Doped Carbon Nitride Synthesis
- How does a laboratory tube furnace achieve controlled atmosphere sintering? Master Precision Catalytic Prep
- Why is a vacuum pump used to treat the tube reactor before CVD of g-C3N4? Ensure High-Purity Thin Film Growth
- What is the specific function of a high-temperature tube furnace for MXene-NiCo2Se4? Master the Selenization Process
- How does the horizontal design of these furnaces benefit large volume processing? Boost Efficiency and Uniformity
- What are the main applications of a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Thermal Processing



















