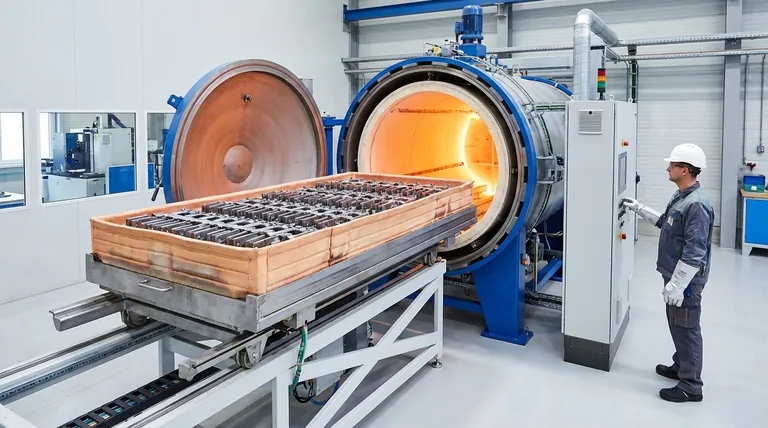
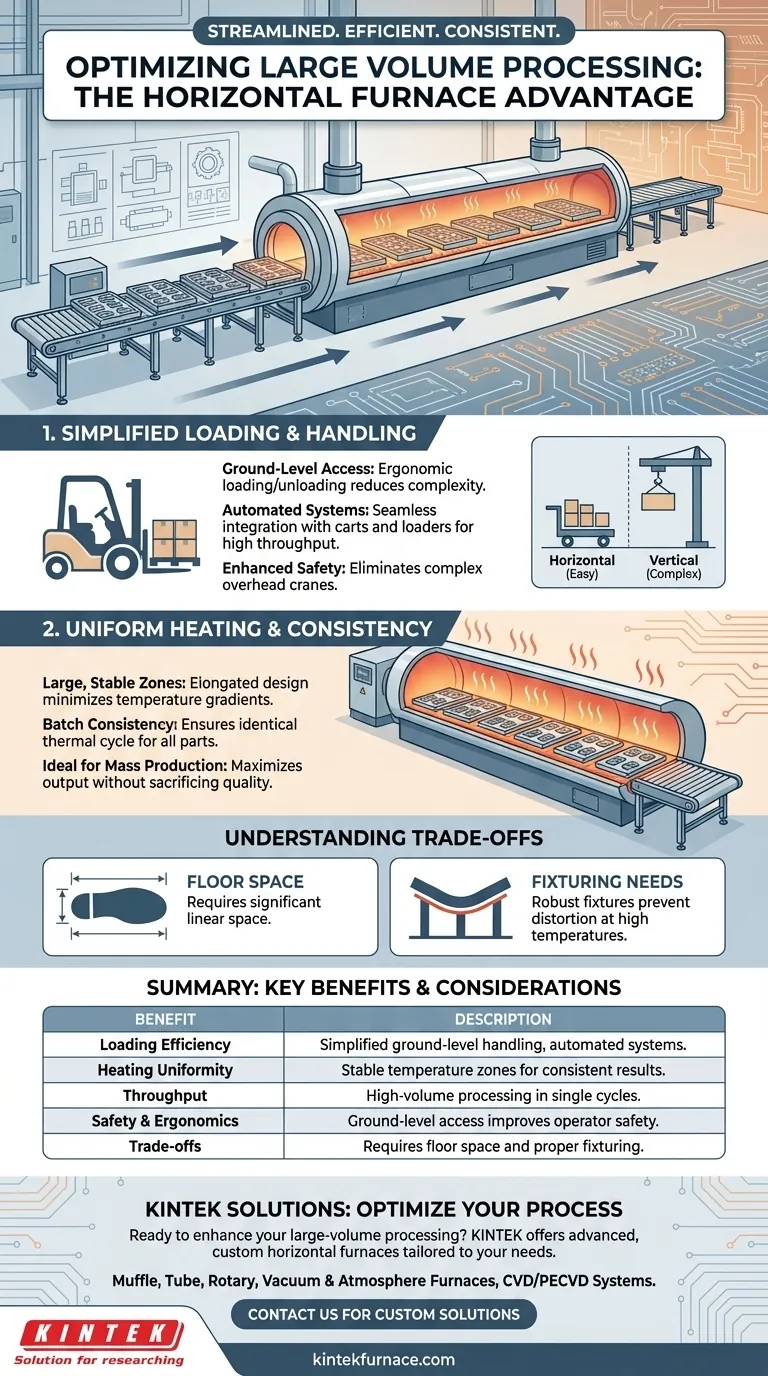
At its core, a horizontal furnace design benefits large-volume processing by simplifying the two most critical stages: loading the material and heating it uniformly. This orientation allows for streamlined, ground-level material handling and creates an ideal environment for consistent thermal treatment across a large batch of parts, making it a cornerstone of high-throughput manufacturing.
The primary advantage of a horizontal furnace is not merely its orientation, but how this design facilitates the use of efficient, automated material handling systems and ensures uniform heating, which are the key requirements for reliable, large-scale production.

The Mechanics of Efficient Loading
The most immediate benefit of a horizontal design is seen before the heating process even begins. The ease of loading and unloading directly translates to higher throughput and reduced operational complexity.
Streamlined Material Handling
Horizontal furnaces are designed for straightforward, linear movement. Workloads are typically placed on trays or in baskets that can be rolled or conveyed directly into the chamber on integrated carts or automated loaders.
This eliminates the need for complex overhead cranes or hoists often required for top-loading vertical furnaces, simplifying the entire material handling workflow.
Enhanced Accessibility and Safety
Loading a furnace at waist or floor level is inherently safer and more ergonomic than managing a suspended load.
Operators can easily access the workload for placement, adjustment, and post-process inspection. This ground-level access simplifies the integration of the furnace into a production line.
Optimizing the Thermal Process
Beyond loading, the horizontal chamber geometry is uniquely suited for processing large volumes of material with high consistency.
Creating Uniform Temperature Zones
The elongated shape of a horizontal hot zone allows for the creation of large, stable areas of uniform temperature. This is critical for processes like brazing, annealing, or sintering, where every part in a large batch must experience the exact same thermal cycle.
This design minimizes temperature gradients, ensuring consistent metallurgical properties across the entire workload.
Ideal for Batch Consistency
The flat, expansive loading area allows numerous parts to be laid out in a single layer or in structured baskets. This arrangement ensures that each part is equally exposed to the heating elements and vacuum environment.
By processing more parts in a single, reliable cycle, the furnace maximizes output without sacrificing quality control.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the horizontal design is not universally superior. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Floor Space Considerations
Horizontal furnaces, by their nature, require a significant amount of linear floor space. In a crowded facility where square footage is at a premium, a vertical furnace with a smaller footprint might be a more practical choice.
The overall length must account for the furnace body, the loading/unloading area, and any associated conveyance systems.
The Need for Proper Fixturing
For long, heavy, or delicate parts, the risk of sagging or distortion at high temperatures can be a concern in a horizontal orientation.
This necessitates the use of robust, well-designed fixtures and supports to maintain the geometric integrity of the parts throughout the thermal cycle. The design and cost of this fixturing must be factored into the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace orientation depends entirely on your specific production goals, facility constraints, and the nature of the parts being processed.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput batch production: The horizontal design is the default choice due to its unmatched efficiency in loading and processing large, standardized workloads.
- If your primary focus is conserving factory floor space: A vertical furnace may be more suitable, as its footprint is significantly smaller for a given chamber volume.
- If your primary focus is processing very long, slender parts that must not distort: A vertical furnace, where the part can be hung to prevent sagging, might offer a distinct advantage.
Understanding these fundamental design principles empowers you to select the equipment that best aligns with your operational and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Loading Efficiency | Simplified ground-level handling with automated systems, reducing complexity and time |
| Heating Uniformity | Elongated chamber design creates stable temperature zones for consistent batch results |
| Throughput | Enables high-volume processing in single cycles, ideal for mass production |
| Safety and Ergonomics | Ground-level access improves operator safety and ease of use |
| Trade-offs | Requires more floor space and proper fixturing to prevent part distortion |
Ready to optimize your large-volume processing with a custom horizontal furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and output!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace contribute to the thermal treatment process of chalcopyrite ore?
- How is the thermal stability of KBaBi compounds evaluated? Discover Precise XRD & Heat Treatment Limits
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics



















