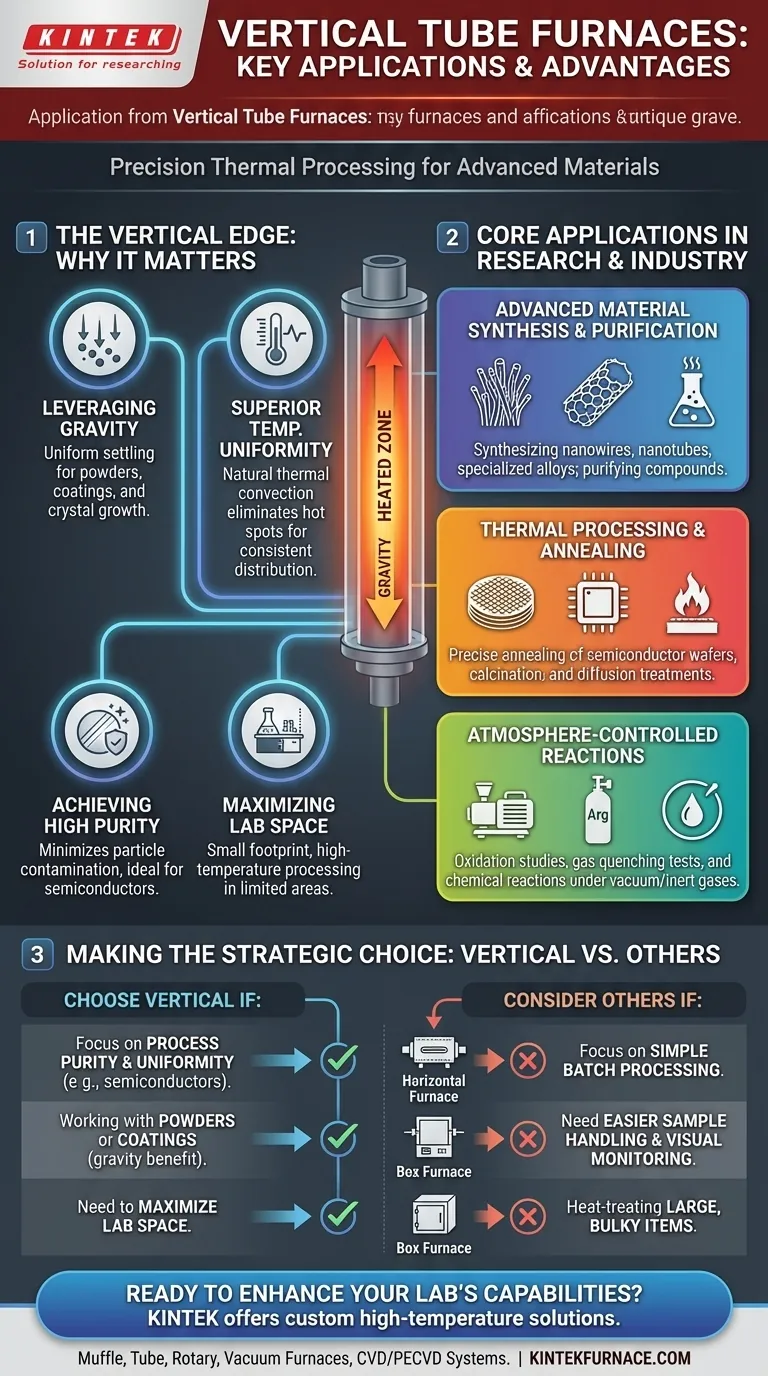
At its core, a vertical tube furnace is a highly specialized piece of equipment designed for precise thermal processing. Its main applications include advanced material synthesis, purification, annealing, calcination, and gas quenching tests, particularly in settings where process purity, temperature uniformity, and the influence of gravity are critical factors for success.
While versatile across many heat treatment tasks, the decision to use a vertical tube furnace over other designs is strategic. Its primary advantage lies in processes that benefit from gravity's influence, require a minimal footprint, or demand the highest level of temperature uniformity and control.

Why the Vertical Orientation Matters
Understanding the applications of a vertical tube furnace begins with appreciating why its orientation is a significant design feature, not an arbitrary choice. The vertical setup provides distinct physical advantages for specific processes.
Leveraging Gravity for Uniformity
The most defining characteristic is its ability to use gravity to its advantage. For processes involving powders, liquids, or vapors, gravity ensures even settling and uniform coating on substrates.
This is also essential for applications like crystal growth or certain types of chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where a downward flow helps create a more consistent final product. Some processes even involve dropping samples from the top into a precise heat zone, a method unique to this design.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
A vertical tube naturally promotes more stable and uniform thermal convection. As air or process gas is heated, it rises, creating a natural circulatory loop within the tube.
This consistent flow helps eliminate hot spots and cold spots, resulting in exceptionally uniform temperature distribution along the length of the sample. This is critical for sensitive processes like the thermal annealing of semiconductor wafers.
Achieving High Purity
The vertical orientation helps minimize particle generation and contamination. Any loose particles from the sample or the tube itself are more likely to fall to the bottom, away from the critical processing zone.
This design feature makes vertical furnaces essential in high-purity environments like semiconductor manufacturing, where even microscopic contaminants can ruin a product.
Maximizing Laboratory Space
On a practical level, vertical furnaces have a significantly smaller footprint than their horizontal counterparts. For laboratories where floor space is a premium, this vertical design allows for high-temperature processing capabilities without occupying extensive bench space.
Core Applications in Research and Industry
The physical advantages of the vertical design make it the preferred tool for a range of demanding applications.
Advanced Material Synthesis and Purification
Vertical furnaces are widely used for synthesizing advanced materials like nanowires, nanotubes, and specialized alloys. The controlled atmosphere and uniform heating are perfect for creating materials with precise structural and chemical properties. They are also used for purifying compounds through sublimation or zone refining.
Thermal Processing and Annealing
The process of annealing—heating and slowly cooling a material to alter its microstructure—requires extreme temperature precision. Vertical furnaces excel at this, particularly for semiconductor wafers where uniform treatment across the entire surface is non-negotiable. Other key processes include calcination (heating solids to high temperatures) and diffusion treatments.
Atmosphere-Controlled Reactions
Like all tube furnaces, vertical models allow for precise atmosphere control. They can be operated under vacuum, with inert gases like argon or nitrogen, or with reactive gases. This makes them ideal for studying oxidation, performing gas quenching tests, and conducting other chemical reactions that cannot happen in ambient air.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vertical tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Sample Handling and Accessibility
Loading and unloading samples can be more complex compared to a horizontal furnace. Supporting a sample in the middle of the vertical heat zone may require specialized crucibles or fixtures, whereas a horizontal furnace often allows you to simply slide a sample boat into position.
Process Observation
It is inherently more difficult to visually monitor a process occurring inside a vertical tube. Horizontal furnaces can more easily accommodate viewing windows on the end flanges, providing a direct line of sight to the sample.
Suitability for Large, Bulky Items
Tube furnaces, by their nature, are limited by the tube's diameter. They are not designed for heat-treating large, irregularly shaped objects. For those tasks, a box furnace or muffle furnace would be a more appropriate choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching the equipment's fundamental design to your specific scientific or production goal.
- If your primary focus is process purity and uniformity: The vertical design's superior temperature control and minimal particle generation make it the ideal choice, especially for semiconductor or crystal growth applications.
- If your primary focus is working with powders or coatings: The furnace's use of gravity ensures even material distribution and consistent results that are difficult to achieve horizontally.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lab space: The smaller footprint of a vertical furnace is a significant practical advantage over a comparable horizontal model.
- If your primary focus is simple batch processing of solid objects: A horizontal tube furnace or a box furnace may offer more straightforward and flexible sample handling.
Ultimately, selecting a vertical tube furnace is a strategic decision to leverage gravity and thermal dynamics for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Advanced Material Synthesis | Precise control, uniform heating for nanowires, nanotubes |
| Annealing and Calcination | Superior temperature uniformity, ideal for semiconductors |
| High-Purity Processes | Minimal contamination, perfect for CVD and crystal growth |
| Atmosphere-Controlled Reactions | Supports vacuum, inert, and reactive gases for oxidation tests |
| Space-Efficient Labs | Compact vertical design saves valuable floor space |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom vertical tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in semiconductor research, material synthesis, or any demanding thermal process, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















