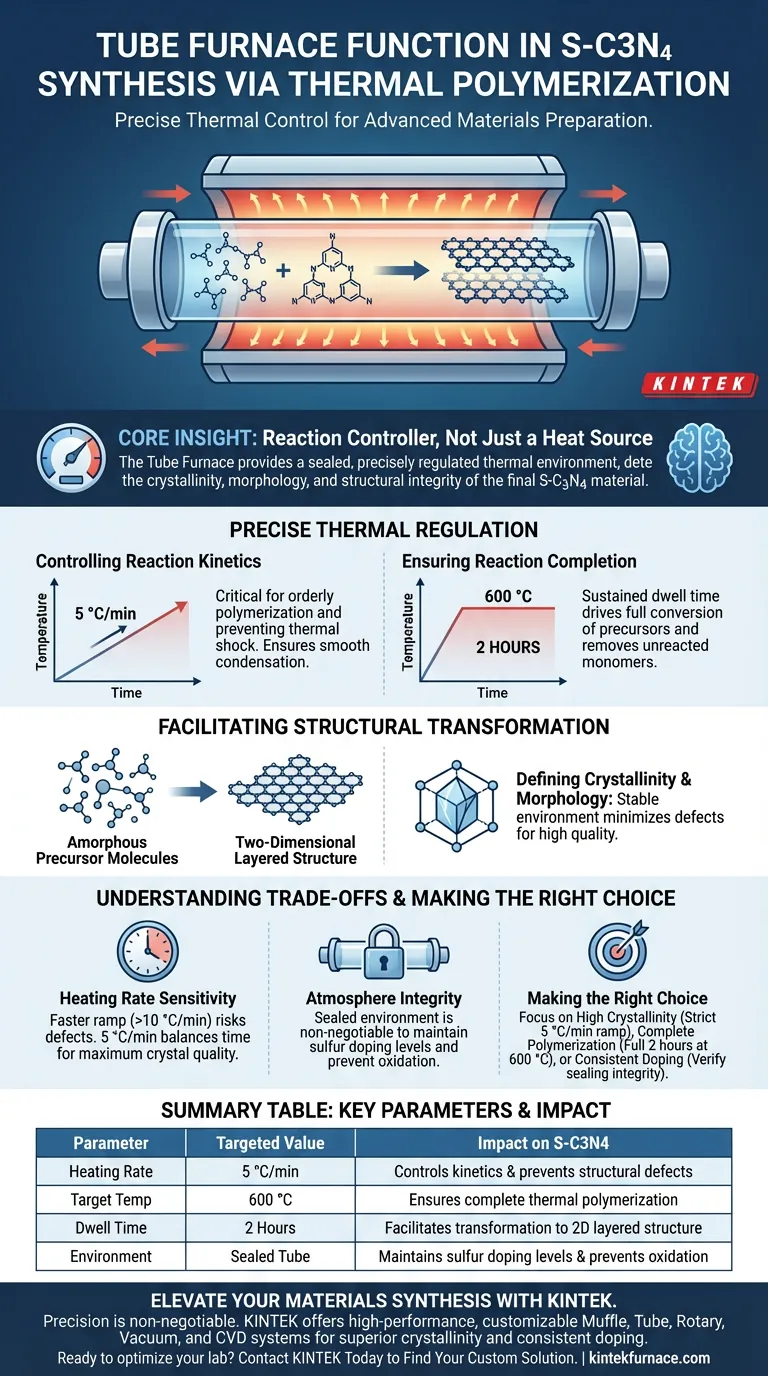
The primary function of a Tube Furnace in this context is to provide a sealed, precisely regulated thermal environment that drives the polymerization of sulfur-doped graphitic carbon nitride (S-C3N4). By subjecting trithiocyanuric acid precursors to a controlled heating ramp of 5 °C/min up to 600 °C, the furnace facilitates the chemical transformation of monomers into a stable, crystalline two-dimensional layered structure.
Core Insight: The Tube Furnace is not merely a heat source; it is a reaction controller. Its ability to maintain a specific heating rate and a sealed environment is the deciding factor in determining the crystallinity, morphology, and structural integrity of the final S-C3N4 material.

The Role of Precise Thermal Regulation
The synthesis of S-C3N4 is a thermal polymerization process, meaning the quality of the final material depends entirely on how heat is applied over time.
Controlling the Reaction Kinetic
The tube furnace allows for a specific heating rate, in this case, 5 °C/min. This slow, steady ramp is critical because it prevents thermal shock and allows the trithiocyanuric acid precursors to polymerize in an orderly fashion. A controlled rate ensures the condensation reactions occur smoothly, rather than chaotically, which is essential for forming a regular structure.
Ensuring Reaction Completion
The furnace maintains a high temperature of 600 °C for a duration of 2 hours. This sustained thermal treatment (dwell time) ensures that the polymerization is not just initiated but fully completed. It drives the transformation of the precursor materials into the final graphitic network, ensuring no unreacted monomers remain to compromise the material's purity.
Facilitating Structural Transformation
Beyond simple heating, the tube furnace creates the physical conditions necessary for the specific morphology of S-C3N4.
Promoting Two-Dimensional Layering
The thermal environment provided by the furnace facilitates the condensation of precursors into a two-dimensional layered structure. This layered architecture is a defining characteristic of graphitic carbon nitride and is essential for its electronic and photocatalytic properties.
Defining Crystallinity and Morphology
The stability of the temperature within the tube furnace directly impacts the crystallinity of the product. Fluctuations in temperature can lead to defects or amorphous regions. By providing a stable static environment, the furnace ensures the resulting S-C3N4 possesses high crystallinity and a well-defined morphology.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube furnace is the optimal tool for this synthesis, understanding its operational sensitivities is vital for reproducibility.
Heating Rate Sensitivity
There is a trade-off between processing time and material quality. While a faster heating rate (e.g., >10 °C/min) might save time, it risks creating structural defects or incomplete polymerization. The specific 5 °C/min rate is a calculated balance to maximize crystal quality, even though it extends the total synthesis time.
Atmosphere Integrity
The "sealed" nature of the environment is non-negotiable. Because sulfur doping involves volatile components, any breach in the tube's seal can lead to the loss of sulfur or the introduction of oxygen. This would degrade the doping level and alter the chemical composition of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your S-C3N4 preparation, align your furnace settings with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is high crystallinity: Strictly adhere to the 5 °C/min heating rate to allow the crystal lattice to form without defects.
- If your primary focus is complete polymerization: Ensure the dwell time at 600 °C is never shortened below 2 hours to guarantee the full conversion of trithiocyanuric acid.
- If your primary focus is consistent doping: Double-check the sealing integrity of the tube prior to heating to prevent the escape of volatile sulfur species.
Success in synthesizing S-C3N4 relies less on the maximum temperature reached and more on the precision of the ramp and the stability of the hold.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Targeted Value | Impact on S-C3N4 |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | 5 °C/min | Controls kinetics & prevents structural defects |
| Target Temp | 600 °C | Ensures complete thermal polymerization |
| Dwell Time | 2 Hours | Facilitates transformation to 2D layered structure |
| Environment | Sealed Tube | Maintains sulfur doping levels & prevents oxidation |
Elevate Your Materials Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when synthesizing advanced materials like S-C3N4. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable to your unique research needs. Our furnaces ensure the stable heating ramps and airtight integrity required for superior crystallinity and consistent doping.
Ready to optimize your lab's high-temperature processes? Contact KINTEK Today to Find Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Yuhong Lin, Dongchu Chen. Preparation of S-C3N4/AgCdS Z-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalyst and Its Effectively Improved Photocatalytic Performance. DOI: 10.3390/molecules29091931
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role do tubular furnaces play in heat treatment processes? Precision Control for Material Properties
- What is the purpose of the gas circulation system in a tube furnace? Control Chemical Atmospheres for Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the function of a vacuum tube furnace in the regeneration of expanded graphite? Deep Pore Restoration Expert
- What safety features are included in an atmosphere tube furnace? Essential Systems for Secure High-Temp Operations
- How does a three-zone tube furnace facilitate the synthesis of germanium nanowires? Achieve High-Quality SVG Results
- How does the temperature controller function in a 70mm tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- How do the components of a tube furnace contribute to its overall performance? Optimize Your Lab's Heat Processing Efficiency
- What is the mechanism by which the presulfidation process influences the coking behavior of cracking furnace tubes?



















