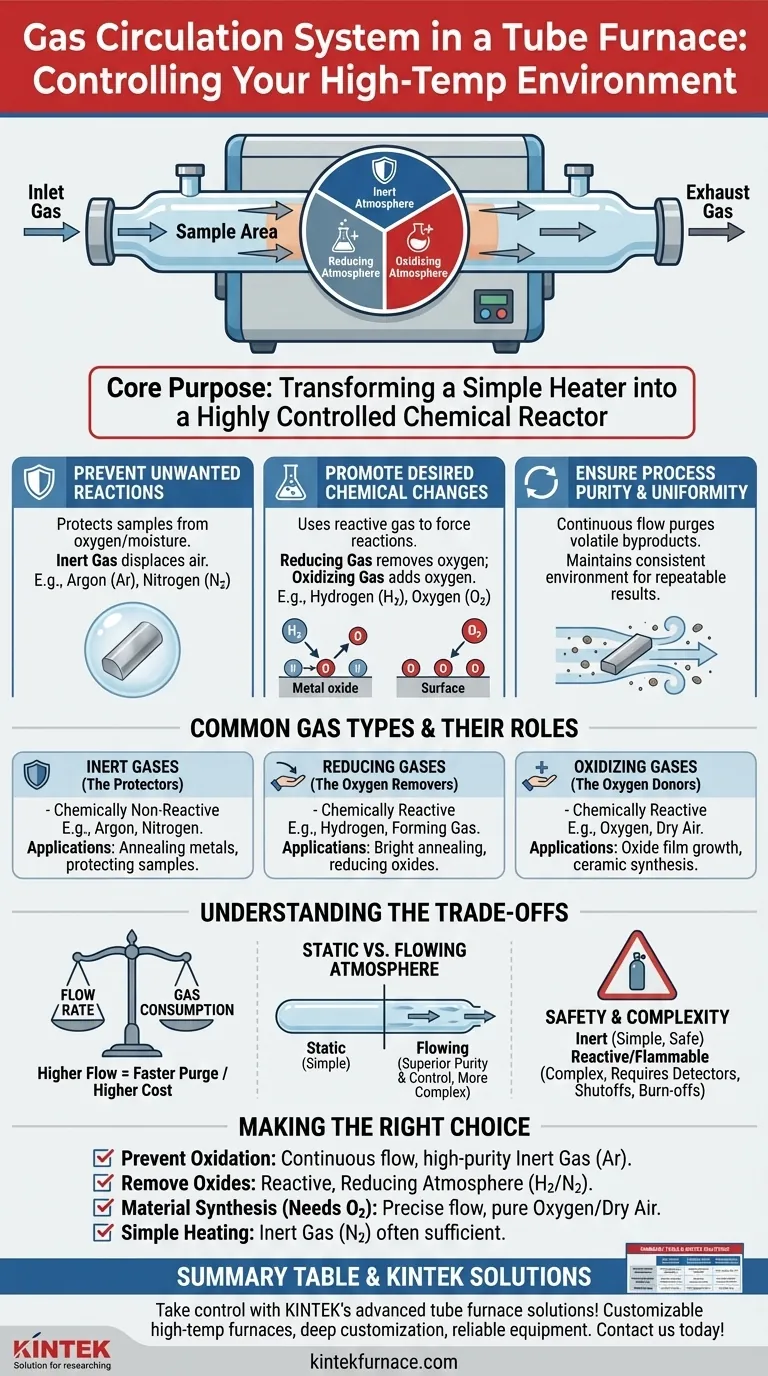
At its core, a gas circulation system in a tube furnace serves one critical purpose: to precisely create and control the chemical atmosphere surrounding your material during high-temperature processing. This system replaces the ambient air inside the furnace tube with a specific gas or gas mixture, allowing you to dictate the reactions that occur, or more importantly, prevent the ones you don't want.
The fundamental value of a gas circulation system is transforming the furnace from a simple heater into a highly controlled chemical reactor. It gives you the power to protect a material from air, actively change its chemical composition, or ensure a pure environment for predictable results.
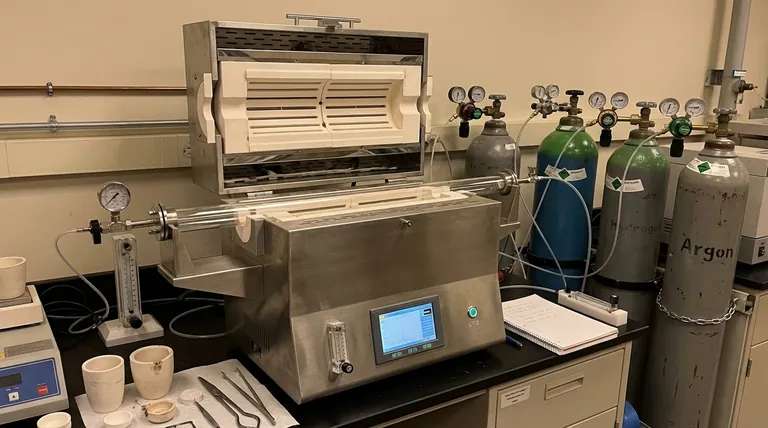

The Core Function: Why Atmosphere Matters
Controlling the atmosphere is not an optional feature for many advanced material processes; it is a fundamental requirement. Air, composed primarily of nitrogen, oxygen, and water vapor, is highly reactive at high temperatures and will unpredictably alter most materials.
Preventing Unwanted Reactions
For many applications, the primary goal is to protect the sample from oxygen and moisture in the air. This is known as creating an inert atmosphere.
At high temperatures, oxygen will readily oxidize most metals and many other materials, fundamentally changing their properties. An inert gas displaces the oxygen, acting as a protective chemical shield.
Promoting Desired Chemical Changes
Conversely, sometimes the goal is to use a specific gas to force a chemical reaction. This is known as creating a reactive atmosphere.
For example, introducing a reducing gas can strip oxygen atoms from a metal oxide, purifying it back into its metallic form. Introducing an oxidizing gas might be necessary to intentionally grow a specific oxide layer on a semiconductor wafer.
Ensuring Process Purity and Uniformity
A continuous, gentle flow of gas does more than just set the atmosphere; it maintains it. This flow purges any volatile byproducts released from the sample during heating, preventing them from re-depositing or interfering with the process.
This ensures that the entire sample is exposed to the same, consistent gas environment throughout the process, leading to more uniform and repeatable results.
Common Gas Types and Their Roles
The choice of gas is entirely dependent on your desired outcome. Gases are typically grouped into three categories.
Inert Gases (The Protectors)
These gases are chemically non-reactive. Their sole purpose is to displace air and prevent oxidation or other unwanted reactions.
The most common are Argon (Ar) and Nitrogen (N₂). Argon is heavier and provides a more stable blanket, while Nitrogen is often more cost-effective.
Reducing Gases (The Oxygen Removers)
These gases are chemically reactive and work to strip oxygen from materials. This is essential for processes like bright annealing of metals, where a perfectly clean, oxide-free surface is required.
The most common is Hydrogen (H₂), often used in a safer, diluted mixture with Nitrogen known as forming gas.
Oxidizing Gases (The Oxygen Donors)
These gases are used when the goal is to intentionally form an oxide. This is common in the synthesis of ceramics or for creating specific dielectric layers on electronic components.
The most common are **Oxygen (O₂) ** or simply purified, dry air.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A gas circulation system is more than just a valve; it involves a balance of competing factors.
Flow Rate vs. Gas Consumption
A higher flow rate purges the tube of contaminants more quickly and effectively. However, it also increases gas consumption, raising operational costs.
The ideal flow rate is just enough to maintain the desired purity without wasting gas or creating excessive thermal turbulence inside the tube.
Static vs. Flowing Atmosphere
You can simply fill the tube with gas and seal it (a static atmosphere), or you can have a continuous flow.
A flowing atmosphere provides superior control over purity by constantly removing outgassed contaminants, but it requires a more complex setup with inlet and outlet ports, flow controllers, and a proper exhaust.
Safety and System Complexity
Using inert gases like Argon is relatively simple and safe. Introducing reactive and flammable gases like Hydrogen, however, drastically increases system complexity.
A system designed for Hydrogen requires leak detectors, emergency shutoffs, and a "burn-off" apparatus at the exhaust to safely convert unused hydrogen into water.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your process goal dictates your gas strategy. Use these guidelines to make a decision.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation (e.g., annealing metals): Use a continuous, low flow of a high-purity inert gas like Argon to create a protective shield.
- If your primary focus is actively removing oxides (e.g., reducing a ceramic): Use a reactive, reducing atmosphere like a Hydrogen/Nitrogen mixture (forming gas).
- If your primary focus is material synthesis that requires oxygen (e.g., growing an oxide film): Use a precise flow of pure Oxygen or clean, dry air to control the oxidation process.
- If your primary focus is simply heating a stable material (e.g., calcination): An inert gas like Nitrogen is often sufficient to ensure a clean and repeatable environment.
Mastering the gas environment gives you direct control over your material's final chemistry and properties.
Summary Table:
| Function | Gas Type | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent oxidation | Inert (Argon, Nitrogen) | Annealing metals, protecting samples |
| Remove oxygen | Reducing (Hydrogen, Forming Gas) | Bright annealing, reducing oxides |
| Add oxygen | Oxidizing (Oxygen, Dry Air) | Oxide film growth, ceramic synthesis |
| Ensure purity | Flowing atmosphere | Uniform processing, volatile removal |
Take control of your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced tube furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with customizable high-temperature furnaces, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, such as gas circulation for inert, reducing, or oxidizing atmospheres. Enhance your material processing with reliable, efficient equipment—contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive better results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















