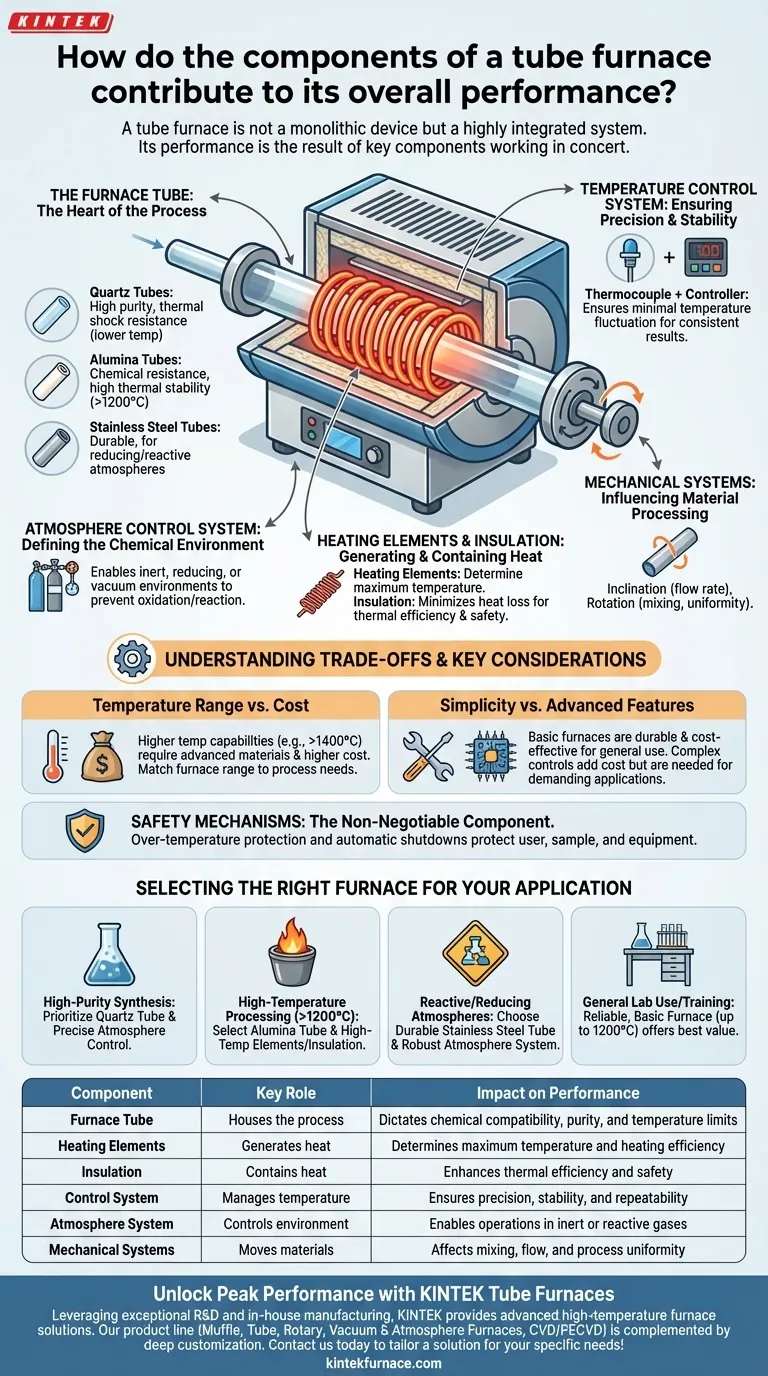
At its core, a tube furnace's performance is the direct result of how its key components—the furnace tube, heating elements, insulation, and control systems—work in concert. The specific materials and technologies chosen for each component dictate the furnace's maximum temperature, chemical compatibility, atmospheric control, and overall process precision.
A tube furnace is not a monolithic device but a highly integrated system. Understanding that each component choice represents a specific trade-off between temperature, purity, and cost is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific scientific or industrial goal.
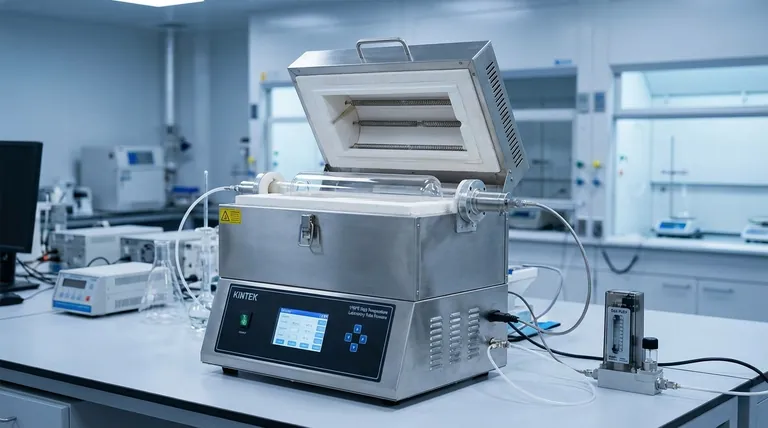

The Core Components of a High-Performance Tube Furnace
Each part of a tube furnace has a distinct role. The synergy between them determines the unit's capabilities and limitations.
The Furnace Tube: The Heart of the Process
The tube itself is the vessel where your process occurs, making its material the most critical choice for chemical compatibility and purity.
- Quartz Tubes: These are the standard for high-purity applications where avoiding contamination is paramount. They offer excellent thermal shock resistance but are typically limited to lower temperature ranges.
- Alumina Tubes: Offering superior chemical resistance and higher thermal stability than quartz, alumina is ideal for processes running at temperatures above 1200°C.
- Stainless Steel Tubes: When durability is key, especially in reducing or reactive atmospheres that might damage ceramic tubes, stainless steel provides a robust and resilient option.
Heating Elements and Insulation: Generating and Containing Heat
The ability to reach and maintain high temperatures is defined by the heating device and the quality of the thermal insulation.
Heating elements, often high-resistance coils, are embedded around a ceramic support structure. The material of these coils directly determines the maximum achievable temperature.
The insulation chamber minimizes heat loss, which is crucial for thermal efficiency and temperature stability. This directly impacts power consumption and the external surface temperature, a key safety consideration.
Temperature Control System: Ensuring Precision and Stability
Repeatable and accurate results depend entirely on precise temperature control.
This system relies on a thermocouple, a sensor that measures the internal temperature, and a controller. The controller interprets the thermocouple's feedback and adjusts the power to the heating elements to maintain the desired setpoint.
A high-quality control system ensures minimal temperature fluctuation, which is critical for sensitive material processing and consistent experimental outcomes.
Atmosphere Control System: Defining the Chemical Environment
Many modern processes require a controlled atmosphere. This system enables the introduction of specific gases or the creation of a vacuum.
It allows for operations under inert atmospheres (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, reducing atmospheres (like hydrogen), or other specific gaseous environments required by the experiment.
Mechanical Systems: Influencing Material Processing
For certain applications, mechanical movement is a key performance factor.
The inclination angle of the furnace tube can be adjusted to control the flow rate of materials in continuous processes. The rotation speed (typically 3-7 RPM) ensures materials are mixed and heated evenly, directly impacting residence time and process efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
Choosing a tube furnace involves balancing performance requirements with practical constraints. Making the wrong trade-off can lead to failed experiments or unnecessary expense.
Temperature Range vs. Cost
The single biggest factor influencing furnace structure and price is the working temperature.
Furnaces are often designed for specific ranges (e.g., up to 1100°C, 1200-1300°C, 1400-1700°C). Higher temperature capabilities require more advanced (and expensive) heating elements, insulation, and tube materials. It is inefficient and costly to purchase a 1700°C furnace if your process never exceeds 1000°C.
Simplicity vs. Advanced Features
The basic tube furnace is a mature, reliable technology with a simple structure that reduces maintenance. This makes it a durable and cost-effective workhorse for many labs.
However, demanding applications requiring extremely high heat intensity or precise material residence times may necessitate furnaces with high-temperature alloy tubing and more complex control systems, which adds to the initial cost and operational complexity.
Safety Mechanisms: The Non-Negotiable Component
While not a performance variable in the traditional sense, safety mechanisms are a critical part of any furnace's design. Features like over-temperature protection and automatic shutdowns are essential for protecting the user, the sample, and the equipment itself.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your final choice should be guided by the primary goal of your work.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis: Prioritize a furnace with a quartz tube and precise atmosphere control to prevent any sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material processing (>1200°C): You must select a furnace equipped with an alumina tube and the appropriate high-temperature heating elements and insulation.
- If your primary focus is working with reactive or reducing atmospheres: Choose a durable stainless steel tube and a robust, well-sealed atmosphere control system.
- If your primary focus is general lab use or student training: A reliable, basic furnace rated to 1200°C offers the best balance of capability, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
By understanding how each component contributes to the whole, you can confidently select the precise tool your work demands.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Role | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Tube | Houses the process | Dictates chemical compatibility, purity, and temperature limits |
| Heating Elements | Generates heat | Determines maximum temperature and heating efficiency |
| Insulation | Contains heat | Enhances thermal efficiency and safety |
| Control System | Manages temperature | Ensures precision, stability, and repeatability |
| Atmosphere System | Controls environment | Enables operations in inert or reactive gases |
| Mechanical Systems | Moves materials | Affects mixing, flow, and process uniformity |
Unlock Peak Performance with KINTEK Tube Furnaces
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Whether you're focused on high-purity synthesis, high-temperature processing, or general lab use, our tube furnaces deliver superior temperature control, durability, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and elevate your research outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















