Beyond acting as a passive containment vessel, graphite molds function as critical process tools that actively facilitate the densification and microstructural development of the material. They serve as a high-strength medium for transmitting hydraulic pressure to the powder and act as a thermal conduit to ensure uniform heating, all while maintaining dimensional stability under extreme mechanical loads.
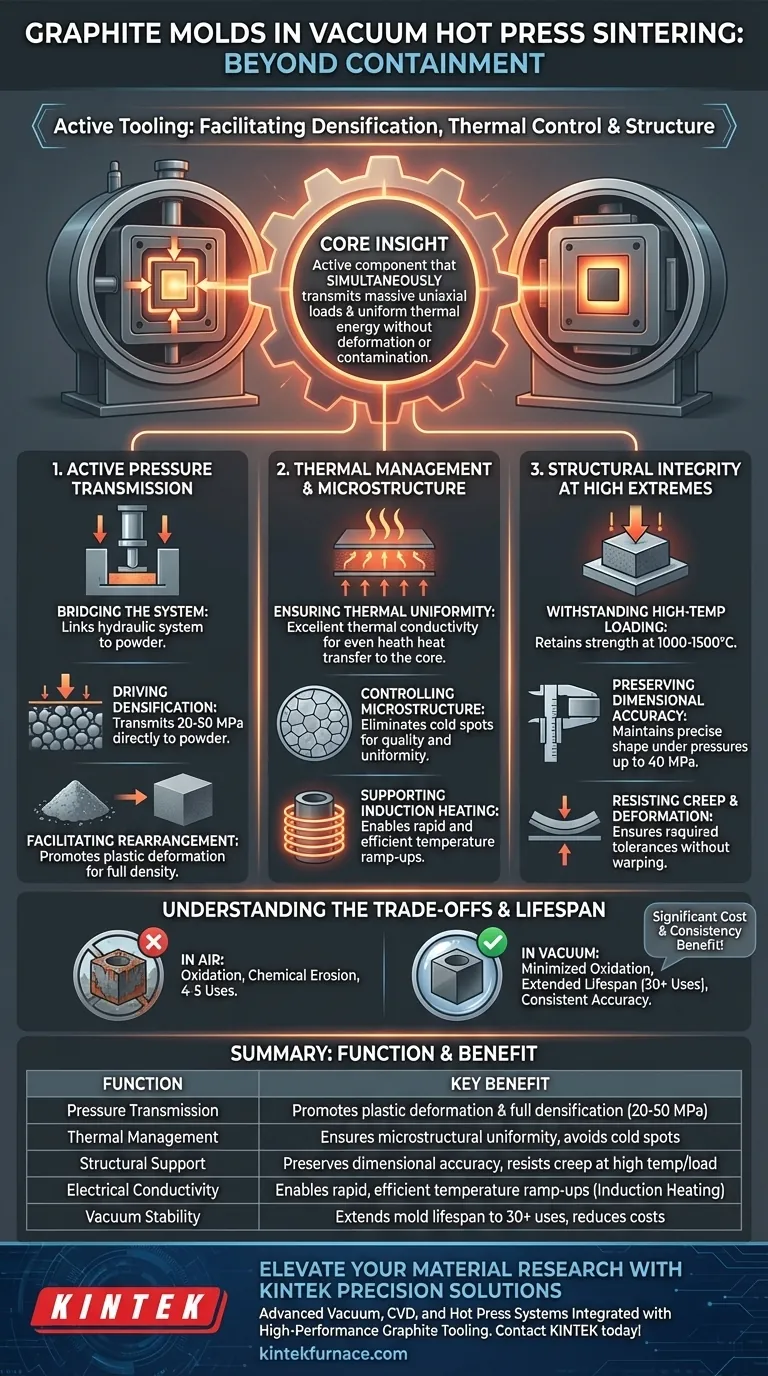
Core Insight: In vacuum hot press sintering, the graphite mold is an active component of the tooling system. Its primary value lies in its ability to simultaneously transmit massive uniaxial loads and uniform thermal energy without deforming or chemically contaminating the workpiece.
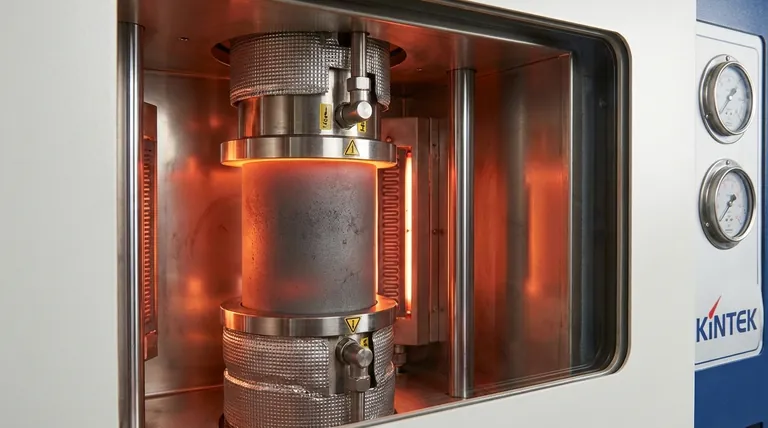
The Role of Active Pressure Transmission
Bridging the Hydraulic System and the Powder
The mold does not simply hold the material in place; it is the physical link between the machine's hydraulic system and the powder sample.
Driving Densification
The mold must transmit significant uniaxial pressure—often ranging from 20 to 50 MPa—directly to the internal powder.
Facilitating Particle Rearrangement
By effectively transferring this axial load, the mold forces the powder particles to rearrange. This mechanical pressure promotes plastic deformation, which is essential for transforming loose powder into a fully dense, solid bulk material.
Thermal Management and Microstructure
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
Graphite possesses excellent thermal conductivity. This property allows the mold to transfer heat evenly from the heating elements to the core of the powder sample.
Controlling Microstructure
Uniform heat transfer is vital for the quality of the final product. By eliminating cold spots or thermal gradients, the graphite mold ensures microstructural uniformity throughout the sintered composite.
Supporting Induction Heating
Because graphite is electrically conductive, it also serves as a critical medium for induction heating processes, allowing for rapid and efficient temperature ramp-ups.
Structural Integrity at High Extremes
Withstanding High-Temperature Loading
Standard materials often soften or deform under heavy loads at high temperatures (e.g., 1000°C to 1500°C). Graphite retains exceptional structural strength in these environments.
Preserving Dimensional Accuracy
The mold must maintain the precise shape and dimensions of the composite material while under pressures up to 40 MPa.
resisting Creep and Deformation
Even during the softening phase of the matrix material, the graphite mold resists deformation. This ensures the final sintered product achieves the required geometric tolerances without warping.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Chemical Stability vs. Reactivity
While generally chemically inert, graphite must be high-purity to prevent reactions with the ceramic or alloy powders. In a vacuum, it effectively avoids adverse chemical erosion, but users must ensure the specific powder chemistry does not react with carbon at sintering temperatures.
The Impact of Oxidation
Graphite is susceptible to oxidation at high temperatures in air. However, in a vacuum hot pressing environment, this oxidation loss is minimized.
Lifespan Considerations
Operating in a vacuum significantly extends the mold's lifespan—often from 4-5 uses in air to over 30 uses in vacuum. This drastically reduces tooling costs and maintains consistent dimensional accuracy over multiple cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting or designing graphite tooling for hot pressing, consider your specific processing objectives:
- If your primary focus is High Densification: Ensure the graphite grade used has high compressive strength to transmit loads exceeding 30 MPa without fracture.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Homogeneity: Prioritize graphite grades with superior thermal conductivity to prevent thermal gradients within large samples.
- If your primary focus is Dimensional Precision: Select high-density, high-strength graphite to minimize mold deflection or creep at peak sintering temperatures.
The graphite mold is the guarantor of your material's final density and shape; treating it as precision tooling rather than a consumable consumable is key to process consistency.
Summary Table:
| Function | Role in Sintering Process | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Transmission | Bridges hydraulic systems to powder at 20-50 MPa | Promotes plastic deformation and full densification |
| Thermal Management | Conducts heat evenly from elements to the core | Ensures microstructural uniformity and avoids cold spots |
| Structural Support | Maintains integrity under high-temp mechanical loads | Preserves dimensional accuracy and resists creep/warping |
| Electrical Conductivity | Acts as a medium for induction heating | Enables rapid and efficient temperature ramp-ups |
| Vacuum Stability | Minimizes oxidation and chemical erosion | Extends mold lifespan to 30+ uses and reduces tooling costs |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision Solutions
Achieving perfect material densification requires more than just high temperatures; it demands the right tooling and environment. KINTEK provides industry-leading Vacuum, CVD, and Hot Press systems designed to integrate seamlessly with high-performance graphite tooling.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, and Rotary furnaces tailored to your specific lab needs. Whether you are focusing on high-density composites or precise microstructural control, our team is ready to provide the technical expertise and equipment to ensure your success.
Ready to optimize your sintering process? Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a sealed quartz glass tube play in hot press sintering? Achieve Oxide-Free Aluminum Composites
- What types of heating elements are used in vacuum hot press furnaces? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- In which fields is hot pressing technology applied? Essential for Aerospace, Defense, and Advanced Manufacturing
- What are the advantages of hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Density and Superior Material Properties
- How does a vacuum hot press sintering furnace densify SiC ceramics? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density with KINTEK
- What is the core function of a flat tablet press in CSP? Achieve High-Pressure Densification for CaF2 Ceramics
- What applications does Vacuum Hot Press technology have in the electronics and semiconductor industry? Unlock High-Performance Component Manufacturing
- What is the impact of precise temperature control in a sintering furnace? Optimize Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs Composites



















