In short, hot pressing is a critical technology used to manufacture high-performance materials across demanding fields like aerospace, defense, electronics, and advanced manufacturing. It is applied in both fundamental research to develop new materials and in industrial production for specialized, high-value components where maximum density and strength are non-negotiable.
While conventional manufacturing methods are suitable for many applications, hot pressing occupies a specialized niche. It is the go-to process when the goal is to create fully dense, high-purity components from materials that are otherwise difficult or impossible to consolidate, such as advanced ceramics and metal matrix composites.

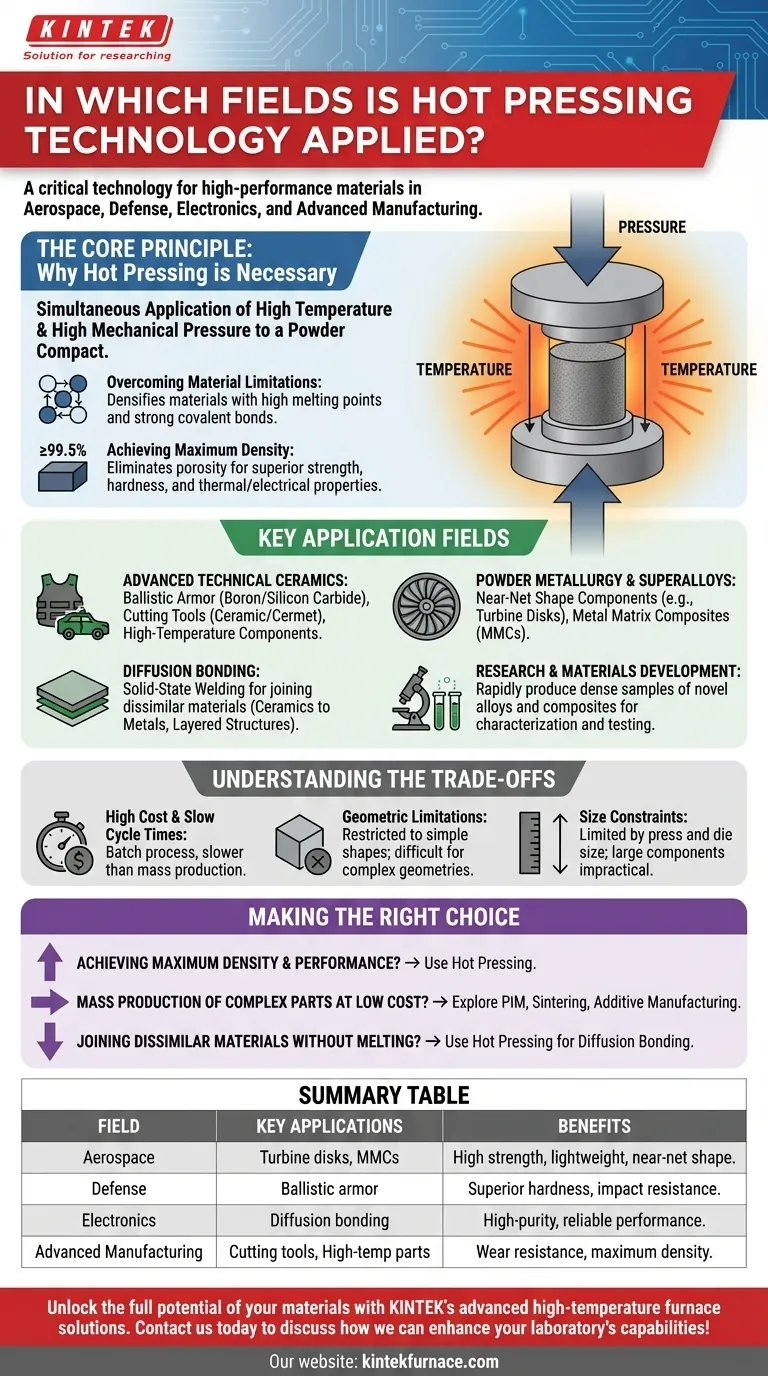
The Core Principle: Why Hot Pressing is Necessary
Hot pressing is a material processing technique that involves the simultaneous application of high temperature and high mechanical pressure to a powder compact within a die. This combination of forces provides a powerful advantage over other methods.
Overcoming Material Limitations
Many advanced materials, like silicon carbide or boron nitride, have extremely high melting points and strong covalent bonds. This makes them very difficult to densify using traditional sintering, which relies only on heat. The external pressure applied during hot pressing forces the powder particles together, accelerating diffusion and eliminating porosity at temperatures below the material's melting point.
Achieving Maximum Density
The primary goal of hot pressing is to produce a material with near-total density (typically >99.5%). Porosity, or empty space within a material, acts as a stress concentrator and is the primary origin point for cracks and failure. By eliminating this porosity, hot pressing produces components with vastly superior mechanical strength, hardness, and thermal and electrical properties.
Key Application Fields
The unique capabilities of hot pressing make it indispensable for producing components that must perform under extreme conditions. Its application spans several key high-technology sectors.
Advanced Technical Ceramics
This is arguably the most common application. Hot-pressed ceramics are used for:
- Ballistic Armor: Boron carbide and silicon carbide plates for body armor and vehicle protection rely on hot pressing to achieve the hardness and strength needed to defeat projectiles.
- Cutting Tools: Ceramic and cermet (ceramic-metal composite) cutting inserts for high-speed machining are hot-pressed to ensure extreme hardness and wear resistance.
- High-Temperature Components: Parts for furnaces, engines, and other high-heat environments are made from hot-pressed ceramics due to their thermal stability.
Powder Metallurgy and Superalloys
While many metal parts are cast or forged, hot pressing is used for niche applications involving metal powders, especially for the aerospace industry.
- Near-Net Shape Components: It can produce parts, like turbine disks for jet engines, from superalloy powders that are close to their final dimensions, reducing material waste and machining time.
- Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs): Hot pressing is used to consolidate metal powders with ceramic reinforcing fibers (e.g., aluminum with silicon carbide fibers) to create lightweight materials with exceptional stiffness and strength.
Diffusion Bonding
Hot pressing is an excellent method for joining dissimilar materials without melting or using filler materials.
- Solid-State Welding: By applying heat and pressure, atoms from two different materials can diffuse across the boundary, creating a strong, continuous bond. This is used to join ceramics to metals or to create layered composite structures for electronic and aerospace applications.
Research and Materials Development
In a laboratory setting, hot pressing is an invaluable tool for fundamental research. It allows scientists to quickly produce dense samples of novel alloys, composites, and ceramic formulations for characterization and testing, accelerating the discovery of new materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why It's Not Used Everywhere
Despite its advantages, hot pressing is not a universal solution. It comes with a specific set of limitations that are critical to understand.
High Cost and Slow Cycle Times
Hot pressing is a batch process, not a continuous one. The heating, pressing, and cooling cycles can take several hours, making it significantly slower and more expensive per part compared to mass-production methods like injection molding or conventional sintering.
Geometric Limitations
The process is generally restricted to simple shapes, such as discs, blocks, and cylinders. The rigid die assembly makes it difficult and expensive to produce parts with complex geometries, undercuts, or internal cavities.
Size Constraints
The size of the final component is limited by the size of the hot press and the die materials, which must withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. Producing very large components via hot pressing is often impractical or prohibitively expensive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use hot pressing depends entirely on your project's technical requirements and economic constraints.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material density and mechanical performance: Hot pressing is the superior choice, especially for advanced ceramics and difficult-to-sinter materials.
- If your primary focus is mass production of complex parts at a low cost: You should explore other methods like powder injection molding (PIM), die compaction followed by sintering, or additive manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials without melting: Hot pressing for diffusion bonding is a leading technique for creating high-integrity, solid-state joints.
Ultimately, hot pressing is the definitive solution when performance cannot be compromised and the material itself presents a fundamental manufacturing challenge.
Summary Table:
| Field | Key Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine disks, metal matrix composites | High strength, lightweight, near-net shape production |
| Defense | Ballistic armor (e.g., boron carbide plates) | Superior hardness, impact resistance |
| Electronics | Diffusion bonding for layered structures | High-purity, reliable performance in extreme conditions |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Cutting tools, high-temperature components | Wear resistance, thermal stability, maximum density |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether you're in aerospace, defense, or R&D, our expertise in hot pressing and custom furnace design ensures you achieve maximum density and performance. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-performance laboratory hot press machine play in curing? Unlock Superior Composite Strength
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What considerations guide the selection of heating elements and pressurization methods for a vacuum hot press furnace?
- What role does a high-pressure press play in the preparation of zinc sample pellets? Optimize Carbothermic Reduction
- Why are precision molds and laboratory presses critical for niobium-doped TiO2 ceramics? Achieve 94% Theoretical Density



















