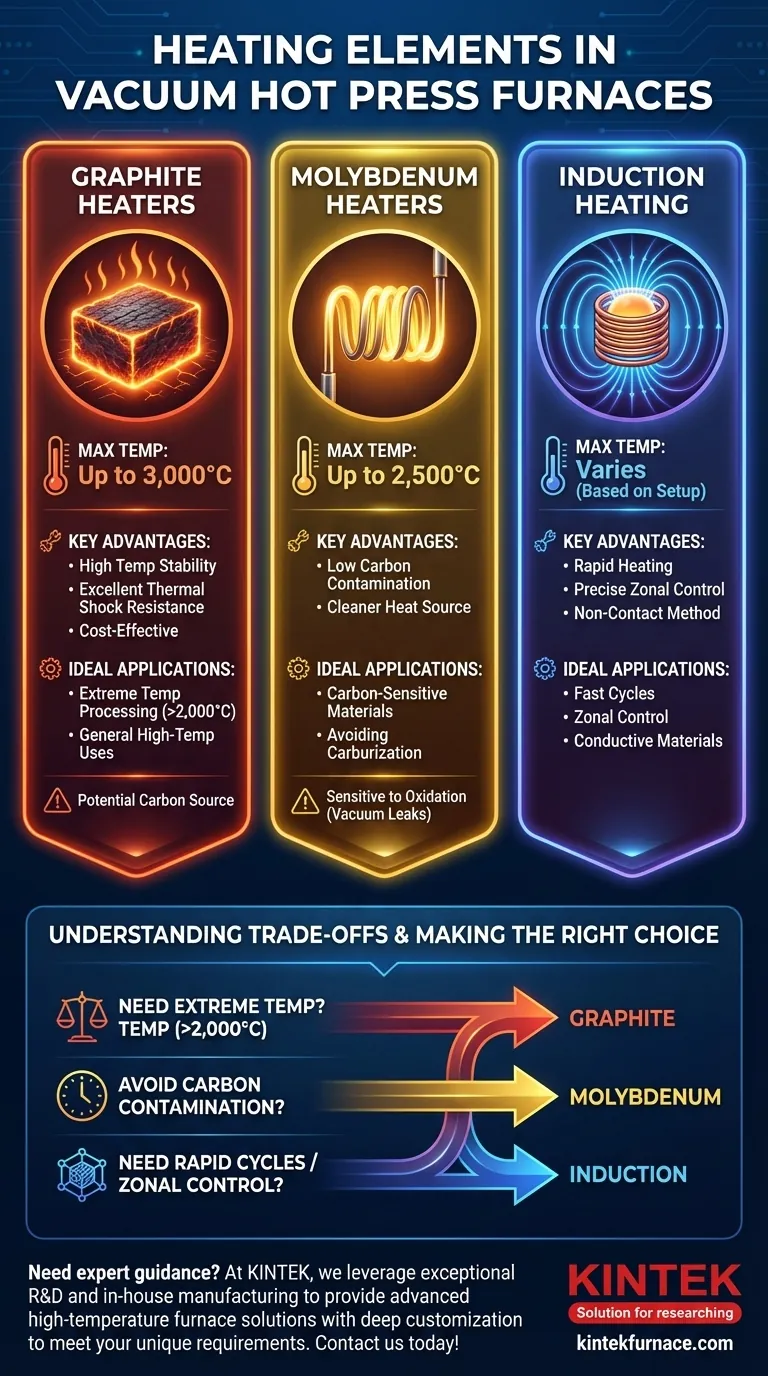
The primary heating elements used in vacuum hot press furnaces are graphite, molybdenum, and induction coils. Graphite heaters are the most common, capable of reaching temperatures up to 3,000°C, while refractory metal elements like molybdenum are used for applications up to 2,500°C where carbon contamination must be avoided. Induction heating offers a fundamentally different, non-contact method for rapid and precise temperature control.
The selection of a heating element is not merely about reaching a target temperature. It is a critical decision that balances material compatibility, heating speed, furnace atmosphere integrity, and long-term operational costs.

The Role of Heating in a Vacuum Hot Press
A vacuum hot press combines high temperature and mechanical pressure in a controlled, low-pressure environment. This process is used for densification, diffusion bonding, and creating advanced materials like composites and ceramics.
The heating system's job is to deliver precise, uniform thermal energy without contaminating the workpiece or reacting with the trace atmosphere. The two dominant principles for achieving this are resistance heating and induction heating.
Resistance Heating: The Foundation
Resistance heating is the most common method. It works by passing a large electrical current through a material with moderate electrical resistance, causing it to heat up—much like the filament in an incandescent light bulb.
This heat then radiates through the vacuum and onto the workpiece. The primary difference between resistance elements lies in the material used.
Graphite Heaters: The High-Temperature Standard
Graphite is the workhorse for high-temperature vacuum furnaces. Due to its unique properties, it can operate stably at temperatures up to 3,000°C in a vacuum or inert atmosphere.
Key advantages include its high melting point, excellent thermal shock resistance, and chemical inertness in most applications. Graphite is also relatively easy to machine into complex shapes, allowing for optimized element designs that promote temperature uniformity.
Molybdenum Heaters: The Refractory Metal Option
Molybdenum is a refractory metal used for heating elements that can operate up to 2,500°C. Its primary advantage is for processes where the presence of carbon is detrimental.
While graphite is inert, at very high temperatures it can lead to the carburization of sensitive materials. Molybdenum provides a "cleaner" heat source in these specific scenarios, though it is more susceptible to oxidation if the vacuum is compromised.
Induction Heating: A Fundamentally Different Approach
Induction heating does not rely on a traditional radiating element. Instead, it uses an external copper coil to generate a powerful, high-frequency electromagnetic field.
Direct and Indirect Heating
This magnetic field can heat the material in two ways. If the workpiece itself is electrically conductive, the field induces eddy currents directly within it, causing it to heat up rapidly from the inside out.
If the workpiece is not conductive (like many ceramics), a conductive crucible, typically made of graphite, is used. The induction coil heats this graphite susceptor, which then radiates its heat onto the part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right heating system involves navigating a series of critical trade-offs that go beyond maximum temperature. Your decision directly impacts process outcomes and operational reliability.
Temperature vs. Material Interaction
The highest temperature is not always the best. While graphite offers the highest range, it is a source of carbon. For processing certain alloys or ceramics, this can be an unwanted contaminant. In these cases, a lower-temperature molybdenum element is the superior choice.
Atmosphere Integrity and Element Durability
Heating elements are sensitive to their environment. Molybdenum elements will rapidly oxidize and fail if a vacuum leak introduces oxygen while at temperature.
Graphite is far more resistant to damage from vacuum excursions but can be more brittle than metallic elements. All elements rely on clean ceramic or quartz insulators; accumulated dust or metallic condensates can cause electrical short-circuits.
Heating Speed and Uniformity
Induction heating offers the fastest heating rates, as it can heat the workpiece or susceptor directly. This is a significant advantage for cycle time.
Resistance elements heat more slowly via radiation. Uniformity is achieved through the careful placement of the elements, which may be arranged radially around the part or mounted on furnace walls and doors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your process goals should dictate your choice of heating technology. Use these guidelines to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature processing (>2,000°C): Graphite resistance heaters are the default choice for their unmatched stability, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is processing carbon-sensitive materials: Molybdenum resistance heaters or a clean induction setup (without a graphite susceptor) are necessary to prevent workpiece contamination.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating cycles or precise zonal control: Induction heating provides superior speed and control, especially for conductive materials or when using a susceptor.
Ultimately, understanding the core principles of each heating method empowers you to select the ideal system for achieving your specific material properties.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Max Temperature | Key Advantages | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Up to 3,000°C | High temp stability, thermal shock resistance, cost-effective | Extreme temp processing, general high-temp uses |
| Molybdenum | Up to 2,500°C | Low carbon contamination, cleaner heat source | Carbon-sensitive materials, avoiding carburization |
| Induction Coils | Varies (based on setup) | Rapid heating, precise control, non-contact method | Fast cycles, zonal control, conductive materials |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right heating element for your vacuum hot press furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity



















