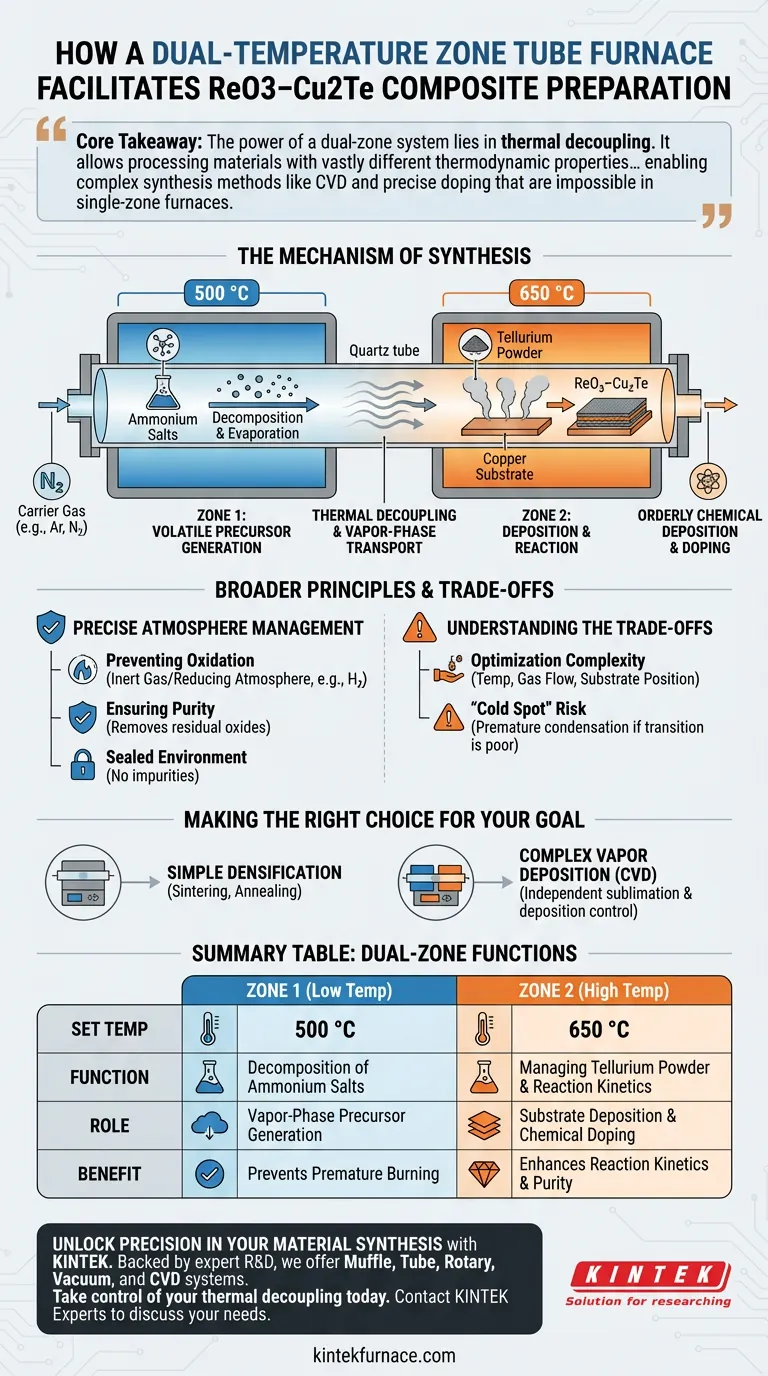
A dual-temperature zone tube furnace facilitates the preparation of ReO3–Cu2Te by creating two distinct thermal environments within a single reactor, allowing for the simultaneous but independent management of different precursors. Specifically, it enables the decomposition of ammonium salts at 500 °C in one zone while maintaining tellurium powder at 650 °C in the second zone, ensuring that vapor-phase components deposit and react in an orderly fashion on a copper substrate.
Core Takeaway The power of a dual-zone system lies in thermal decoupling. It allows you to process materials with vastly different thermodynamic properties—such as a volatile precursor and a stable substrate—in a single continuous workflow, enabling complex synthesis methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and precise doping that are impossible in single-zone furnaces.
The Mechanism of Synthesis
Decoupling Thermal Requirements
In the synthesis of complex composites like ReO3–Cu2Te, the precursors often require contradictory thermal conditions. A single temperature would likely burn off the volatile component before the stable component is ready to react.
The Two-Zone Configuration
The dual-zone furnace solves this by establishing a spatial temperature gradient.
- Zone 1 (500 °C): This zone is set to the optimal temperature for decomposing or evaporating volatile precursors, such as ammonium salts.
- Zone 2 (650 °C): This zone maintains a higher temperature to manage the tellurium powder and facilitate the final reaction kinetics.
Vapor-Phase Transport
By independently heating these zones, the furnace generates specific vapors at controlled rates. Carrier gases then transport these vapor-phase components downstream. This results in an orderly chemical deposition and doping process onto the copper substrate, rather than a chaotic mixture.
Broader Principles of Control
Precise Atmosphere Management
While thermal control is the primary mechanism, the tube furnace's ability to maintain a specific atmosphere is equally critical for composite preparation.
Preventing Oxidation
As seen in similar processes (such as biomass carbonization or selenization), the tube furnace provides a sealed environment. This allows for the introduction of inert gases (like Argon or Nitrogen) or reducing atmospheres (like Hydrogen).
Ensuring Purity
This atmospheric control removes residual oxide films and prevents "undesirable oxidation side reactions." In the context of ReO3–Cu2Te, this ensures that the doping process occurs without introducing impurities that would degrade the material's electronic properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity of Optimization
While a dual-zone furnace offers superior control, it introduces significantly more variables. You must optimize not only two distinct temperatures but also the gas flow rate and the position of the substrate relative to the temperature gradient.
The "Cold Spot" Risk
If the transition area between the two zones is not managed correctly, vapors generated in the high-temperature zone may condense prematurely before reaching the substrate. This requires precise calibration of the thermal profile along the length of the tube.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a furnace for material synthesis, the complexity of your precursors should dictate your equipment choice.
- If your primary focus is simple densification: A standard single-zone furnace is sufficient for processes like sintering or annealing where the material behaves as a single thermal mass.
- If your primary focus is complex vapor deposition (CVD): You require a dual-temperature zone furnace to independently control sublimation and deposition rates, preventing precursor degradation.
Success in composite synthesis depends not just on reaching high temperatures, but on controlling exactly where and when those temperatures are applied.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Zone 1 (Low Temp) | Zone 2 (High Temp) |
|---|---|---|
| Set Temperature | 500 °C | 650 °C |
| Primary Function | Decomposition of ammonium salts | Managing Tellurium powder & reaction kinetics |
| Process Role | Vapor-phase precursor generation | Substrate deposition & chemical doping |
| Core Benefit | Prevents premature burning | Enhances reaction kinetics and material purity |
Unlock Precision in Your Material Synthesis
Are you looking to master complex CVD processes or produce high-purity composites like ReO3–Cu2Te? KINTEK provides the cutting-edge thermal technology you need to succeed.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you require independent dual-zone control for vapor-phase transport or a fully customizable high-temp furnace tailored to your unique research needs, our solutions ensure orderly chemical deposition and zero oxidation.
Take control of your thermal decoupling today. Contact KINTEK Experts to discuss your specific laboratory requirements and discover how our precision equipment can enhance your research outcomes.
Visual Guide
References
- Aruna Vijayan, N. Sandhyarani. Efficient and sustainable hydrogen evolution reaction: enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of ReO<sub>3</sub>-incorporated Cu<sub>2</sub>Te catalysts. DOI: 10.1039/d4ya00023d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a tube furnace play in the carbonization of porous carbon? Master Precise Thermal Control
- What types of heating mechanisms are employed in drop tube furnaces? Choose Between Resistive and Induction Heating
- What are the selection criteria for a quartz tube reactor used in RWGS testing? Optimize Your Catalyst Performance
- What is the role of a three-zone vertical furnace in the growth of alpha-Mg3Bi2 single crystals? | KINTEK Solution
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the pre-carbonization of biomass? Optimize Carbon Yield Today
- Why is a multi-stage programmable tube furnace necessary for sintering spinel hollow fiber membrane green bodies?
- What is the purpose of a Split Tube Furnace (Single Zone)? Ideal for Easy Access and Uniform Heating
- Why is a vacuum pump used to treat the tube reactor before CVD of g-C3N4? Ensure High-Purity Thin Film Growth



















