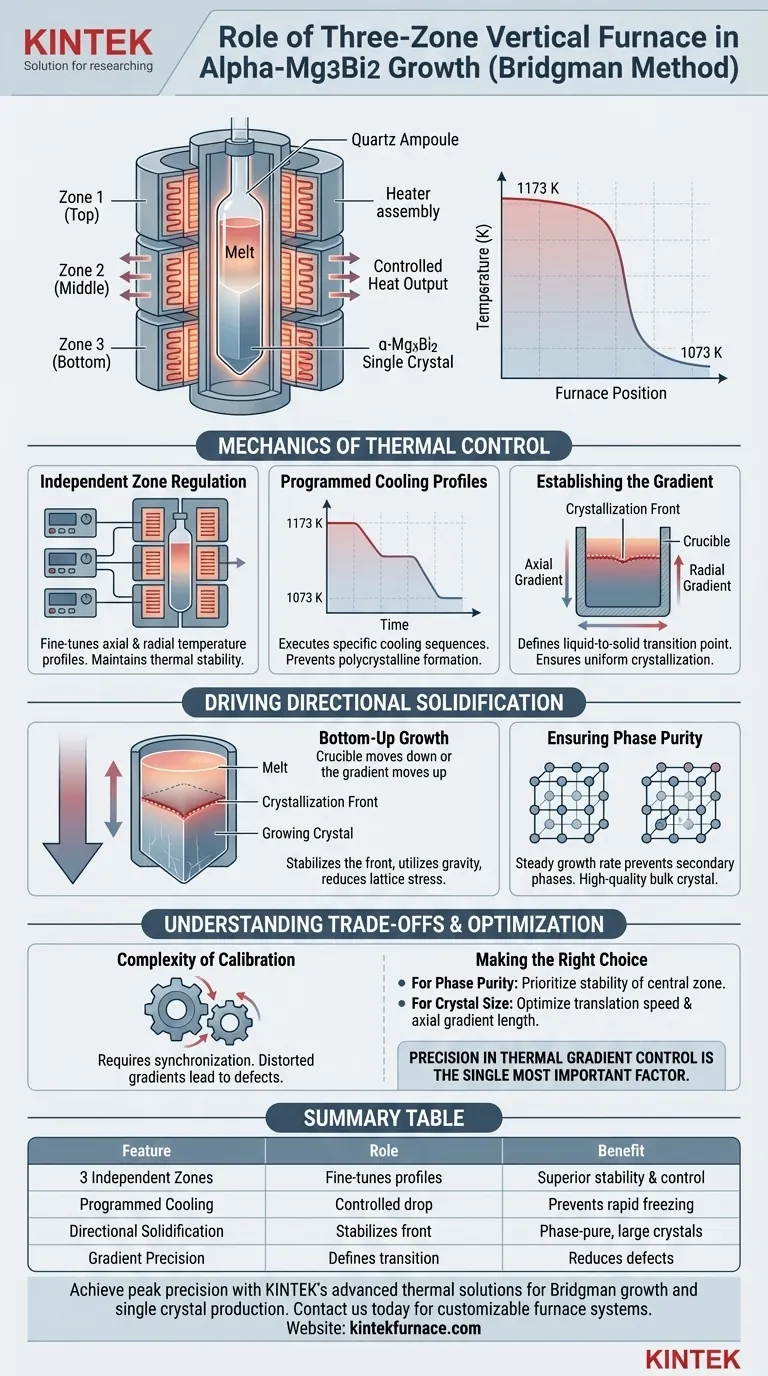
The primary role of a three-zone vertical furnace in the growth of $\alpha$-Mg3Bi2 is to establish a rigorous, stable thermal environment that allows for precise directional solidification. By controlling temperature gradients across three independent zones, the furnace facilitates a specific programmed cooling cycle—such as cooling from 1173 K to 1073 K—to ensure the material crystallizes uniformly.
The three-zone configuration allows for the fine-tuning of axial and radial temperature gradients, which is essential for driving the crystallization front at a stable rate. This precision results in large-sized, phase-pure bulk single crystals that are free from the defects common in less controlled environments.

The Mechanics of Thermal Control
Independent Zone Regulation
The defining feature of this furnace is the use of three independent heating zones.
Rather than a single heat source, this configuration allows for the manipulation of the temperature profile along the vertical axis of the furnace.
This independence is critical for maintaining thermal stability, ensuring that the environment remains constant around the crucible even as external conditions might fluctuate.
Programmed Cooling Profiles
The furnace does not simply heat and cool; it executes programmed cooling sequences.
For $\alpha$-Mg3Bi2, the primary reference highlights a cooling transition from 1173 K to 1073 K.
This specific, controlled drop in temperature is what initiates and sustains the growth process, preventing rapid freezing that would result in polycrystalline material.
Establishing the Gradient
Successful Bridgman growth relies on a sharp, well-defined temperature gradient.
The three-zone setup creates precise axial and radial temperature gradients.
These gradients define the exact point where the material transitions from liquid to solid, known as the crystallization front.
Driving Directional Solidification
Controlling the Crystallization Front
The ultimate goal of the furnace is to ensure the crystallization front advances at a stable rate.
As the melt moves through the gradient zone (or the gradient moves over the melt), solidification occurs gradually from one end to the other.
This prevents the entrapment of impurities and ensures the crystal lattice aligns correctly as it forms.
Bottom-Up Growth
In a Vertical Bridgman setup, crystallization is induced from the bottom upward.
This directional approach utilizes gravity to help stabilize the melt.
It allows the newly formed crystal to support the remaining liquid, reducing stress on the growing lattice.
Ensuring Phase Purity
The stability provided by the three-zone system directly contributes to phase purity.
By maintaining a steady growth rate, the furnace allows the $\alpha$-Mg3Bi2 structure to form without the inclusion of secondary phases.
This results in a high-quality bulk crystal suitable for advanced applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Complexity of Calibration
While a three-zone system offers superior control, it introduces complexity in calibration.
If the three zones are not perfectly synchronized, it can create non-linear gradients.
A distorted gradient can disrupt the crystallization front, leading to structural defects or multi-grain growth rather than a single crystal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a three-zone vertical furnace for $\alpha$-Mg3Bi2, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Prioritize the stability of the central heating zone to ensure the solid-liquid interface remains absolutely distinct during the transition.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Size: Focus on optimizing the translation speed and the axial gradient length to allow the crystal to grow continuously without thermal shock.
Precision in thermal gradient control is the single most important factor in transitioning from raw melt to a high-quality single crystal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in alpha-Mg3Bi2 Growth | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 3 Independent Zones | Fine-tunes axial and radial temperature profiles | Superior thermal stability and gradient control |
| Programmed Cooling | Controlled drop (e.g., 1173 K to 1073 K) | Prevents polycrystalline formation and rapid freezing |
| Directional Solidification | Stabilizes the bottom-up crystallization front | Ensures phase-pure, large-sized bulk single crystals |
| Gradient Precision | Defines the exact liquid-to-solid transition point | Reduces structural defects and lattice stress |
Achieve peak precision in your material synthesis with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—including specialized three-zone vertical furnaces—designed to meet the rigorous demands of Bridgman growth and single crystal production. Whether you are targeting phase purity or maximizing crystal size, our high-temp lab furnaces provide the stability your research deserves. Contact our experts today to find your ideal furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Mingyuan Hu, Jiaqing He. Helical dislocation-driven plasticity and flexible high-performance thermoelectric generator in α-Mg3Bi2 single crystals. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55689-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role do vacuum tube furnaces play in ceramic and glass manufacturing? Unlock High-Purity, Dense Materials
- What is the core role of a tubular furnace in the direct pyrolysis of biomass into biochar? Master Carbon Engineering
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What type of thermocouple is used in three-zone split tube furnaces? Choose the Right Sensor for Precise Control
- What role does a tube furnace play in the preparation of biochar-filled PVC composite precursors? Expert Synthesis Guide
- How are tube furnaces designed for temperatures exceeding 1200°C? Unlock High-Temp Precision with Advanced Elements
- What factors should be considered when choosing a tube furnace for a lab? Ensure Precision and Safety in Your Experiments
- What is a multi zone tube furnace used for? Unlock Precision Thermal Processing for Advanced Materials



















