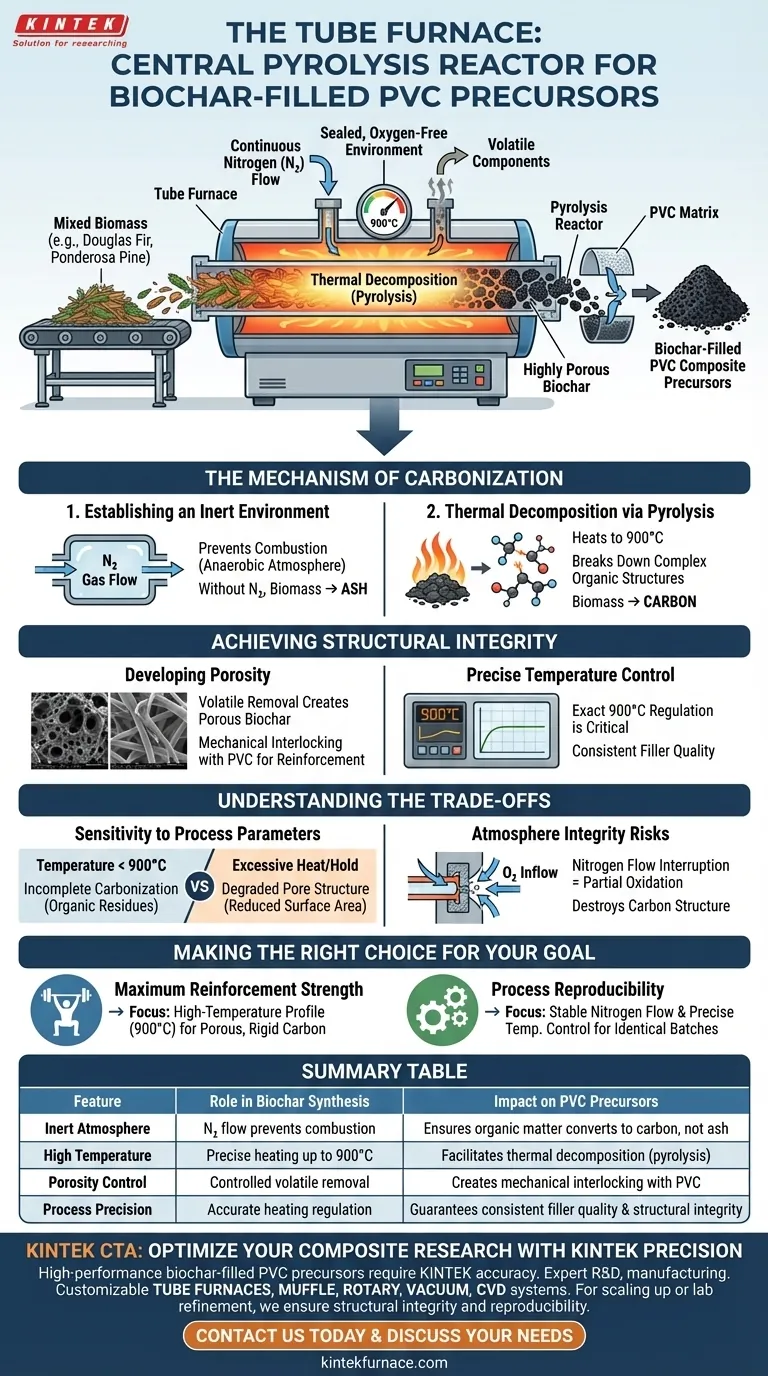
The tube furnace serves as the central pyrolysis reactor in the synthesis of biochar-filled PVC precursors. It provides a sealed, oxygen-free environment to heat mixed biomass, such as Douglas fir and Ponderosa pine, to temperatures as high as 900°C. By maintaining a continuous flow of nitrogen, the furnace facilitates the thermal decomposition necessary to convert complex organic matter into the highly porous carbonized materials that act as reinforcing fillers.
By isolating the biomass from oxygen and applying precise high heat, the tube furnace transforms organic raw material into structural carbon. This process prevents combustion and ensures the development of the specific porosity required to reinforce PVC composites.

The Mechanism of Carbonization
Establishing an Inert Environment
The fundamental role of the tube furnace is to prevent combustion. To do this, the system is sealed and purged with a continuous flow of nitrogen gas.
This creates an anaerobic (oxygen-free) atmosphere. Without this protective gas layer, the high temperatures would simply burn the biomass into ash rather than converting it into useful carbon.
Thermal Decomposition via Pyrolysis
Once the inert atmosphere is established, the furnace initiates pyrolysis, the thermal decomposition of organic material.
The furnace heats the biomass mixture to extreme temperatures, specifically 900°C for materials like Douglas fir and Ponderosa pine. This intense heat breaks down the complex organic structures found in the raw wood.
Achieving Structural Integrity
Developing Porosity
The high-temperature treatment drives off volatile components from the biomass. The result is a highly porous carbonized material, or biochar.
This porosity is not a byproduct; it is the defining feature that makes the biochar effective. The porous structure allows the biochar to mechanically interlock with the PVC matrix, serving as a robust reinforcing filler.
Precise Temperature Control
The tube furnace allows for exact regulation of the heating profile.
Maintaining the temperature at exactly 900°C is critical for consistency. Fluctuations in heat can alter the degree of carbonization, leading to inconsistent filler quality that could weaken the final PVC composite.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sensitivity to Process Parameters
While the tube furnace offers precision, the quality of the biochar is extremely sensitive to the chosen parameters.
If the temperature drops significantly below the target (e.g., 900°C), the carbonization may be incomplete, leaving behind organic residues that degrade PVC performance. Conversely, excessive heat or hold times can degrade the pore structure, reducing the material's surface area.
Atmosphere Integrity Risks
The reliability of the process is entirely dependent on the nitrogen flow.
Any leak in the seal or interruption in the gas flow allows oxygen to enter the reaction zone. Even trace amounts of oxygen at these temperatures will induce partial oxidation, destroying the carbon structure and ruining the batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your biochar-filled PVC precursors, you must tailor the furnace operation to your specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum reinforcement strength: Ensure your furnace creates a high-temperature profile (around 900°C) to fully develop a highly porous, rigid carbon structure.
- If your primary focus is process reproducibility: Prioritize the stability of the nitrogen flow rate and the precision of the temperature controller to ensure identical carbonization across batches.
The tube furnace is not just a heater; it is the precision instrument that dictates the structural potential of your final composite material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Biochar Synthesis | Impact on PVC Precursors |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Continuous Nitrogen flow prevents combustion | Ensures organic matter converts to carbon, not ash |
| High Temperature | Precise heating up to 900°C | Facilitates thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) |
| Porosity Control | Controlled removal of volatile components | Creates mechanical interlocking with the PVC matrix |
| Process Precision | Accurate regulation of heating profiles | Guarantees consistent filler quality and structural integrity |
Optimize Your Composite Research with KINTEK Precision
High-performance biochar-filled PVC precursors require the uncompromising accuracy that only KINTEK can provide. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Tube Furnaces, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific pyrolysis temperatures and atmospheric requirements.
Whether you are scaling up production or refining laboratory-scale material properties, our advanced thermal solutions ensure the structural integrity and reproducibility your research demands.
Ready to elevate your material science? Contact us today to discuss your unique needs with our technical team!
Visual Guide
References
- Dylan Jubinville, Tizazu H. Mekonnen. Effect of Biochar on the Thermal and Dimensional Stability of Poly(Vinyl Chloride) <scp>(PVC)</scp> Composites. DOI: 10.1002/vnl.70003
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of horizontal tube furnaces? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment and Synthesis
- What role does a tube furnace play in producing activated carbon? Master Walnut Shell Activation for High Adsorption
- What role does a tube furnace play in the high-temperature heat treatment of vermiculite? Precision Control Expert
- How does the heat treatment temperature in a tube furnace influence RPW electrodes? Optimize Carbonization Performance
- What is the primary function of high-vacuum quartz tube sealing in Mo2S3 synthesis? Ensure Phase Purity and Precision
- What are the primary functions of a precision gas filtration device? Maximize Data Integrity in Drop Tube Furnaces
- What role does a tube atmosphere furnace play in the carbonization of GO films? Enhance rGOF Conductivity and Quality
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing



















