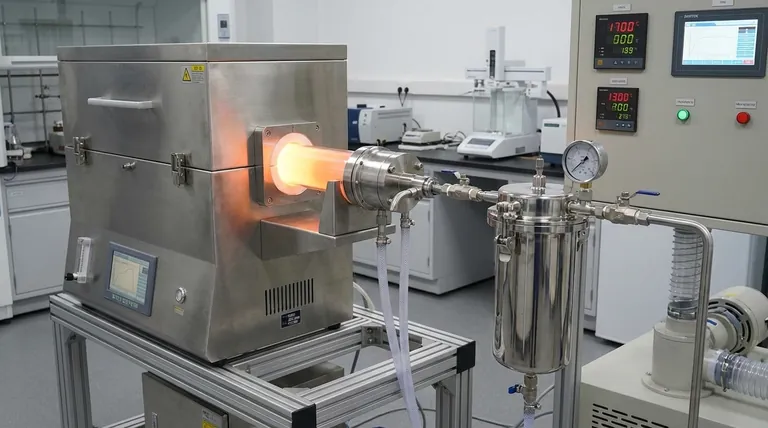
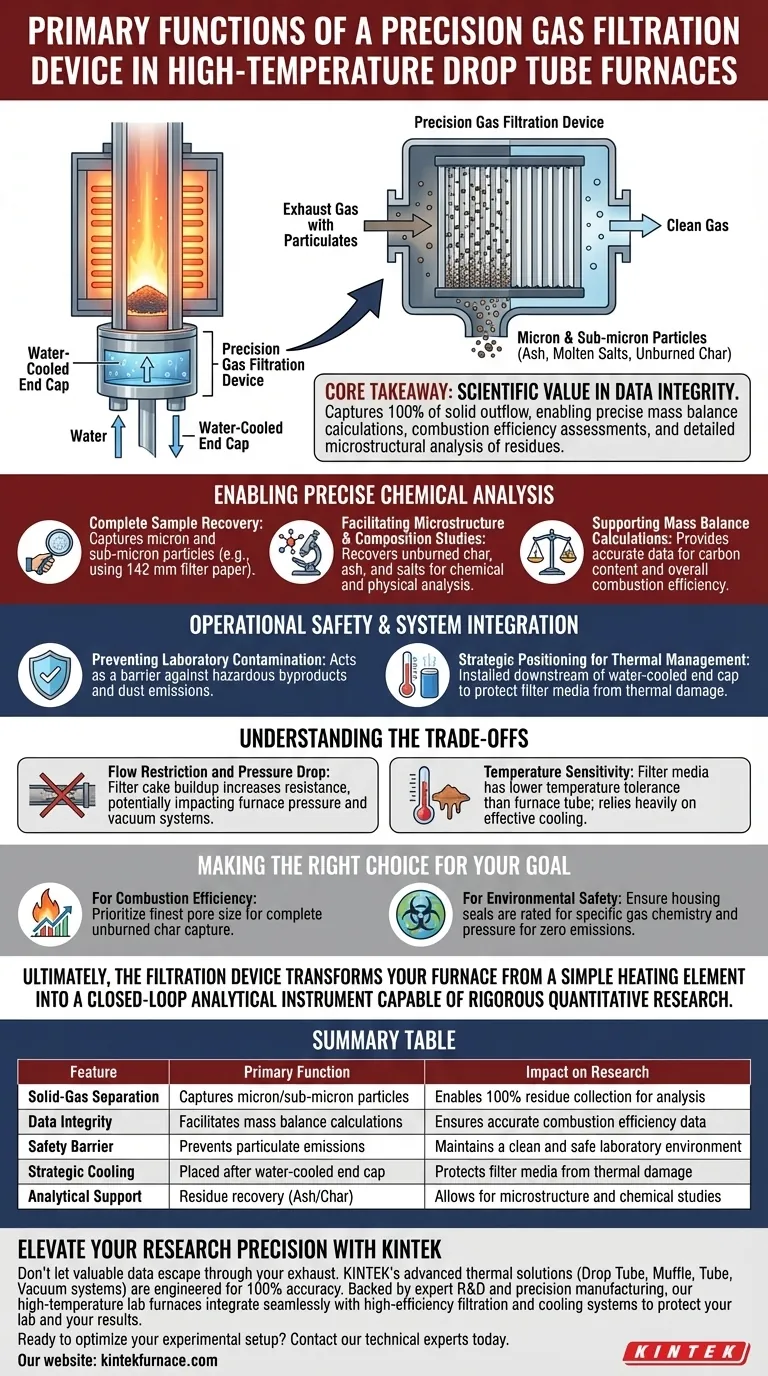
The primary function of a precision gas filtration device installed at the outlet of a high-temperature Drop Tube Furnace is to act as a high-efficiency solid-gas separator. Positioned immediately downstream of the water-cooled end cap, it captures micron and sub-micron particles from the exhaust gas, ensuring the complete collection of solid residues like ash, molten salts, and unburned char before the gas is discharged.
Core Takeaway While this device serves a critical safety role by preventing laboratory pollution, its scientific value lies in data integrity. By capturing 100% of the solid outflow, it enables precise mass balance calculations, combustion efficiency assessments, and detailed microstructural analysis of residues that would otherwise be lost.

Enabling Precise Chemical Analysis
Complete Sample Recovery
The device is engineered to capture solid residues that exit the furnace stream.
Unlike standard filters, precision devices (often using specifications like 142 mm filter paper) are designed to trap particles at the micron and sub-micron level. This ensures that even the finest particulate matter is retained for study rather than escaping with the flue gas.
Facilitating Microstructure and Composition Studies
The collected solids—specifically unburned char, ash, and molten salts—are the physical evidence of the reactions that occurred inside the furnace.
Recovering these materials allows researchers to perform necessary chemical composition analyses. It also provides the raw material required for microstructure analysis, which reveals physical changes undergone by the sample during heating.
Supporting Mass Balance Calculations
Accurate experimental data relies on accounting for all matter entering and exiting the system.
By capturing the solid fraction of the exhaust, the filtration device provides the data points necessary for accurate mass balance calculations. Without this step, determining carbon content and overall combustion efficiency becomes chemically impossible.
Operational Safety and System Integration
Preventing Laboratory Contamination
Beyond data collection, the filtration system acts as a barrier between the furnace internals and the laboratory environment.
Functioning similarly to a high-efficiency bag filter, it scrubs the flue gas of dust and particulate emissions. This prevents the release of potentially hazardous byproducts into the lab, maintaining a safe working environment.
Strategic Positioning for Thermal Management
The device is specifically installed downstream of the water-cooled end cap.
This placement is critical because the exhaust gas must be cooled to a safe temperature before it reaches the filter media. This protects the filter paper and housing from thermal damage while ensuring the solidified particulates are cool enough to be captured effectively.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Flow Restriction and Pressure Drop
As the filter effectively captures micron-sized particles, the accumulation of "filter cake" (residue buildup) will inevitably increase flow resistance.
If not monitored, this pressure drop can alter the internal pressure of the furnace tube. In systems relying on precise vacuum or controlled atmosphere conditions (often managed by SS KF flanges and pumps), substantial blockage can disrupt the intended experimental parameters or strain the vacuum pumps.
Temperature Sensitivity
While the device captures high-temperature residues, the filtration media itself generally has a lower temperature tolerance than the furnace tube (quartz or alumina).
Reliance on the upstream water-cooled end cap is absolute. Failure in the cooling stage can result in the destruction of the filter media, leading to immediate sample loss and potential contamination of the exhaust system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of your Drop Tube Furnace, select your filtration protocol based on your specific analytical requirements.
- If your primary focus is Combustion Efficiency: Prioritize a filter medium with the finest pore size to capture all unburned char, ensuring your carbon content analysis and mass balance calculations are mathematically accurate.
- If your primary focus is Environmental Safety: Ensure the housing seals are rated for the specific gas chemistry and pressure of your experiment to guarantee zero emissions into the laboratory.
Ultimately, the filtration device transforms your furnace from a simple heating element into a closed-loop analytical instrument capable of rigorous quantitative research.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Primary Function | Impact on Research |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-Gas Separation | Captures micron/sub-micron particles | Enables 100% residue collection for analysis |
| Data Integrity | Facilitates mass balance calculations | Ensures accurate combustion efficiency data |
| Safety Barrier | Prevents particulate emissions | Maintains a clean and safe laboratory environment |
| Strategic Cooling | Placed after water-cooled end cap | Protects filter media from thermal damage |
| Analytical Support | Residue recovery (Ash/Char) | Allows for microstructure and chemical studies |
Elevate Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Don't let valuable data escape through your exhaust. KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions, including customizable Drop Tube, Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems, are engineered for researchers who demand 100% accuracy. Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our high-temperature lab furnaces are designed to integrate seamlessly with high-efficiency filtration and cooling systems to protect your lab and your results.
Ready to optimize your experimental setup? Contact our technical experts today to discuss a tailored solution for your unique high-temperature processing needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Tor Sewring, Fredrik Weiland. The Influence of Oxyfuel Combustion Conditions on the Behavior of Inorganic Cooking Chemicals during Black Liquor Conversion. DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5c02613
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a tube furnace for small-volume samples or low-throughput operations? Achieve Precision and Control in Your Lab
- What are the specifications for large volume single zone tube furnaces? Find Your Ideal High-Temp Solution
- How does the working temperature range affect the choice of a tube furnace? Match Your Lab's Thermal Needs for Precision and Cost-Efficiency
- How do multi zone tube furnaces contribute to materials science research? Unlock Precise Temperature Control for Advanced Synthesis
- Why is the design of a two-zone furnace critical for ZrTe5 crystal growth? Master CVT with Precision Control
- What role does a Tube Furnace play in the CVD growth of carbon nanotubes? Achieve High-Purity CNT Synthesis
- How do vertical fluidized bed tube furnaces contribute to the new energy field? Unlock Next-Gen Energy Material Development
- How is a laboratory tube furnace utilized in electronic and semiconductor research? Unlock Precision Thermal Processing for Advanced Devices



















