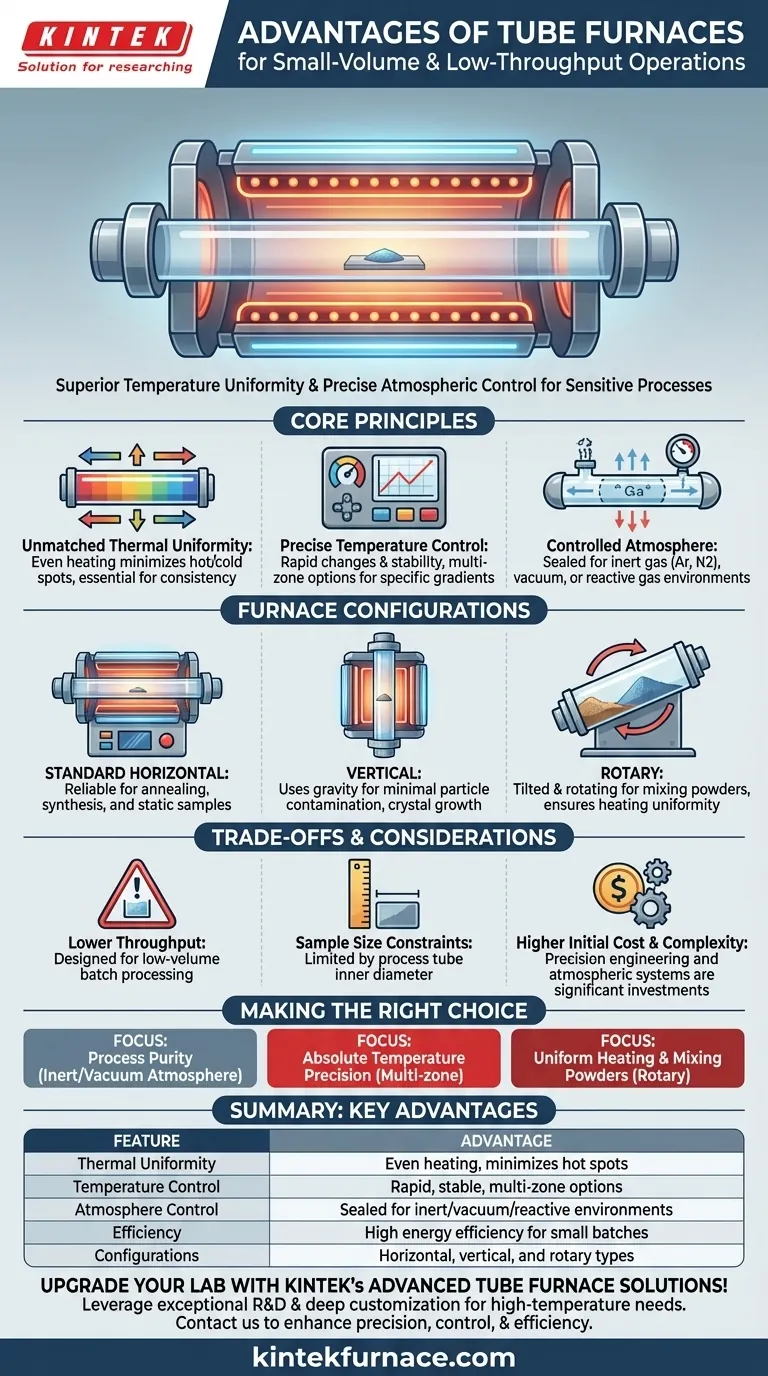
For processing small-volume samples, a tube furnace offers significant advantages over conventional ovens, stemming from its specialized cylindrical design. This geometry enables superior temperature uniformity, precise atmospheric control, and high efficiency, which are critical for sensitive thermal processes where consistency and purity are paramount.
A tube furnace's primary advantage lies in its enclosed, cylindrical heating chamber. This geometry enables exceptional temperature uniformity and precise atmospheric control, conditions that are often compromised in the larger, less-contained chambers of standard laboratory ovens.

The Core Principles of Tube Furnace Design
To understand why a tube furnace excels, we must look at how its fundamental design directly impacts the processing environment.
Unmatched Thermal Uniformity
The cylindrical shape of the heating chamber allows heating elements to completely encircle the sample tube.
This arrangement ensures heat is applied evenly from all directions, minimizing hot spots and cold spots. The result is a highly uniform temperature zone along the length of the tube, which is essential for achieving consistent material properties and reliable experimental data.
Precise Temperature Control
Tube furnaces are designed for precision. Their smaller chamber volume and direct heating method allow for rapid temperature changes and exceptional stability at the setpoint.
Many models feature multiple heating zones, each with its own controller. This allows you to create specific temperature gradients or further refine the uniformity within the central processing area.
Controlled Processing Atmosphere
Perhaps the most significant advantage for many applications is the ability to completely control the atmosphere around the sample.
The sealed process tube can be purged and filled with an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, subjected to a vacuum, or filled with a reactive gas for specific chemical processes. This level of atmospheric purity is nearly impossible to achieve in a standard benchtop oven.
Exploring Different Furnace Configurations
The versatility of the tube furnace is enhanced by several common configurations, each tailored to specific operational needs.
The Standard Horizontal Furnace
This is the most common configuration, used for a vast range of applications from annealing and tempering to synthesis and purification. It is straightforward, reliable, and suitable for most static samples.
Vertical Tube Furnaces
By orienting the tube vertically, these furnaces use gravity to their advantage. They are ideal for processes where minimal particle contamination is critical, as any loose particles will fall to the bottom rather than settling on the sample. They are also used for crystal growth and drop-quenching experiments.
Rotary Tube Furnaces
For processes involving powders or granular materials, a rotary furnace is unmatched. The process tube rotates and often tilts, simultaneously heating and mixing the material.
This continuous movement ensures every particle is exposed to the same heat, leading to exceptional heating uniformity and efficiency. It is the ideal tool for processes like calcination or sintering powders where batch consistency is key.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a tube furnace is a specialized tool with specific limitations that make it unsuitable for certain tasks.
Lower Throughput
By design, tube furnaces are intended for low-throughput or batch processing. Their limited internal volume makes them inefficient for processing large quantities of material.
Sample Size Constraints
The physical dimensions of the sample are strictly limited by the inner diameter of the process tube. This makes them unsuitable for large or irregularly shaped components that would fit easily in a box furnace.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
The precision engineering, advanced temperature controllers, and systems for atmospheric control make tube furnaces a more significant investment than simple ovens. The setup for vacuum or gas flow also adds a layer of operational complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right heating equipment depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is process purity and preventing oxidation: A tube furnace's ability to maintain a controlled inert or vacuum atmosphere is its definitive advantage.
- If your primary focus is absolute temperature precision for a static sample: A multi-zone horizontal or vertical tube furnace offers unparalleled uniformity and control.
- If your primary focus is uniformly heating and mixing powders or granular materials: A rotary tube furnace is the ideal tool for ensuring consistent results throughout the batch.
Ultimately, selecting a tube furnace is a decision for precision and environmental control over sheer volume.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Thermal Uniformity | Even heating from all directions, minimizing hot spots for consistent results |
| Temperature Control | Rapid changes and stability with multi-zone options for precise gradients |
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed tube for inert gas, vacuum, or reactive environments to prevent oxidation |
| Efficiency | High energy efficiency and ideal for sensitive, small-batch operations |
| Configurations | Horizontal, vertical, and rotary types for varied applications like powder mixing |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced tube furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for small-volume samples and low-throughput operations. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your precision, control, and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control



















