In the new energy sector, vertical fluidized bed tube furnaces are critical tools for creating and testing the high-performance materials that power next-generation technologies. They are specifically used for synthesizing battery and solar cell components, converting biomass into renewable fuels, and developing materials for carbon capture and fuel cells. Their unique heating method provides the precise and uniform temperature control essential for these advanced applications.
The core value of a vertical fluidized bed tube furnace is not just its ability to generate heat, but its capacity to create an exceptionally uniform and efficient thermal environment. This control is the key that unlocks the development and scalable production of next-generation energy materials.

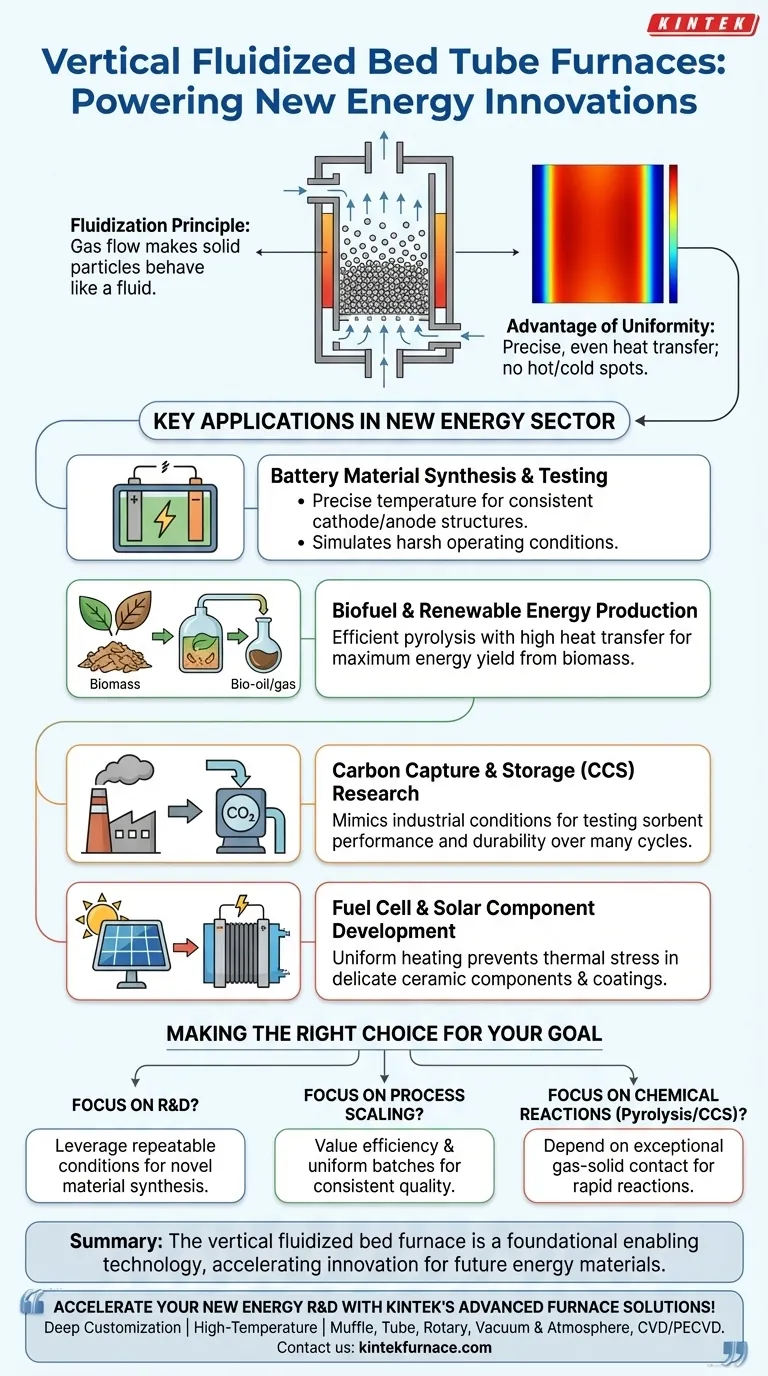
The Core Principle: Why Fluidization Matters
What is a Fluidized Bed?
A fluidized bed is created when a flow of gas is passed upward through a bed of solid granular material, like sand or a catalyst. At the right velocity, the gas flow counteracts gravity, causing the solid particles to behave like a boiling liquid.
This "fluidized" state is the furnace's key advantage. It ensures that every particle is in constant motion and surrounded by the heating gas.
The Advantage of Uniformity
This fluid-like behavior results in extremely high and uniform heat transfer throughout the entire volume of the material being processed. There are no hot or cold spots.
This level of thermal consistency is crucial in new energy applications, where minuscule variations in material structure can dramatically impact performance, whether in a battery electrode or a solar cell coating.
Key Applications in the New Energy Sector
Battery Material Synthesis and Testing
The performance and safety of modern batteries depend on the precise crystal structure of their cathode and anode materials.
Vertical fluidized bed furnaces provide the stable, repeatable temperature profiles needed to synthesize these materials with consistent quality. They are also used to simulate harsh operating conditions to test the degradation and lifespan of new battery chemistries.
Biofuel and Renewable Energy Production
These furnaces are ideal for pyrolysis, a process that thermally decomposes organic matter—like wood chips or agricultural waste—in the absence of oxygen to produce biofuels.
The excellent mixing and heat transfer in a fluidized bed ensure the biomass is converted efficiently into bio-oil and syngas, maximizing the energy yield from the renewable feedstock.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Research
A major area of CCS research involves developing solid "sorbent" materials that can capture CO₂ from flue gas at industrial plants.
Researchers use fluidized bed furnaces to test how effectively these sorbents perform under various temperatures and how they hold up over many cycles of capturing and releasing CO₂. The furnace environment closely mimics the conditions inside a power plant or industrial facility.
Fuel Cell and Solar Component Development
The creation of components for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and advanced solar panels often involves heat-treating ceramics and applying specialized coatings.
The uniform heating of a fluidized bed furnace prevents thermal stress and ensures that these delicate components are processed to exact specifications, which is critical for their efficiency and durability.
Understanding the Broader Context
An Industrial Workhorse, Adapted for New Energy
It is important to understand that fluidized bed technology is not new. It has been a workhorse in heavy industries like petroleum refining, chemical production, and coal power generation for decades.
Its application in the new energy field represents a strategic adaptation of a proven, reliable, and scalable technology to solve new, complex material science challenges.
The Trade-off: Precision vs. Simplicity
While incredibly effective, a fluidized bed system is more operationally complex than a simple box furnace.
Achieving the desired "fluidization" requires precise control over gas flow rates, particle size, and temperature. This complexity is the trade-off for achieving a level of process control that simpler heating methods cannot match.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The primary benefit of this technology is its ability to deliver precise, uniform heat for complex chemical and physical transformations.
- If your primary focus is material R&D: You will leverage the furnace's ability to provide highly repeatable thermal conditions for synthesizing and testing novel materials.
- If your primary focus is process scaling: You will value its efficiency and capability to produce highly uniform batches, ensuring consistent quality from the lab to pilot production.
- If your primary focus is chemical reactions like pyrolysis or CCS: You will depend on the exceptional gas-solid contact to drive reactions quickly and efficiently.
Ultimately, the vertical fluidized bed furnace serves as a fundamental enabling technology, accelerating the innovation cycle for the materials that will define the future of energy.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Battery Material Synthesis | Precise temperature control for consistent cathode/anode quality |
| Biofuel Production | Efficient pyrolysis with high heat transfer for maximum energy yield |
| Carbon Capture Research | Mimics industrial conditions for sorbent testing and durability |
| Fuel Cell/Solar Development | Uniform heating prevents thermal stress in delicate components |
Accelerate your new energy R&D with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs—whether for battery material synthesis, biofuel production, or carbon capture research. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your material development and process scaling!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















