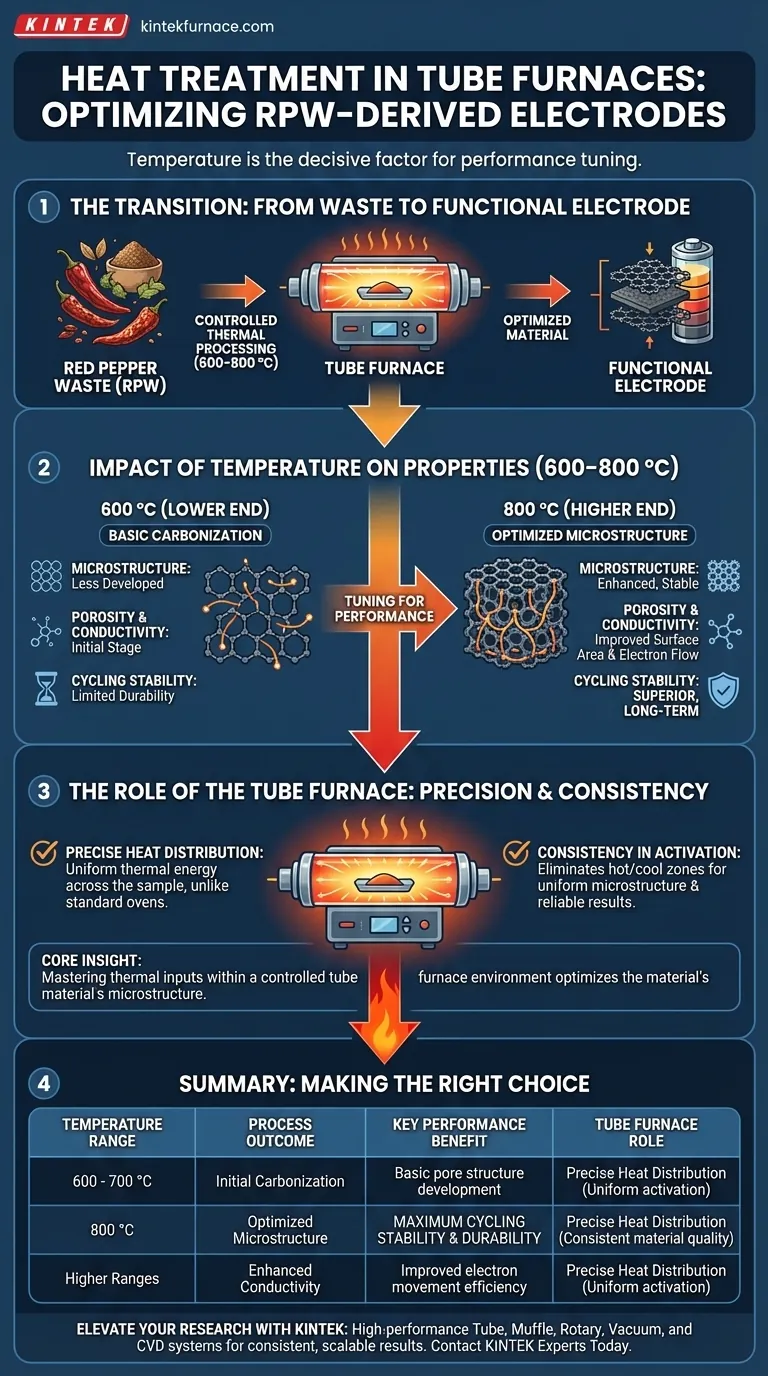
Heat treatment temperature is the decisive factor in determining the electrochemical performance of electrodes derived from Red Pepper Waste (RPW). Specifically, operating within a temperature range of 600–800 °C allows for the tuning of physical characteristics, with temperatures at the higher end (800 °C) notably improving the electrode's cycling stability. A tube furnace is essential in this process to ensure the precise heat distribution required for uniform carbonization.
Core Insight: The transition from raw organic waste to a functional electrode relies on mastering thermal inputs. Higher processing temperatures (up to 800 °C) within a controlled tube furnace environment optimize the material’s microstructure, resulting in superior electrical conductivity and durability.

The Impact of Temperature on Material Properties
The performance of an RPW electrode is not accidental; it is engineered through heat. The specific temperature applied during carbonization dictates the fundamental architecture of the final carbon material.
Regulating Microstructure
As the temperature rises within the 600–800 °C window, the internal structure of the biomass evolves. This structural rearrangement is critical for establishing the material's physical stability.
At 800 °C, the carbonization process reaches a state that favors enhanced cycling stability. This means the electrode can undergo repeated charge and discharge cycles with less degradation compared to materials processed at lower temperatures.
Tuning Porosity and Conductivity
Temperature directly controls two vital performance metrics: porosity and electrical conductivity.
Heat treatment modifies the pore structure, creating the surface area necessary for charge storage. Simultaneously, higher temperatures generally improve electrical conductivity, facilitating the efficient movement of electrons during electrode operation.
The Role of the Tube Furnace
Achieving the correct temperature is only half the battle; applying it correctly is equally important. The equipment used plays a vital role in the consistency of the results.
Precision Heat Distribution
Using a tube furnace is critical because it offers controlled heat distribution. Unlike standard ovens, a tube furnace ensures that the thermal energy is applied uniformly across the sample.
Consistency in Activation
This precise thermal control allows for the effective regulation of the carbonization and activation processes. By eliminating hot spots or cool zones, the tube furnace ensures that every part of the RPW material develops the optimal microstructure required for high-performance charge storage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While higher temperatures in this range generally yield better stability, it is important to view temperature as a lever for balancing different properties.
The Limits of Lower Temperatures
Operating at the lower end of the spectrum (closer to 600 °C) may result in carbon materials that are not fully optimized for long-term use. While they may function, they often lack the robust cycling stability observed at 800 °C.
The Necessity of Control
Heat without precision leads to variability. If the heat distribution is not regulated effectively (as provided by a tube furnace), the resulting electrodes will exhibit inconsistent porosity and conductivity, rendering them unreliable for practical applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of Red Pepper Waste in energy storage, align your processing parameters with your performance objectives.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability: Target a heat treatment temperature of 800 °C to maximize cycling stability and structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: Utilize a tube furnace to ensure uniform heat distribution, which guarantees predictable porosity and electrical conductivity across the entire batch.
Mastering the thermal environment is the single most effective way to turn agricultural waste into a high-value energy storage asset.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Process Outcome | Key Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 600 - 700 °C | Initial Carbonization | Basic pore structure development |
| 800 °C | Optimized Microstructure | Maximum cycling stability & durability |
| Higher Ranges | Enhanced Conductivity | Improved electron movement efficiency |
| Tube Furnace Role | Precise Heat Distribution | Uniform activation & consistent material quality |
Elevate Your Energy Storage Research with KINTEK
Maximize the potential of biomass-derived materials with precision thermal processing. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to deliver the uniform heat distribution your electrode materials require. Whether you are optimizing Red Pepper Waste or developing next-generation carbon structures, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces ensure consistent, scalable results for your unique research needs.
Ready to achieve superior cycling stability? Contact KINTEK Experts Today
Visual Guide
References
- Perseverance Dzikunu, Pedro Vilaça. Waste-to-carbon-based supercapacitors for renewable energy storage: progress and future perspectives. DOI: 10.1007/s40243-024-00285-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a tube furnace with an external heating module? Isolating Catalytic Mechanisms
- What are the specifications for three-zone and three-phase horizontal tube furnace models? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab
- What role does a tube furnace play in the high-temperature modification of La-EPS-C-450? Key Synthesis Insights
- What is an alumina tube furnace? Essential for High-Temp, Contamination-Free Material Processing
- What makes the multi gradient experimental tube furnace capable of creating temperature gradients? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Your Experiments
- What makes tube furnaces suitable for large-scale production? Unlock Modular Scalability for High-Throughput
- What metallurgical processes benefit from tube furnaces? Achieve Precise Heat Treatment and Material Control
- How does a fixed-bed reactor system simulate complex flue gas environments? Optimize Mercury Adsorption Testing



















