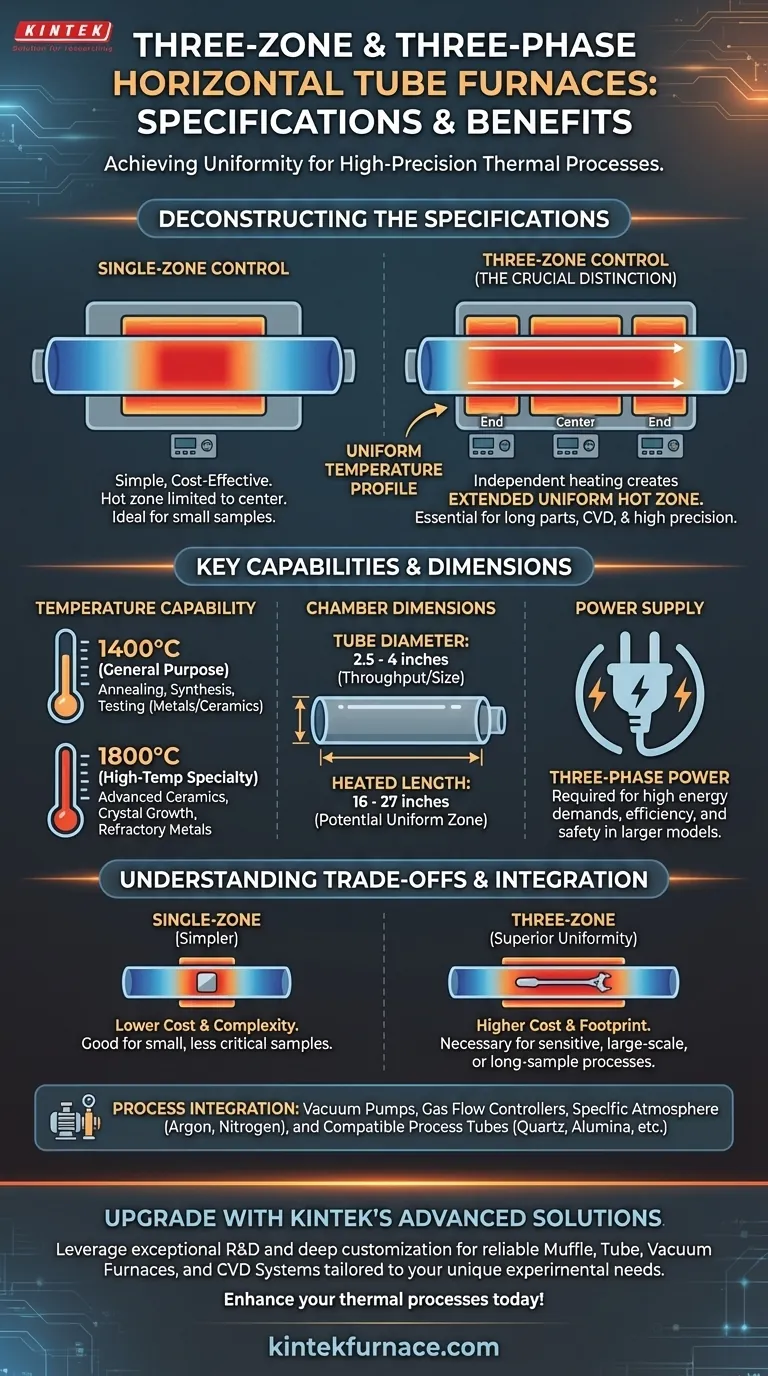
To directly answer your question, the primary specifications for common three-zone, three-phase horizontal tube furnaces involve maximum temperature and chamber dimensions. Models like the 575H14HT and 3H14HT2.5x27 operate up to 1400°C (2552°F), while the 3H18-40HT2.5x27 can reach 1760°C or even 1800°C (3272°F). Tube dimensions typically range from 2.5 to 4 inches in diameter with heated lengths from 16 to 27 inches.
The crucial distinction of a "three-zone" furnace isn't just its specifications, but its purpose. It uses independent heating elements for the center and two ends to create a significantly longer and more uniform hot zone, which is essential for sensitive, large-scale, or high-precision thermal processes.

Deconstructing Furnace Specifications
Choosing a furnace requires looking beyond the maximum temperature. The number of heating zones, the chamber dimensions, and the power requirements are what truly define its capability and suitability for your specific application.
The Significance of "Three-Zone" Control
A single-zone furnace has one heating element and controller. This creates a "hot zone" in the center, but the temperature naturally drops off toward the ends of the tube.
A three-zone furnace divides the heating chamber into three distinct sections (a center and two ends), each with its own thermocouple and controller.
By adjusting the power to the end zones, you can compensate for heat loss and actively extend the area of uniform temperature. This is critical for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or annealing long parts where a consistent temperature profile along the tube's length is non-negotiable.
Temperature Capability: 1400°C vs. 1800°C
The maximum temperature dictates the materials you can process.
A 1400°C furnace is a versatile workhorse for general-purpose annealing, synthesis, and material testing for a wide range of metals and ceramics.
An 1800°C furnace is a high-temperature specialty tool. It's required for processing advanced ceramics, certain refractory metals, and specialized crystal growth where extreme thermal energy is needed.
Chamber Dimensions: Diameter and Length
The tube diameter (e.g., 2.5 or 4 inches) determines your sample throughput or the maximum size of the object you can process. A larger diameter allows for more material or larger components per batch.
The heated length (e.g., 16 or 27 inches) directly relates to the potential size of your uniform hot zone. A longer furnace, especially a three-zone model, can achieve a longer, stable temperature profile.
The Role of "Three-Phase" Power
"Three-phase" refers to the electrical power supply. While smaller lab furnaces may run on single-phase power, larger industrial-scale models, particularly high-temperature and three-zone furnaces, require three-phase power to meet their higher energy demands efficiently and safely.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A more capable furnace is not always the better choice. The selection process involves balancing performance against complexity and cost.
Three-Zone vs. Single-Zone
A single-zone furnace is simpler, less expensive, and perfectly adequate for small samples that fit entirely within its limited uniform hot zone.
A three-zone furnace provides superior temperature uniformity over a much greater length but is more expensive, complex to program, and has a larger physical and electrical footprint. The added control is only valuable if your process requires it.
Process Tube vs. Furnace Capability
The furnace's maximum temperature is only half the story. The process tube material—typically quartz, alumina, or mullite—is what contains your sample and atmosphere.
This tube has its own temperature and thermal shock limits. For example, a quartz tube is excellent for purity and observation but typically cannot be used above ~1200°C. You must match the tube material to your furnace's operating temperature and your process chemistry.
Atmosphere and Process Integration
Your furnace choice is constrained by your process needs. If you require a vacuum or a specific gas atmosphere (e.g., Argon, Nitrogen), you must ensure the furnace system can be integrated with vacuum pumps, gas flow controllers, and end seals that create an airtight environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Base your decision on the specific, unchangeable demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is processing small samples where absolute uniformity is not critical: A simpler, more cost-effective single-zone furnace is likely sufficient.
- If your primary focus is achieving the most uniform temperature possible over a long sample: A three-zone furnace is the only reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis (>1500°C) or processing large batches: You will need a high-temperature model with a larger diameter tube, which will almost certainly require three-phase power.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's zone control and thermal capabilities to the precise requirements of your process ensures repeatable, successful results.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1400°C or 1800°C |
| Tube Diameter | 2.5 to 4 inches |
| Heated Length | 16 to 27 inches |
| Heating Zones | Three zones for uniform temperature |
| Power Supply | Three-phase for high energy demands |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs for superior performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















