In manufacturing advanced ceramics and glass, vacuum tube furnaces are primarily used for high-temperature sintering and melting. Their function is to create a controlled, oxygen-free environment that allows for the tight bonding of material particles, which significantly enhances the final product's density, purity, and mechanical strength.
The critical role of a vacuum furnace is not just to provide heat, but to eliminate atmospheric contamination. This controlled environment is what enables the production of high-purity, high-density ceramics and glass with properties unattainable through conventional atmospheric firing.

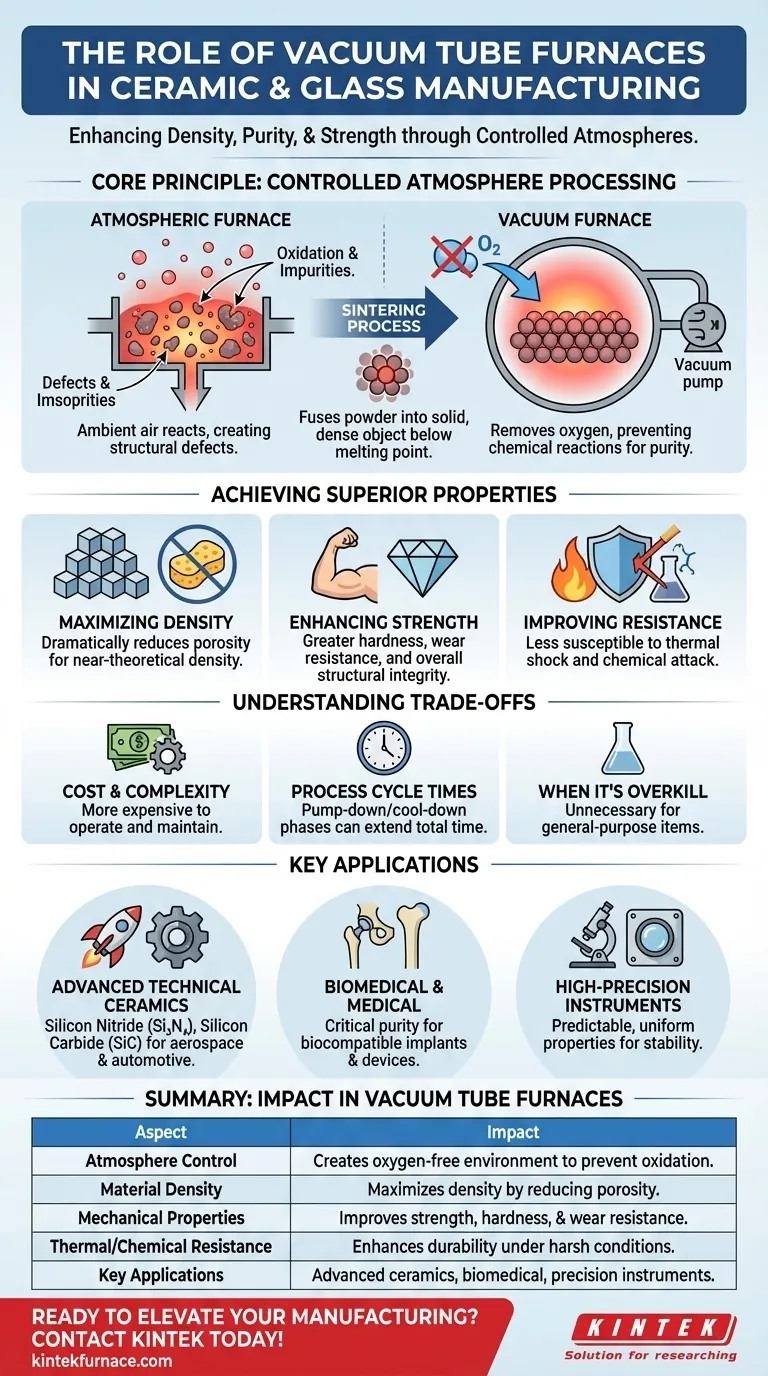
The Core Principle: Processing in a Controlled Atmosphere
The fundamental advantage of a vacuum furnace is its ability to remove reactive gases—primarily oxygen—from the processing chamber. This unlocks a level of material quality that is otherwise impossible.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal process that consolidates a powder compact into a solid, dense object. Heat is applied to the material below its melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse, reducing voids and increasing density.
Why a Vacuum Changes Everything
In a standard furnace, ambient air reacts with the material at high temperatures, a process known as oxidation. This introduces impurities and creates structural defects.
A vacuum furnace removes the air, preventing these unwanted chemical reactions. This ensures the material's chemical composition remains pure and its final structure is uniform and free from atmospheric contamination.
Achieving Superior Material Properties
By preventing oxidation and removing trapped gases, vacuum processing directly translates to superior physical and mechanical characteristics in the final product.
Maximizing Density and Eliminating Porosity
During sintering, a vacuum helps pull residual gases out from between the material particles. This process dramatically reduces porosity (the presence of tiny voids) and allows the material to achieve near-theoretical density.
A denser material is inherently stronger and more durable.
Enhancing Mechanical Strength and Hardness
The reduction in porosity and elimination of impurities result in a ceramic or glass with significantly enhanced mechanical properties. This includes greater hardness, wear resistance, and overall structural strength.
These characteristics are critical for components used in high-stress or extreme environments, such as aerospace parts or industrial cutting tools.
Improving Thermal and Chemical Resistance
A dense, non-porous structure is less susceptible to thermal shock and chemical attack. With fewer pathways for heat or chemicals to penetrate, the material's integrity is maintained even under harsh operating conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While offering unmatched quality, vacuum furnaces are not the solution for every application. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum systems are more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than standard atmospheric furnaces. They require specialized pumps, seals, and control systems that add to their complexity.
Process Cycle Times
Achieving a high vacuum and then executing a controlled heating and cooling cycle can be time-consuming. The pump-down and cool-down phases often make the total process time longer than conventional firing.
When It Is Overkill
For many general-purpose ceramics or decorative glass items, the level of purity and density provided by a vacuum furnace is unnecessary. A standard atmospheric furnace is often more than sufficient and far more cost-effective for these applications.
Key Applications Driven by Vacuum Processing
The unique capabilities of vacuum furnaces make them essential for manufacturing the most demanding materials.
Advanced Technical Ceramics
Materials like silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) and silicon carbide (SiC) are processed in vacuum furnaces. Their exceptional strength and thermal resistance make them vital for aerospace, automotive, and defense components.
Biomedical and Medical Devices
The inherent purity of vacuum-sintered ceramics is critical for medical implants and devices. The process ensures biocompatibility and eliminates contaminants that could cause adverse reactions in the human body.
High-Precision Instruments
Components for high-precision scientific and industrial instruments demand materials with predictable, uniform properties and extreme stability. Vacuum processing provides the control necessary to meet these stringent quality standards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing technology depends entirely on the required performance and cost constraints of your final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and purity for critical applications: A vacuum furnace is essential to achieve the required density, strength, and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of general-purpose materials: A conventional atmospheric furnace is the more practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is research and development of novel materials: The precise control over atmosphere and temperature in a vacuum furnace makes it an invaluable tool for innovation.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching the process capabilities to the material's intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact in Vacuum Tube Furnaces |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Creates oxygen-free environment to prevent oxidation and contamination |
| Material Density | Maximizes density by reducing porosity through gas removal |
| Mechanical Properties | Improves strength, hardness, and wear resistance |
| Thermal/Chemical Resistance | Enhances durability under harsh conditions |
| Key Applications | Used in advanced ceramics, biomedical devices, and precision instruments |
Ready to elevate your ceramic and glass manufacturing with advanced high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with cutting-edge furnace technologies. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Achieve superior purity, density, and performance in your materials—contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















