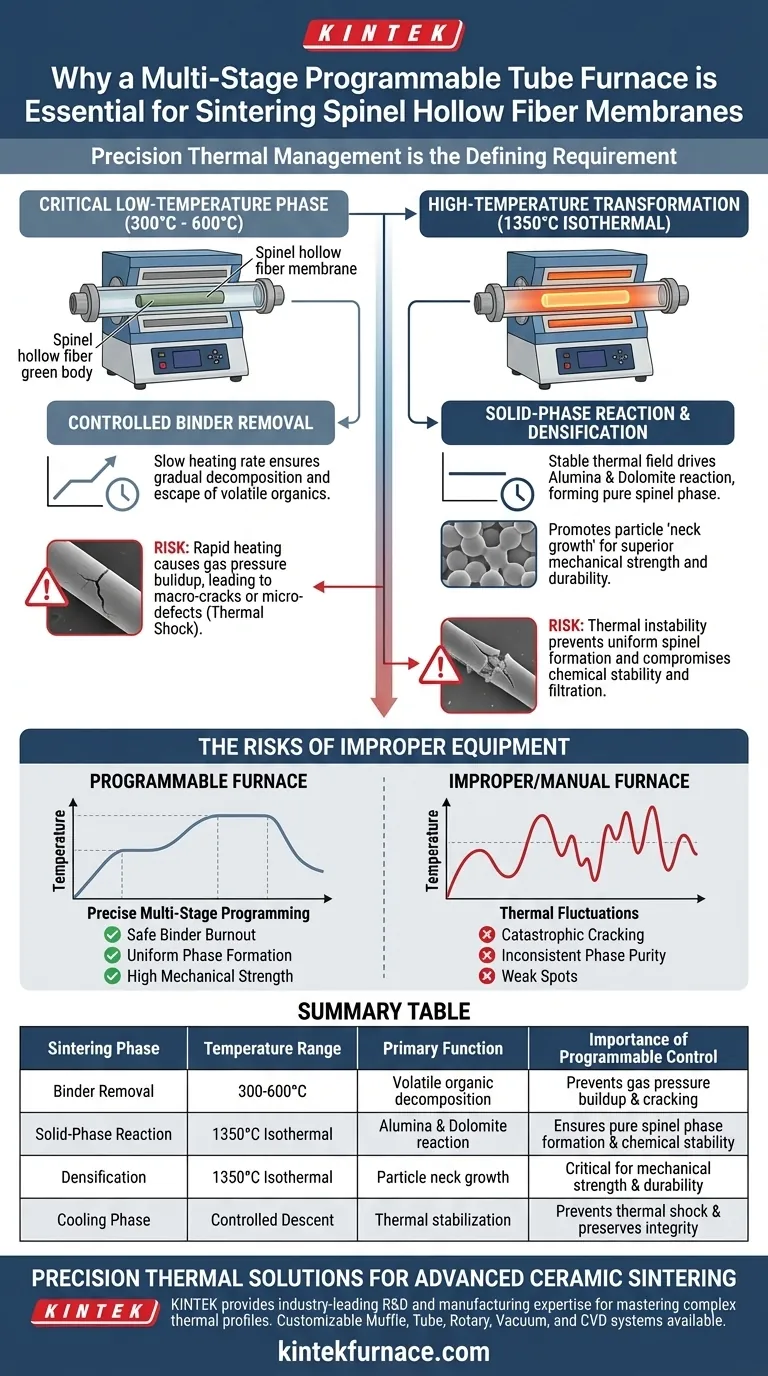
Precision thermal management is the defining requirement for successfully sintering spinel hollow fiber membrane green bodies. A multi-stage programmable tube furnace is necessary because it automates the complex heating profiles required to navigate two distinct critical phases: the delicate removal of organic binders at lower temperatures and the robust chemical transformation at high temperatures. Without this level of programmable control, the membrane is liable to suffer from structural cracking or incomplete phase formation.
The core challenge in sintering these membranes is balancing the gentle heating required to degas polymers with the intense thermal stability needed for densification. A programmable furnace bridges this gap by executing precise ramp rates and dwell times that manual or single-stage furnaces cannot replicate.

Managing the Critical Low-Temperature Phase
Controlled Binder Removal
The initial stage of sintering, occurring between 300°C and 600°C, is strictly focused on removing polymer binders and additives. A programmable furnace allows you to set a specifically slow heating rate during this window. This controlled pace ensures that volatile organics decompose and escape the green body gradually.
Preventing Structural Defects
If the temperature rises too quickly during the low-temperature phase, gas pressure builds up inside the membrane. This rapid off-gassing causes stress that leads to macro-cracks or micro-defects. The programmable nature of the furnace acts as a safeguard, preventing thermal shock and ensuring the membrane retains its structural integrity before high heat is applied.
Facilitating the High-Temperature Transformation
The Solid-Phase Reaction
Once the binders are removed, the furnace must transition to a high-temperature isothermal stage, specifically at 1350°C. At this peak temperature, a stable thermal field is required to drive the in-situ solid-phase reaction. This specific thermal environment allows alumina and dolomite to react chemically, forming the desired spinel phase.
Achieving Mechanical Strength
Beyond chemical composition, the high-temperature dwell time is critical for physical densification. The stable heat provided by the tube furnace promotes "neck growth" between ceramic particles. This bonding process is what ultimately grants the ceramic membrane its superior mechanical strength and durability.
Understanding the Risks of Improper Equipment
The Danger of Thermal Instability
Using a furnace without precise multi-stage programming often leads to thermal fluctuations. In the low-temperature range, even minor spikes can accelerate binder burnout, resulting in catastrophic cracking. In the high-temperature range, instability prevents the uniform formation of the spinel phase, leading to weak spots in the fiber.
Inconsistent Phase Purity
If the furnace cannot maintain the 1350°C isotherm accurately, the reaction between alumina and dolomite may remain incomplete. This results in a membrane with mixed phases rather than pure spinel. Such inconsistencies compromise the chemical stability and filtration performance of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To ensure high-quality production of spinel hollow fiber membranes, your thermal profile must be tailored to the specific needs of the materials involved.
- If your primary focus is defect reduction: Prioritize a furnace program with extremely conservative ramp rates in the 300-600°C zone to ensure safe binder burnout.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: Ensure your furnace is calibrated to hold a precise, stable isotherm at 1350°C to maximize particle necking and phase conversion.
Success in ceramic membrane fabrication is less about maximum heat and more about the precision of the thermal journey.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Phase | Temperature Range | Primary Function | Importance of Programmable Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binder Removal | 300°C - 600°C | Volatile organic decomposition | Prevents gas pressure buildup and structural cracking. |
| Solid-Phase Reaction | 1350°C (Isothermal) | Alumina & Dolomite reaction | Ensures pure spinel phase formation and chemical stability. |
| Densification | 1350°C (Isothermal) | Particle neck growth | Critical for achieving mechanical strength and durability. |
| Cooling Phase | Controlled Descent | Thermal stabilization | Prevents thermal shock and preserves membrane integrity. |
Precision Thermal Solutions for Advanced Ceramic Sintering
Fabricating high-quality spinel hollow fiber membranes requires more than just heat; it requires an exact thermal journey. KINTEK provides the industry-leading R&D and manufacturing expertise needed to master these complex profiles.
Backed by our specialized knowledge in high-temperature systems, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all of which are fully customizable to meet your specific ramp rates and isothermal requirements.
Whether you are focusing on eliminating micro-defects during binder burnout or maximizing phase purity at 1350°C, KINTEK has the solution to elevate your lab's output.
Ready to optimize your sintering process? Contact KINTEK today for a custom furnace consultation.
Visual Guide
References
- Kristopher Rodrigues Dorneles, Miria Hespanhol Miranda Reis. Clarification of Clove Basil Extract Using Spinel Hollow Fiber Membranes. DOI: 10.3390/ceramics8020057
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do researchers utilize the heating elements in tubular furnaces? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials Research
- How do resistance heating tube furnaces generate heat? Master Precise Temperature Control
- How does a laboratory tube diffusion furnace facilitate pre-deposition? Precision Doping for Silicon Wafer Processing
- What type of processing environment do high-temperature tube and muffle furnaces provide? Master Thermal Precision
- How is a laboratory tube furnace utilized to convert metal-organic precursors? Master Thin Film Pyrolysis Today
- How to operate a tubular furnace? A 5-Phase Guide for Safe and Repeatable Results
- What are the primary functions of a tube furnace during GO thermal reduction? Optimize Graphene Conductivity
- How does high-purity Nitrogen thermal annealing in a tube furnace facilitate the observation of Violet Phosphorus?



















