Operating a tubular furnace is a systematic process that must be approached with methodical precision. In essence, you prepare the equipment and sample, install the process tube, program the desired temperature profile, run the heating cycle while monitoring it, and then execute a controlled shutdown and cooling procedure. This structured approach is essential for both safety and achieving repeatable, accurate results.
Successful and safe operation of a tubular furnace goes beyond just setting a temperature. It hinges on methodical preparation, constant monitoring, and a deep respect for the high temperatures and potential atmospheric conditions involved.
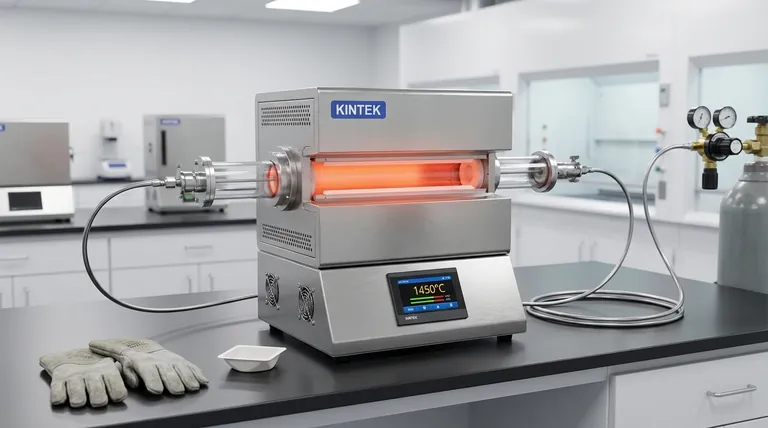

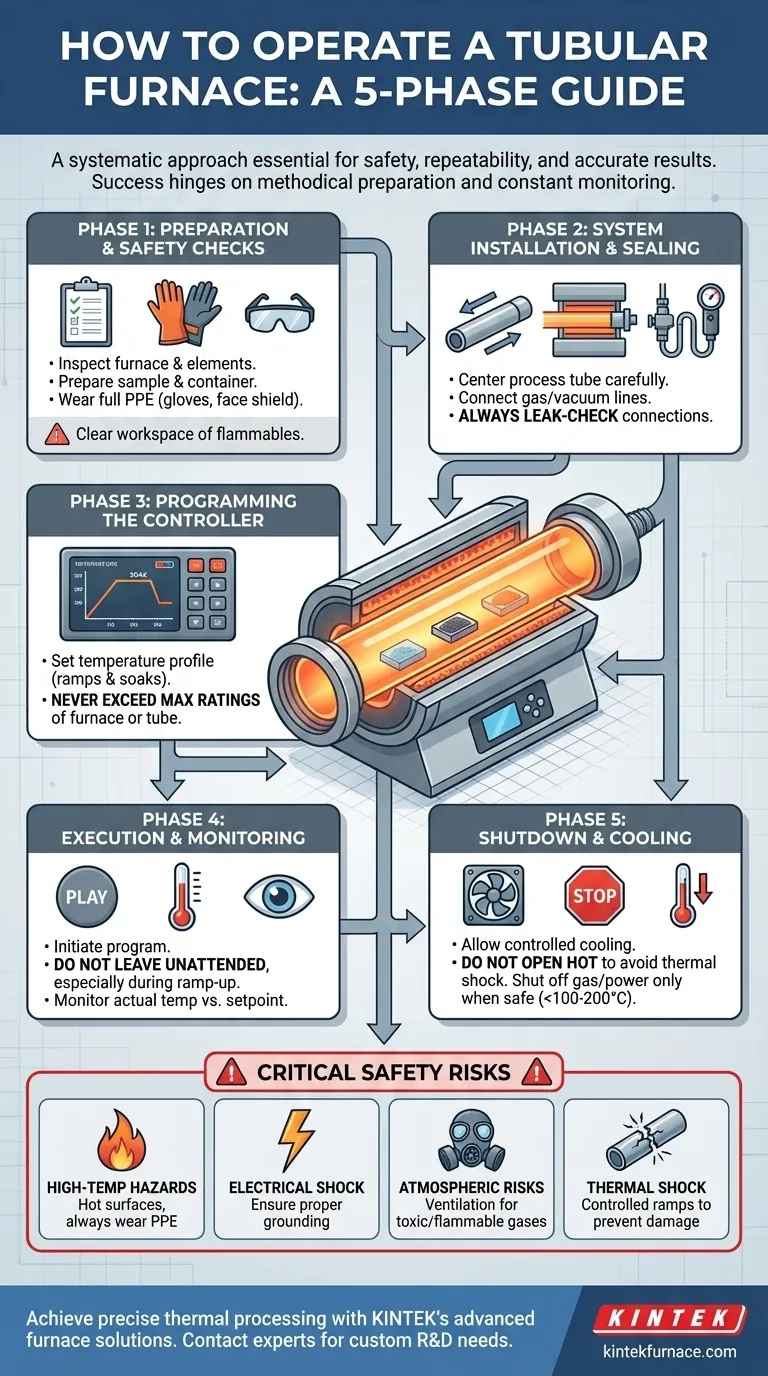
The 5-Phase Operating Procedure
A tubular furnace uses a cylindrical heating chamber to provide exceptional temperature uniformity and control. To leverage this design effectively, operations should be broken down into five distinct phases.
Phase 1: Preparation and Safety Checks
Before any power is applied, a thorough inspection is mandatory. This phase prevents equipment damage and ensures operator safety.
First, inspect the furnace's physical condition, paying close attention to the heating elements and the thermocouple used for temperature feedback. Ensure the workspace is clear of any flammable materials.
Next, prepare your sample and its container (e.g., a crucible or boat). Confirm that the material is suitable for the planned temperatures.
Finally, put on your personal protective equipment (PPE). At a minimum, this includes heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses or a face shield.
Phase 2: System Installation and Sealing
This phase involves setting up the core of the system: the process tube.
Carefully slide the ceramic or quartz process tube into the furnace cavity, ensuring it is centered within the heated zone. Be gentle to avoid cracking the tube.
If you are running the process under a specific atmosphere or vacuum, this is the time to connect the gas lines or vacuum pump to the end flanges. Always leak-check these connections before proceeding.
Phase 3: Programming the Temperature Controller
Modern tubular furnaces are run by a programmable controller. Incorrect programming is a common source of failed experiments.
Power on the main air switch and then the controller itself. You will set the temperature profile, which typically consists of one or more ramps and soaks.
A ramp is the rate at which temperature changes (e.g., 10°C per minute). A soak is a period where the temperature is held constant for a set duration.
Crucially, never set a temperature that exceeds the maximum rating of the furnace, the process tube, or your sample holder.
Phase 4: Execution and Monitoring
With the program set, you can begin the heating cycle.
Press the "run" or "heat" button on the controller to initiate the program. The furnace will now begin to execute your defined temperature profile.
Do not leave the furnace unattended, especially during the initial ramp-up. Monitor the controller's display to ensure the actual temperature is closely tracking your setpoint. Any significant deviation could indicate a problem with the thermocouple or controller.
Phase 5: Shutdown and Cooling
Turning off a furnace is as critical as turning it on. Abrupt cooling can destroy both your sample and the equipment.
Once the heating program is complete, allow the furnace to cool down naturally or via a controlled cooling ramp programmed into the controller.
Do not open the furnace door or remove the sample while the temperature is high. The resulting thermal shock can crack the process tube and ruin your work.
Only after the furnace has cooled to a safe temperature (typically below 100-200°C) should you shut off any gas flows, vent the chamber to equalize pressure, and power down the main system.
Understanding the Critical Safety Risks
Operating a tubular furnace is generally safe when procedures are followed, but the risks are significant if they are ignored.
High-Temperature Hazards
The most obvious risk is severe burns from touching hot surfaces. The furnace exterior, process tube ends, and flanges can all reach extremely high temperatures. Always assume the furnace is hot, and always wear your PPE.
Electrical Shock and Grounding
A tubular furnace is a high-power electrical device. Ensure it is connected to a properly rated circuit and that its chassis has an effective ground connection to prevent the risk of electric shock.
Atmospheric Control Risks
If using process gases, you must ensure proper ventilation, especially if the gas is flammable, toxic, or an asphyxiant. Gas leaks are a serious hazard, reinforcing the need for leak-checking during setup. If operating under vacuum, ensure you are using a vacuum-rated process tube (like quartz) to prevent a dangerous implosion.
Thermal Shock and Equipment Damage
Ceramic and quartz tubes are strong but brittle. Rapid, uncontrolled temperature changes create internal stress that can cause them to crack. Always use controlled heating and cooling ramps to prolong the life of your equipment.
Applying This to Your Process
Your specific procedure will vary based on your goal, but the principles remain the same. Here is how to tailor your approach:
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or annealing: The accuracy of your temperature profile, especially the ramp rates and soak times, is your most critical variable.
- If your primary focus is safety and training: Create a formal Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) checklist based on these five phases and post it directly on or near the equipment.
- If you are using a controlled atmosphere (gas or vacuum): Your most critical step is verifying the integrity of your seals with a leak-check before initiating the heating program.
By treating furnace operation as a systematic, five-phase process, you ensure safety, repeatability, and the integrity of your results.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Key Action | Critical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Inspect furnace, prepare sample, wear PPE | Ensure workspace is clear of flammables |
| 2. Installation | Install and center process tube, connect gas/vacuum | Always perform a leak-check |
| 3. Programming | Set temperature ramps and soaks on controller | Never exceed max temperature ratings |
| 4. Execution | Start program and monitor temperature closely | Never leave the furnace unattended |
| 5. Shutdown | Allow for controlled cooling before opening | Avoid thermal shock to protect equipment |
Achieve precise thermal processing with a furnace built for your unique needs. The methodical operation detailed above is key to success, but it starts with the right equipment. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a reliable, high-performance tubular furnace? Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover the perfect solution for your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















