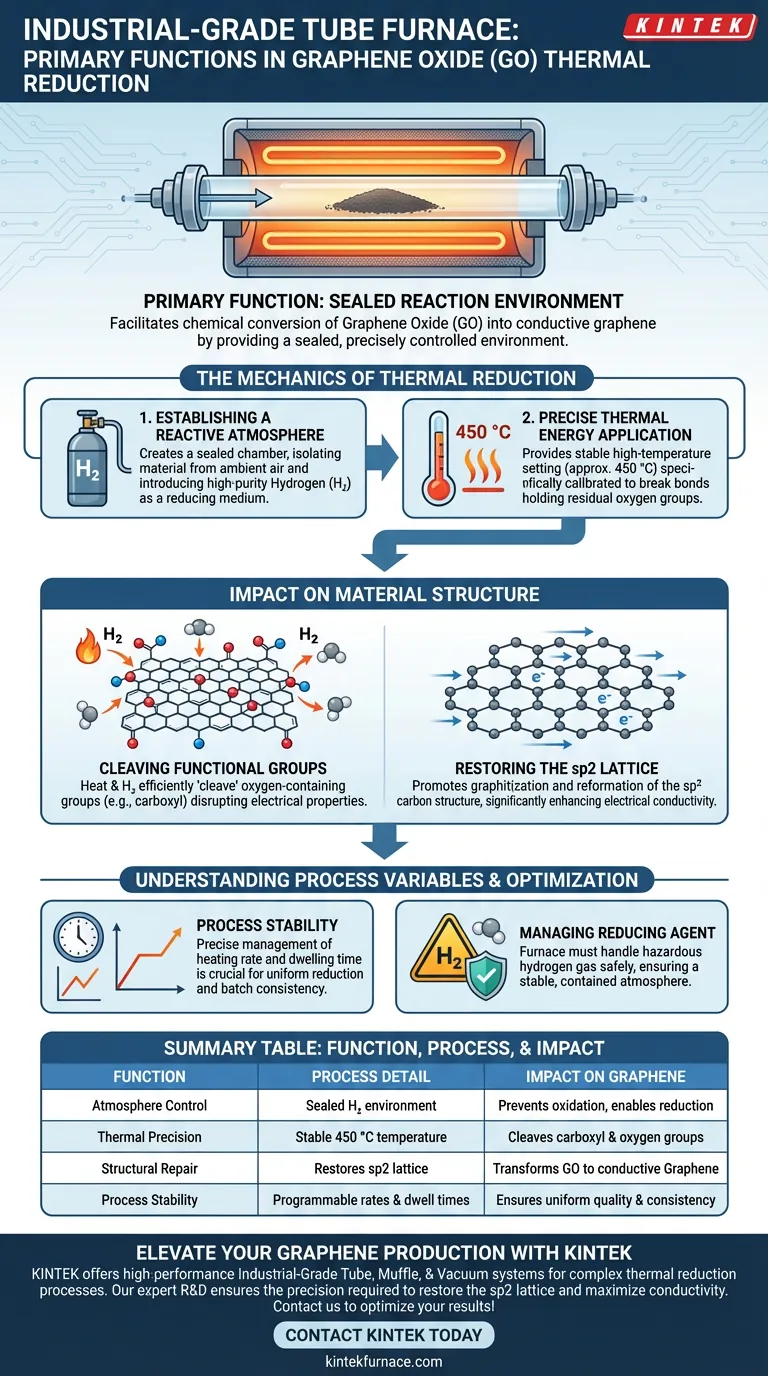
The primary function of an industrial-grade tube furnace in this context is to provide a sealed, precisely controlled reaction environment that facilitates the chemical conversion of Graphene Oxide (GO) into conductive graphene. Specifically, it maintains a high-temperature atmosphere (around 450 °C) while introducing high-purity hydrogen to strip away oxygen functional groups and repair the carbon atomic lattice.
The tube furnace does not merely heat the material; it acts as an environment for structural restoration, using thermal energy and a reducing atmosphere to transform Graphene Oxide from an insulator back into a highly conductive material.

The Mechanics of Thermal Reduction
Establishing a Reactive Atmosphere
The furnace’s most critical role is creating a sealed environment that isolates the material from ambient air.
This allows for the introduction of high-purity hydrogen (H2) as a reducing medium. This hydrogen atmosphere is essential, as it actively participates in the chemical reaction required to strip oxygen from the graphene oxide.
Precise Thermal Energy Application
To trigger the reduction, the furnace provides a stable high-temperature setting, often targeted at 450 °C.
This thermal energy is not arbitrary; it is specifically calibrated to break the chemical bonds holding residual oxygen functional groups to the carbon lattice.
Impact on Material Structure
Cleaving Functional Groups
Graphene Oxide is heavily populated with oxygen-containing groups, such as carboxyl groups, which disrupt its electrical properties.
The combination of heat and hydrogen within the furnace efficiently "cleaves" or severs these groups from the material. This removal is the first step in purifying the graphene structure.
Restoring the sp2 Lattice
The ultimate goal of the process is graphitization, or the restoration of the material's ordered structure.
The furnace environment promotes the reformation of the sp2 carbon structure. This structural repair is directly responsible for significantly enhancing the electrical conductivity of the final product.
Understanding the Process Variables
The Importance of Stability
While the primary reference focuses on temperature and atmosphere, the stability of these variables is paramount.
As noted in broader industrial applications, a tube furnace must precisely manage the heating rate and dwelling time. Inconsistencies in these parameters can lead to incomplete reduction or uneven material properties.
Managing the Reducing Agent
The use of hydrogen requires a furnace capable of handling hazardous gases safely.
The "industrial-grade" designation implies the equipment is built to manage the safety risks associated with heating hydrogen, ensuring the reducing atmosphere remains stable and contained throughout the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting or operating a tube furnace for Graphene Oxide reduction, focus on the capabilities that align with your specific output requirements.
- If your primary focus is Electrical Conductivity: Prioritize a furnace with exceptional seal integrity to maintain high hydrogen purity, as this maximizes the restoration of the sp2 structure.
- If your primary focus is Process Consistency: Ensure the furnace offers precise programmable control over heating rates and dwell times to guarantee uniform reduction across every batch.
The effectiveness of your thermal reduction process depends entirely on the furnace's ability to maintain a rigorous balance between heat and chemical atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Function | Process Detail | Impact on Graphene |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed environment for high-purity H2 | Prevents oxidation and enables chemical reduction |
| Thermal Precision | Stable 450 °C temperature application | Cleaves carboxyl and other oxygen functional groups |
| Structural Repair | Restores the sp2 carbon lattice | Transforms insulator GO into conductive Graphene |
| Process Stability | Programmable heating rates and dwell times | Ensures uniform quality and batch-to-batch consistency |
Elevate Your Graphene Production with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between average and industry-leading materials. KINTEK provides high-performance industrial-grade Tube, Muffle, and Vacuum systems specifically engineered for complex thermal reduction processes. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems ensure the atmosphere integrity and temperature stability required to restore the sp2 lattice and maximize electrical conductivity. Whether you need standard or fully customizable lab high-temp furnaces, we have the solution for your unique research and production needs.
Ready to optimize your thermal reduction results? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Dilek Öztekin, Sena Yaşyerli. Preparation of RGO with Enhanced Electrical Conductivity: Effects of Sequential Reductions of L-Ascorbic Acid and Thermal. DOI: 10.1007/s13369-024-09915-5
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary role of a tubular furnace in industrial production? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing for Superior Materials
- What is the purpose of pre-treating sapphire substrates in a tube furnace? Optimize Your Epitaxial Growth Foundation
- What makes vacuum tube furnaces stand out in terms of equipment diversification? Discover Their Modular Design & Precision Control
- How does a high-precision horizontal tube furnace facilitate the activation stage of catalysts? Optimize Pore Integrity
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace used for AlPO4 calcination? Ensure Safety in Molten Salt Electrolysis
- How vacuum pumping affects Zr2.5Nb nitriding? Achieve pure ZrN surfaces in high-temp tube furnaces.
- What are the applications of a tube furnace? Master Precise Thermal Processing for Advanced Materials
- Why is a tube furnace with argon required for Ti3AlC2 sintering? Protect Your High-Purity MAX Phase Synthesis



















