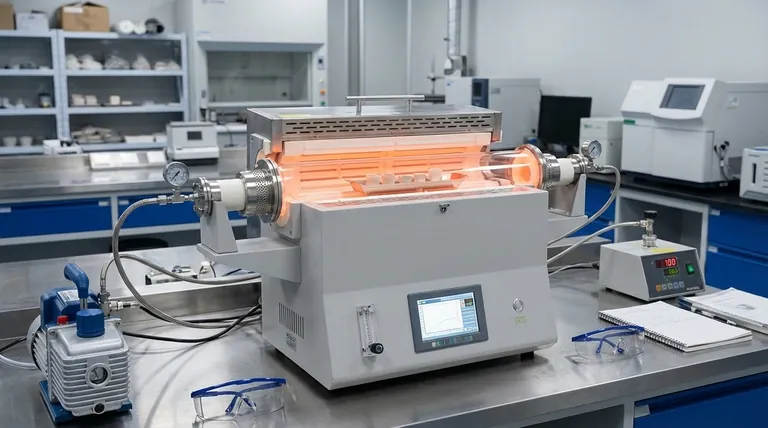
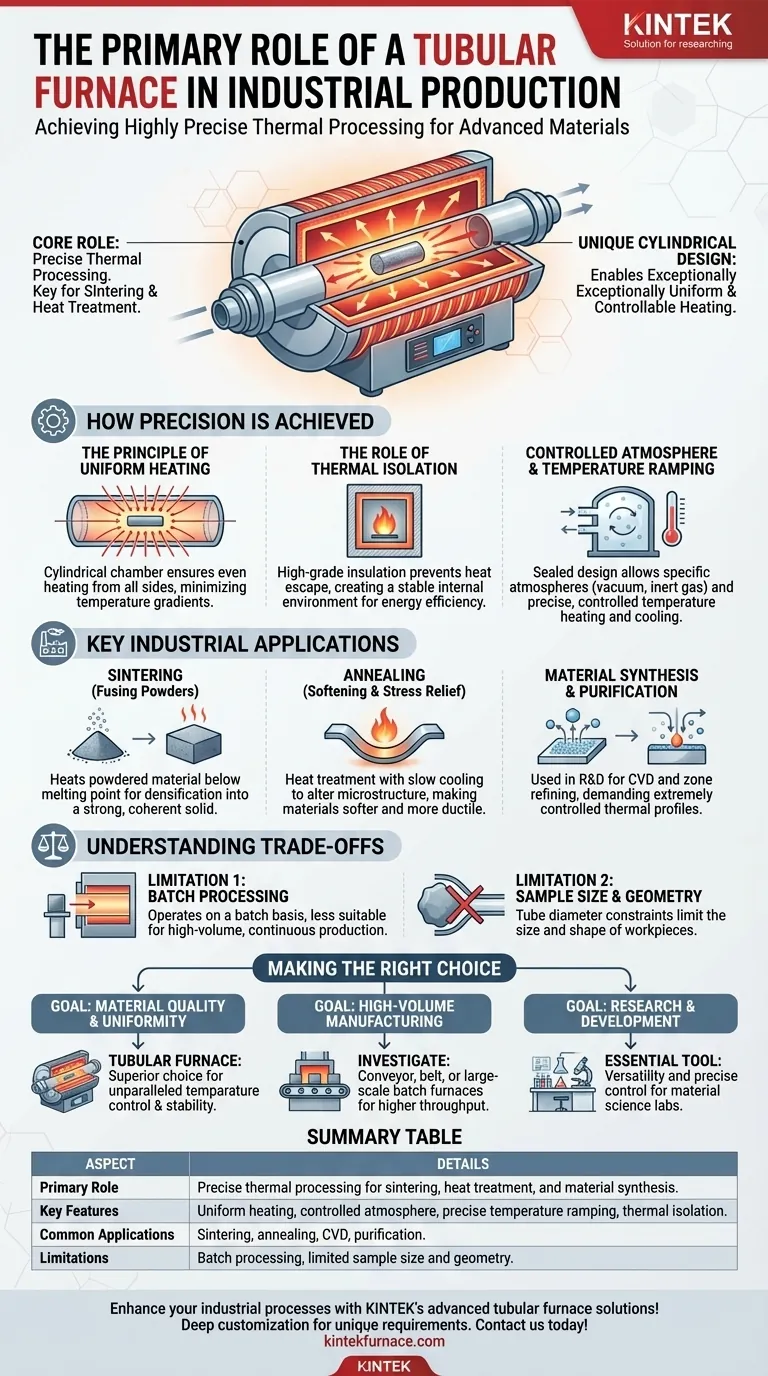
At its core, the primary role of a tubular furnace in industrial production is to perform highly precise thermal processing on materials. This is most commonly applied to critical processes like sintering, where powdered materials are fused into a solid mass, and heat treatment, where the properties of metals and alloys are carefully altered.
The true value of a tubular furnace is not just its ability to generate heat, but its unique cylindrical design. This geometry is the key to creating an exceptionally uniform and controllable heating environment, which is non-negotiable for producing advanced and high-performance materials.

How a Tubular Furnace Achieves Precision
The effectiveness of a tubular furnace comes from its fundamental design, which is engineered for stability and control above all else.
The Principle of Uniform Heating
The furnace's chamber is a tube, which ensures that the material placed inside is heated evenly from all sides. This cylindrical geometry minimizes temperature gradients, preventing hot spots or cold spots that could ruin the material.
This uniformity is critical for processes where every part of the sample must experience the exact same thermal history to achieve consistent material properties.
The Role of Thermal Isolation
These furnaces are constructed with high-grade thermal insulation surrounding the tubular cavity. This design prevents heat from escaping, creating a highly stable internal environment.
By minimizing heat loss, the furnace can maintain a set temperature with remarkable accuracy and use energy more efficiently.
Controlled Atmosphere and Temperature Ramping
Many industrial processes require heating in a specific atmosphere, such as a vacuum or an inert gas like argon, to prevent oxidation or unwanted chemical reactions. The sealed, tubular design is perfectly suited for creating and maintaining these controlled environments.
Furthermore, these systems excel at precise temperature ramping—the ability to increase and decrease temperature at a very specific, controlled rate. This is essential for delicate processes like annealing, where slow cooling is required to relieve internal stresses in a material.
Key Industrial Applications
The precision of a tubular furnace makes it indispensable for several high-value industrial tasks that go beyond simple heating.
Sintering: Fusing Powders into Solids
Sintering involves heating a compact of powdered material to just below its melting point. The uniform heat of a tubular furnace ensures that the entire compact densifies evenly, resulting in a strong, coherent solid part with predictable properties.
Annealing: Softening and Stress Relief
Annealing is a heat treatment process that alters a material's microstructure to make it softer and more ductile. It requires heating the material to a specific temperature and then cooling it very slowly. The excellent thermal control and isolation of a tubular furnace make it ideal for this task.
Material Synthesis and Purification
In advanced manufacturing and R&D, tubular furnaces are used for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where gases react on a heated surface to create a solid film. They are also used for purifying materials through processes like zone refining, which demand an extremely controlled thermal profile.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the tubular furnace is a specialized tool with specific limitations that are important to recognize.
Limitation 1: Batch Processing and Throughput
Most standard tubular furnaces operate on a batch basis—a sample is loaded, processed, and then unloaded. This makes them less suitable for high-volume, continuous production lines where throughput is the primary concern.
Limitation 2: Sample Size and Geometry
The defining feature of the furnace—its tube—also creates its main constraint. The diameter of the tube naturally limits the size and shape of the workpieces that can be processed. Large or irregularly shaped components cannot be accommodated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on your end goal. The tubular furnace is a tool for precision, not mass production.
- If your primary focus is material quality and uniformity: A tubular furnace is the superior choice for its unparalleled temperature control and stable processing environment.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of large parts: You should investigate conveyor, belt, or large-scale batch furnaces designed for higher throughput and larger components.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The versatility and precise control of a tubular furnace make it an essential and non-negotiable tool for material science labs.
Ultimately, a tubular furnace is the instrument of choice when the final properties of your material are more important than the speed at which it is produced.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Role | Precise thermal processing for sintering, heat treatment, and material synthesis |
| Key Features | Uniform heating, controlled atmosphere, precise temperature ramping, thermal isolation |
| Common Applications | Sintering, annealing, CVD, purification |
| Limitations | Batch processing, limited sample size and geometry |
Enhance your industrial processes with KINTEK's advanced tubular furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior material quality and uniformity. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your thermal processing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















