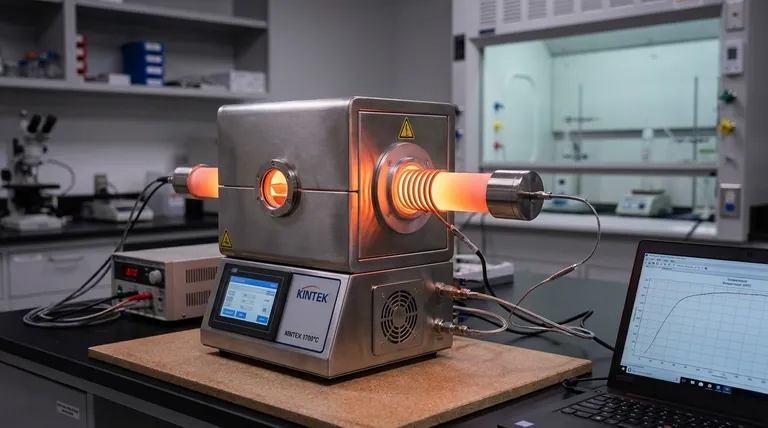
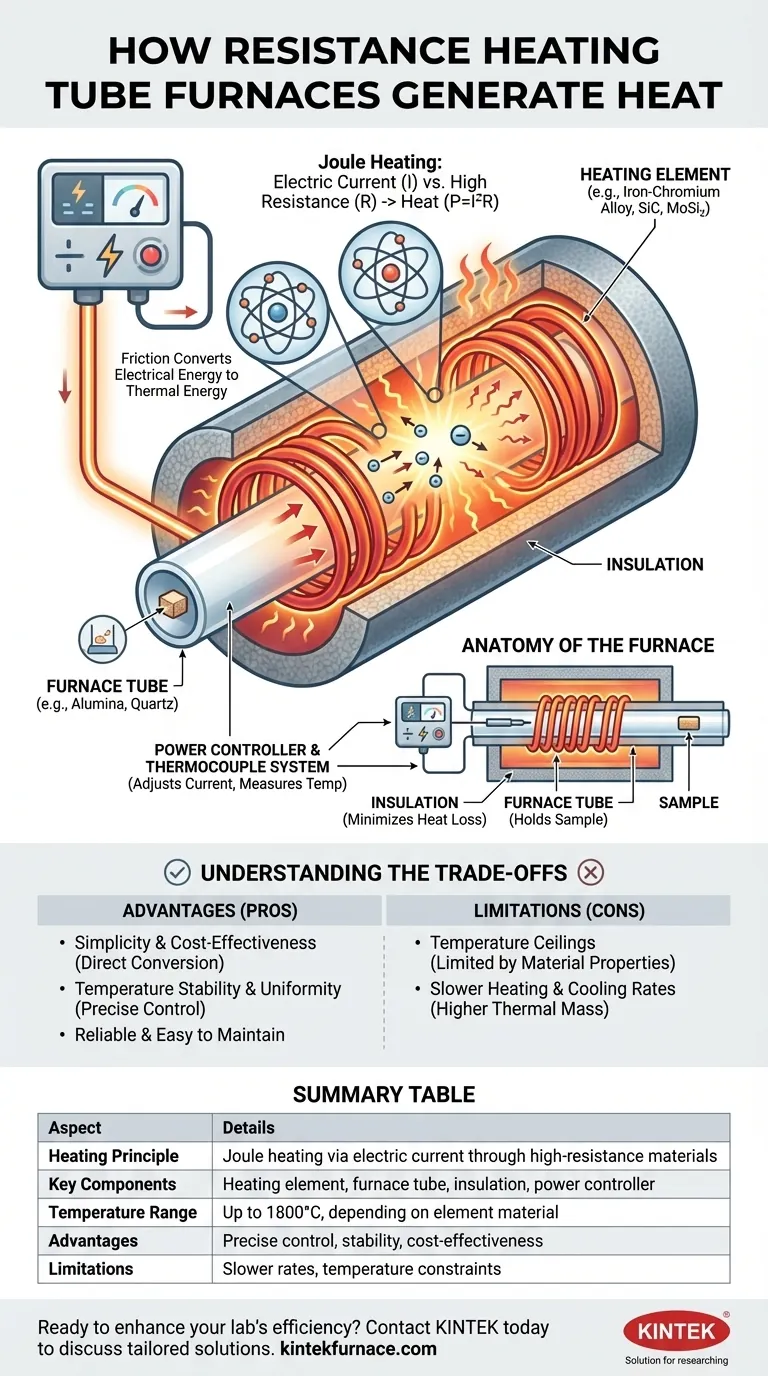
At their core, resistance heating tube furnaces operate on a simple and reliable principle known as Joule heating. An electric current is passed through a specially designed heating element, typically an iron-chromium alloy wire, which has high electrical resistance. This resistance converts the electrical energy directly into thermal energy, generating the precise heat required for the process.
The fundamental mechanism is the controlled conversion of electrical energy into heat. By forcing electricity through a material that resists its flow, the furnace generates a predictable and stable source of high temperature.

The Core Principle: Joule Heating
Joule heating, or resistive heating, is the physical phenomenon that underpins how these furnaces work. It describes the relationship between electricity, resistance, and the generation of heat.
Converting Electricity to Heat
When an electric current flows through any material, the moving electrons collide with the atoms of that material. In a high-resistance material, these collisions are frequent and energetic. This friction at the atomic level transfers kinetic energy from the electrons to the atoms, causing them to vibrate more intensely, which we perceive as an increase in temperature.
The Role of the Heating Element
The furnace's heating element is the component where this energy conversion takes place. It is not made from a typical conductor like copper, which is designed to let current pass with minimal resistance. Instead, it is crafted from a material specifically chosen for its high electrical resistance.
The Physics of Heat Generation
The amount of heat generated is defined by the formula P = I²R, where P is power (heat), I is the electric current, and R is the resistance. This shows that the heat output increases exponentially with the current, allowing for precise temperature control by a power supply unit.
Anatomy of a Resistance Tube Furnace
While the principle is simple, its practical application involves a few key components working in concert to create a controlled thermal environment.
The Heating Element Material
As noted, these elements are often made from an iron-chromium alloy (like Kanthal) or other materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂). These materials are ideal because they not only have high resistance but also possess a high melting point and form a stable, protective oxide layer that prevents them from degrading at extreme temperatures.
The Furnace Tube and Insulation
The heating element is typically wound in spiral grooves on the exterior of a ceramic furnace tube. This tube, often made of alumina or quartz, holds the sample being processed. The entire assembly is then encased in high-grade thermal insulation, which minimizes heat loss and ensures the energy is directed efficiently into the furnace chamber.
The Power Supply and Controller
A sophisticated power controller and thermocouple system are critical for operation. The thermocouple measures the temperature inside the furnace and sends feedback to the controller. The controller then adjusts the electric current flowing to the heating element to precisely maintain the desired setpoint temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Resistance heating is a dominant technology for a reason, but it's essential to understand its advantages and limitations.
Advantage: Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
The direct conversion of electricity to heat is a straightforward and mechanically simple process. This results in furnaces that are highly reliable, easy to maintain, and generally more affordable than those using other heating methods like induction or microwave.
Advantage: Temperature Stability and Uniformity
When well-designed, resistance furnaces provide excellent temperature stability and a uniform hot zone. The ability to finely tune the electric current allows for exceptionally precise temperature control, which is critical for sensitive scientific and industrial processes.
Limitation: Temperature Ceilings
The maximum achievable temperature of a resistance furnace is fundamentally limited by the material properties of the heating element. As you approach the element's melting point or maximum operating temperature, it will degrade and eventually fail.
Limitation: Slower Heating and Cooling Rates
Compared to technologies like induction heating, resistance furnaces have a higher thermal mass (due to the elements and insulation). This means they generally take longer to heat up to the target temperature and cool back down, which can be a factor in high-throughput applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these principles allows you to select and operate a furnace that aligns with your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control and stability: Resistance heating is an excellent choice, offering one of the most stable and uniform heating methods available.
- If your primary focus is reaching ultra-high temperatures (above 1800°C): You must ensure the heating element material (e.g., MoSi₂) is rated for your target, as this is the primary limiting factor.
- If your primary focus is budget and reliability for general-purpose use: The proven design and simplicity of resistance tube furnaces make them an unmatched workhorse for most lab and small-scale production environments.
By grasping how electricity and material resistance are harnessed, you can better leverage this powerful and versatile technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Joule heating via electric current through high-resistance materials |
| Key Components | Heating element (e.g., iron-chromium alloy), furnace tube, insulation, power controller |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1800°C, depending on element material |
| Advantages | Precise control, temperature stability, cost-effectiveness, reliability |
| Limitations | Slower heating/cooling rates, temperature ceiling constraints |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with reliable high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure they meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















