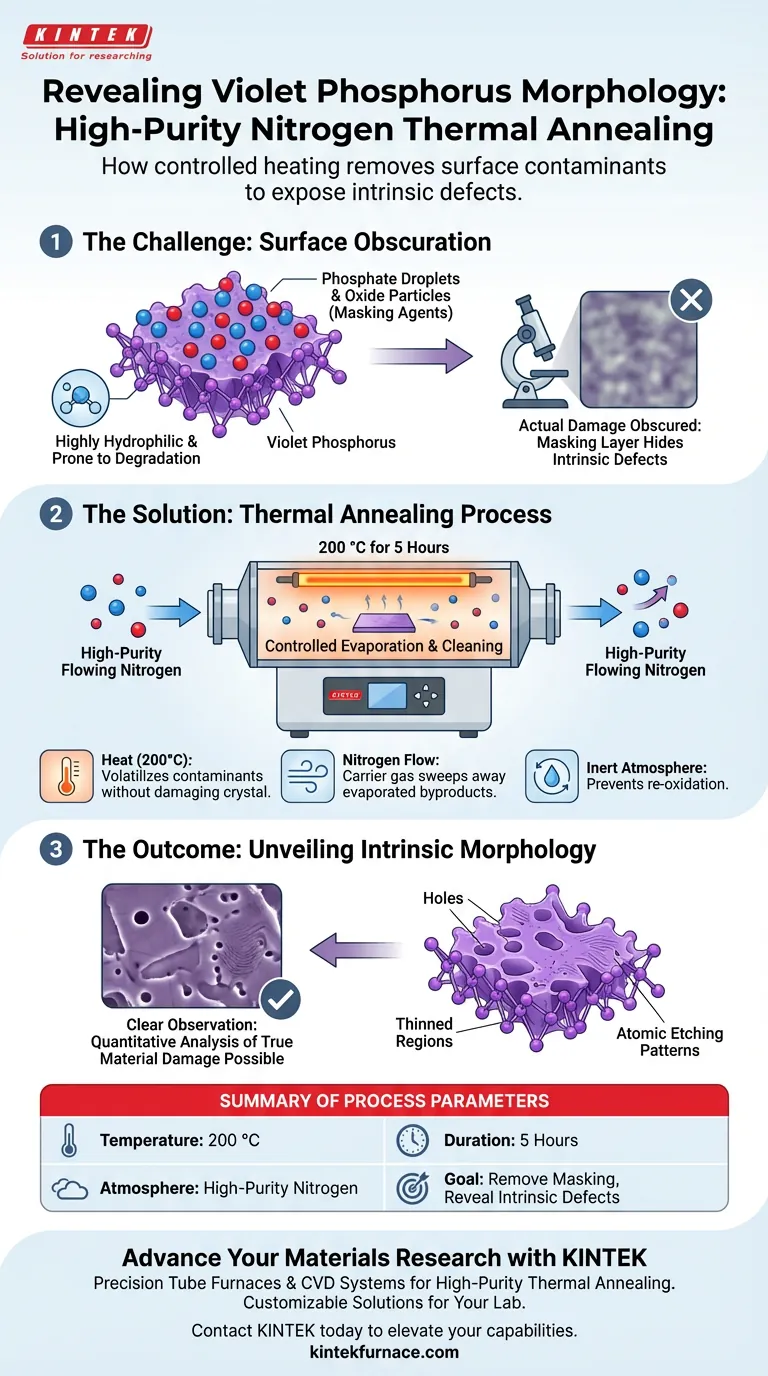
High-purity Nitrogen thermal annealing facilitates observation by effectively cleaning the material's surface of degradation byproducts that otherwise obscure structural details. By heating the sample to 200 °C for 5 hours in a flowing Nitrogen environment, adsorbed phosphate droplets and oxide particles are evaporated, revealing the underlying morphology changes caused by atomic etching.
Core Takeaway Violet Phosphorus is naturally hydrophilic and prone to surface contamination during degradation, which masks true structural damage. Thermal annealing acts as a "reset" mechanism, removing these surface artifacts to allow for the direct, quantitative analysis of intrinsic defects like holes and thinned regions.

The Challenge of Surface Obscuration
The Impact of Hydrophilicity
Violet Phosphorus is a highly hydrophilic material. This property makes it susceptible to interacting with moisture in the environment, accelerating degradation processes that alter the surface chemistry.
Formation of Masking Agents
During photo-degradation, the material produces adsorbed phosphate droplets and oxide particles. These byproducts accumulate on the exterior, creating a layer that effectively "masks" the surface.
The Visibility Problem
This accumulation renders standard imaging techniques ineffective for analyzing structural integrity. The droplets and oxides hide the actual physical changes occurring on the atomic lattice, making it impossible to distinguish between surface debris and actual material damage.
The Mechanism of Thermal Annealing
Controlled Evaporation
The specific protocol of annealing at 200 °C for 5 hours is tuned to target these adsorbents. At this temperature, the phosphate droplets and oxide particles are volatile enough to evaporate off the surface without destroying the underlying Violet Phosphorus crystal.
The Role of Flowing Nitrogen
Using high-purity flowing Nitrogen is critical to this process. It acts as a carrier gas to sweep away the evaporated contaminants.
Preventing Re-oxidation
Crucially, the Nitrogen creates an inert environment. Heating the sample in air would likely cause rapid oxidation and destruction of the material; the Nitrogen atmosphere ensures the process remains a cleaning step rather than a destructive one.
Unveiling Intrinsic Morphology
Revealing Atomic Etching
Once the surface adsorbents are removed, the intrinsic morphology becomes visible. Researchers can clearly observe features that were previously hidden, such as distinct holes and thinned regions on the crystal surface.
Enabling Quantitative Analysis
With the masking layer gone, the observation changes from speculative to quantitative. The clarity provided by the clean surface allows for precise measurement of the degradation, confirming that the damage is driven by atomic etching rather than just surface fouling.
Critical Considerations and Trade-offs
Adherence to Temperature Parameters
The success of this technique relies on precise temperature control. Deviating significantly from 200 °C poses risks: lower temperatures may fail to evaporate the oxides, while higher temperatures could potentially degrade the Violet Phosphorus crystal structure itself.
The Necessity of Purity
The "high-purity" aspect of the Nitrogen is not a suggestion; it is a requirement. Any impurities in the gas flow, particularly oxygen or moisture, could react with the heated sample, exacerbating the very oxidation problem you are trying to resolve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To effectively characterize Violet Phosphorus, you must align your preparation method with your analytical objectives.
- If your primary focus is visualizing intrinsic defects: Ensure your annealing protocol strictly adheres to the 200 °C / 5-hour benchmark to guarantee the complete removal of masking phosphate droplets.
- If your primary focus is studying degradation rates: Use this cleaning method at set intervals to differentiate between the accumulation of surface byproducts and actual material loss via atomic etching.
By systematically removing surface noise, you transform ambiguous data into actionable insight regarding material stability.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification | Purpose in Process |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 200 °C | Volatilizes phosphate droplets & oxides without damaging crystal |
| Duration | 5 Hours | Ensures complete evaporation of surface masking agents |
| Atmosphere | High-Purity Nitrogen | Prevents oxidation and acts as a carrier gas for contaminants |
| Target Material | Violet Phosphorus | Reveals intrinsic morphology and atomic etching patterns |
Advance Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precise morphology analysis of sensitive materials like Violet Phosphorus requires absolute control over temperature and atmosphere. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube Furnaces and CVD systems designed for high-purity thermal annealing and specialized lab applications.
Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique research parameters. Whether you need to eliminate surface obscuration or study intrinsic material defects, our high-temperature solutions deliver the stability and purity your results depend on.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Xiangzhe Zhang, Shiqiao Qin. Photodegradation and van der Waals Passivation of Violet Phosphorus. DOI: 10.3390/nano14050422
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do dual-zone tube furnaces facilitate the growth of BiRe2O6 single crystals? Precision Gradient Control Explained
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized for the calcination of nano-zinc oxide? Master Microstructure Control
- What recent advancements have enhanced the performance of lab tubular furnaces? Achieve Unprecedented Precision & Control
- How does a tube furnace contribute to the CVD of Si-SiO2 composites? Achieve Precise Nanostructure Control
- How are tube furnaces used in the glass and ceramics industry? Unlock Precision Thermal Processing
- How does a vacuum tube nitriding system control the reaction environment? Precision Surface Hardening for AISI 304
- What are the technical advantages of using a high-precision atmosphere tube furnace? Master Sensitive Ceramic Sintering
- What are the advantages of atmosphere control and high-temperature capabilities in a tube furnace? Unlock Precision in Material Processing



















