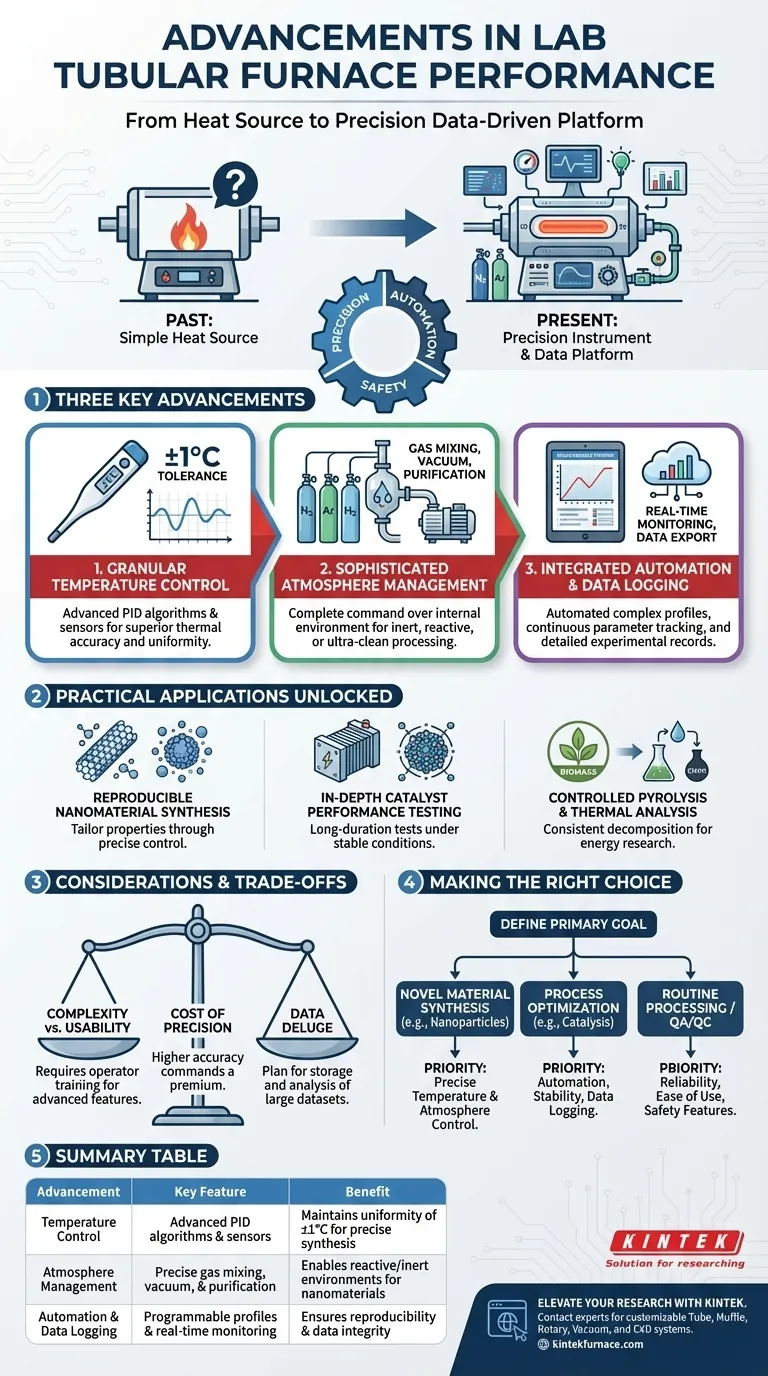
In short, recent advancements in lab tubular furnaces have centered on delivering unprecedented levels of precision, automation, and safety. This has been achieved through superior temperature control algorithms allowing tolerances of ±1°C, sophisticated atmosphere management systems that can mix and purify gases, and integrated automation for real-time monitoring and data logging.
The core evolution is the shift of the tubular furnace from a simple heat source to a highly precise and data-driven experimental platform. This transformation is not about achieving higher temperatures, but about ensuring that every experiment is conducted under perfectly controlled, monitored, and reproducible conditions.

The Evolution from Heat Source to Precision Instrument
Historically, a tubular furnace was a tool for applying heat. Its success was measured in thermal output. Today, its value is measured in control and repeatability, turning it into a sophisticated instrument for modern materials research.
Granular Temperature Control
Modern furnaces now feature advanced temperature sensors and PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control algorithms.
This pairing has dramatically improved thermal accuracy and uniformity, with many systems now capable of maintaining a temperature tolerance of ±1°C or better across the heating zone.
Sophisticated Atmosphere Management
Control now extends far beyond simple heating in ambient air. Advanced systems provide complete command over the internal environment.
This includes capabilities for introducing precise mixtures of inert or reactive gases, creating high-vacuum conditions, and even integrating gas purification technologies to ensure an ultra-clean processing environment.
Integrated Automation and Data Logging
The most significant leap forward is in automation. Modern furnaces can be programmed to run complex thermal profiles without manual intervention.
These automated systems constantly monitor and regulate temperature and atmosphere, logging all parameters in real-time. This creates a detailed, exportable record of the experiment, which is critical for reproducibility and reporting.
What These Advancements Enable in Practice
These technological improvements are not just incremental; they unlock new and more demanding research applications by removing experimental variables.
Reproducible Nanomaterial Synthesis
The synthesis of materials like carbon nanotubes or metal oxide nanoparticles is highly sensitive to process conditions.
Precise control over temperature ramps, hold times, and gas composition allows researchers to reliably tailor the final properties of these nanomaterials, moving from accidental discovery to intentional design.
In-Depth Catalyst Performance Testing
When studying the kinetics of fuel cell catalysts, a stable and controlled environment is non-negotiable.
Automated gas flow and temperature management allow for long-duration tests that accurately simulate operating conditions, while data logging captures the catalyst's performance over time with high fidelity.
Controlled Pyrolysis and Thermal Analysis
In fields like biomass energy research, the goal is to carefully analyze the gases, chars, and oils produced during thermal decomposition.
Advanced atmosphere control and real-time monitoring ensure that the pyrolysis process is consistent, enabling researchers to accurately assess the feasibility and efficiency of converting biomass into a renewable energy source.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While these advancements are powerful, they introduce new factors that must be considered when selecting and operating a modern tubular furnace.
Complexity vs. Usability
A system with advanced gas mixing, vacuum integration, and complex programming capabilities is inherently more complex to operate.
Labs must invest in proper training to ensure that operators can leverage the full power of the instrument without introducing errors.
Cost of Precision
Higher levels of control and accuracy come at a premium. A furnace with ±1°C uniformity and advanced atmospheric controls will have a higher upfront cost than a simpler, less precise model.
It's crucial to match the furnace's capabilities—and cost—to the actual requirements of your research.
The Data Deluge
Integrated data logging is a powerful feature for ensuring reproducibility, but it also generates large amounts of data.
Your team needs a clear plan for how this data will be stored, managed, and analyzed to extract meaningful insights from your experiments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
To select the appropriate furnace, first define the primary goal of your work.
- If your primary focus is novel material synthesis (e.g., nanoparticles): Prioritize the furnace with the most precise temperature control and sophisticated atmosphere management you can acquire.
- If your primary focus is process optimization or kinetic studies (e.g., catalysis): Emphasize automation, long-term stability, and robust data logging capabilities to ensure consistency across experiments.
- If your primary focus is routine thermal processing or QA/QC: Focus on reliability, ease of use, and integrated safety features like over-temperature protection and emergency shut-offs.
Ultimately, modern advancements empower you to select a furnace that operates less like a simple oven and more like a dedicated analytical instrument tailored to your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Advancement | Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Advanced PID algorithms & sensors | Maintains uniformity of ±1°C for precise synthesis |
| Atmosphere Management | Precise gas mixing, vacuum, & purification | Enables reactive/inert environments for nanomaterials |
| Automation & Data Logging | Programmable profiles & real-time monitoring | Ensures experiment reproducibility & data integrity |
Ready to elevate your materials research with a precision tubular furnace?
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD furnace systems, all customizable for your unique experimental needs—from nanomaterial synthesis to catalyst testing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK furnace can become the data-driven core of your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















