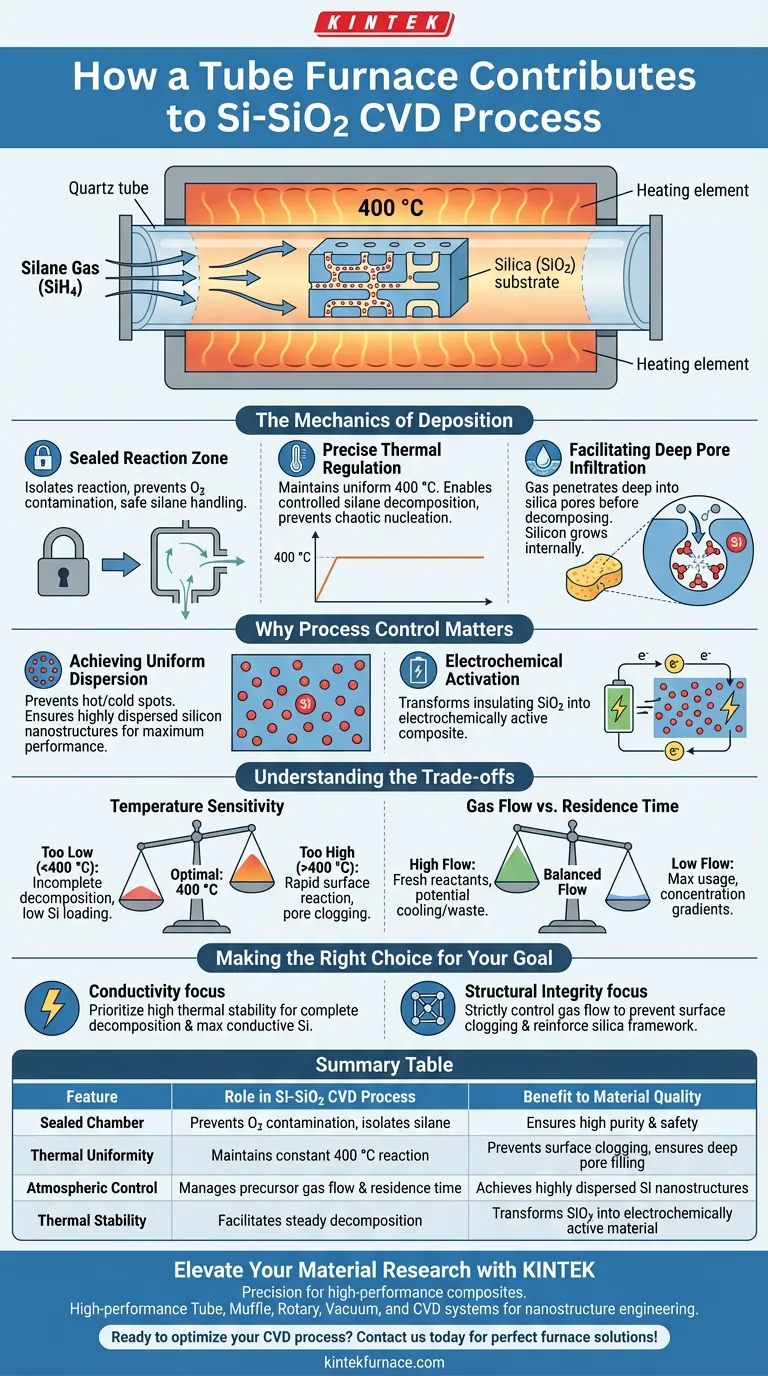
A high-temperature tube furnace serves as the critical reaction chamber for synthesizing Si-SiO2 composites via chemical vapor deposition (CVD). It provides a sealed, thermally stable environment that allows silane gas to permeate a porous silica framework. By maintaining a precise reaction temperature, typically around 400 °C, the furnace ensures the gas decomposes uniformly inside the nanopores rather than on the surface.
Core Takeaway: The tube furnace is not merely a heat source; it is a precision tool that synchronizes temperature and gas flow to drive internal pore filling. This controlled decomposition transforms insulating silica into an electrochemically active composite with highly dispersed silicon nanostructures.

The Mechanics of Deposition
Creating a Sealed Reaction Zone
The fundamental role of the tube furnace is to isolate the reaction from the external environment. For Si-SiO2 preparation, the furnace maintains a hermetically sealed chamber that prevents oxygen contamination.
This isolation is vital for safety and purity, as it allows the controlled introduction of volatile precursors like silane gas without the risk of external combustion or oxidation.
Precise Thermal Regulation
Success in CVD depends on maintaining a specific kinetic window. The tube furnace provides a constant, uniform temperature—specifically around 400 °C for this application.
At this temperature, the thermal energy is sufficient to trigger the decomposition of silane but controlled enough to prevent rapid, chaotic nucleation. This stability ensures the reaction happens at a steady rate throughout the batch.
Facilitating Deep Pore Infiltration
The furnace's design allows the reactant gas to flow continuously over and through the silica substrate. Because the thermal environment is uniform, the silane gas can penetrate deep into the porous silica framework before decomposing.
This "in-pore" deposition is what distinguishes a high-quality composite. Instead of coating the exterior, the silicon grows inside the voids, creating a robust, interlocked structure.
Why Process Control Matters
Achieving Uniform Dispersion
Without the stable thermal profile provided by the tube furnace, silicon would deposit unevenly. Hot spots could cause blockages at pore openings, while cold spots would leave precursors unreacted.
The furnace ensures that silicon nanostructures are highly dispersed throughout the matrix. This uniform distribution is essential for maximizing the material's performance.
Electrochemical Activation
Silica (SiO2) is naturally insulating, which limits its utility in electronic or energy storage applications. The tube furnace process effectively activates the material.
By successfully depositing conductive silicon within the insulating silica structure, the furnace transforms the precursor into an electrochemically active composite capable of storing and transferring charge.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Sensitivity
While 400 °C is cited as optimal for this specific Si-SiO2 reaction, deviation can ruin the product.
If the temperature is too low, the silane will not decompose fully, leading to low silicon loading. If it is too high, the reaction may occur too quickly on the surface, sealing the pores ("pore clogging") and leaving the interior empty.
Gas Flow vs. Residence Time
The tube furnace allows for gas flow control, but this introduces a variable that must be balanced.
High gas flow ensures fresh reactants reach the substrate but may cool the reaction zone or waste precursor. Low flow maximizes usage but creates concentration gradients, potentially leading to uneven deposition across the length of the tube.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your Si-SiO2 composite, you must tailor the furnace parameters to your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is Conductivity: Prioritize high thermal stability to ensure complete decomposition of silane, maximizing the amount of conductive silicon deposited within the matrix.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: strictly control the gas flow rate to prevent surface clogging, ensuring the silicon fills the internal pores to reinforce the silica framework.
By mastering the thermal and atmospheric controls of the tube furnace, you turn a standard heating element into a precision instrument for nanostructure engineering.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Si-SiO2 CVD Process | Benefit to Material Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Sealed Chamber | Prevents oxygen contamination and isolates silane gas. | Ensures high purity and process safety. |
| Thermal Uniformity | Maintains a constant 400 °C reaction window. | Prevents surface clogging and ensures deep pore filling. |
| Atmospheric Control | Manages precursor gas flow and residence time. | Achieves highly dispersed silicon nanostructures. |
| Thermal Stability | Facilitates steady decomposition of precursors. | Transforms insulating SiO2 into electrochemically active material. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a surface coating and a high-performance composite. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of nanostructure engineering. Whether you are synthesizing Si-SiO2 composites or developing next-gen energy materials, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to your unique research needs.
Ready to optimize your CVD process? Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
References
- Michael Karl, Simone Pokrant. Porous MCM‐41 Silica Materials as Scaffolds for Silicon‐based Lithium‐ion Battery Anodes. DOI: 10.1002/celc.202300707
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the high temperature of a tube furnace? Understanding the 1700°C Limit and Key Components
- Why is alumina ceramic tubing selected as the liner for a Drop Tube Furnace? Ensure Purity and High-Temp Stability
- Can split tube furnaces be used in both horizontal and vertical orientations? Maximize Your Lab's Efficiency with Flexible Setup
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for the post-treatment of composite anode materials in argon?
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature tube furnace? Driving Topotactic Reduction of Nickelate Films
- What role does a horizontal tube furnace play in activated carbon production? Master High-Precision Activation
- What role does an externally heated Vertical Tube Furnace play in high-temperature molten salt electrolysis systems?
- Why is the chemical composition of the alloy used in tube reactors critical? Insights into Ethane Cracking Results



















