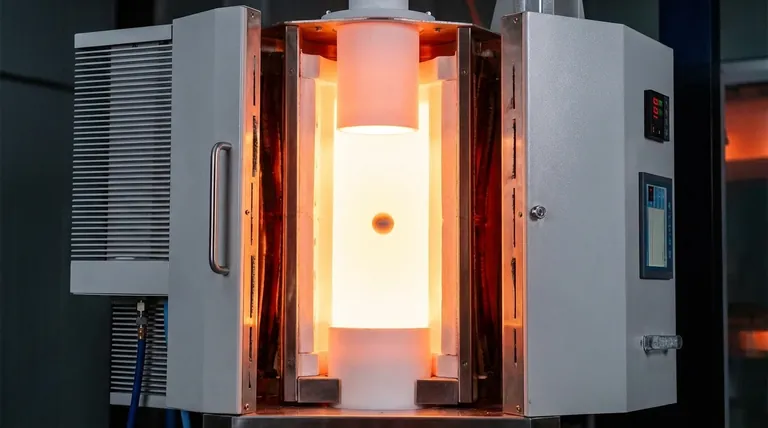
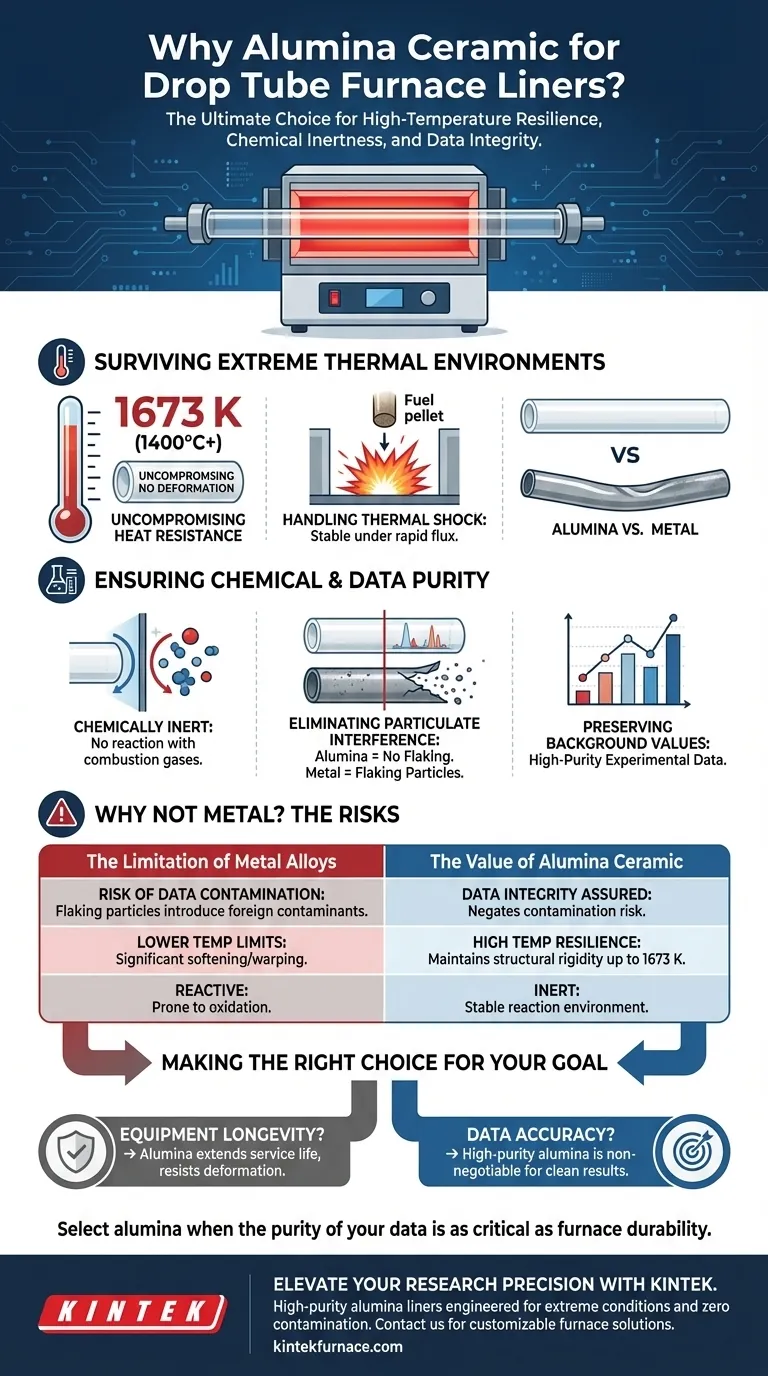
Alumina ceramic tubing is selected as the liner for Drop Tube Furnace reaction chambers because it delivers a unique combination of high-temperature resilience, thermal shock stability, and chemical inertness. This material is critical for maintaining a stable reaction environment capable of withstanding temperatures up to 1673 K without deforming or contaminating the experiment.
The core value of an alumina liner lies in data integrity. By eliminating the chemical reactions and particulate flaking common with metal liners, high-purity alumina ensures that the experimental results reflect the actual sample behavior, not the degradation of the furnace equipment.
Surviving Extreme Thermal Environments
Uncompromising Heat Resistance
Drop Tube Furnaces operate in punishing thermal conditions. Alumina ceramic is chosen because it maintains its structural integrity at operating temperatures reaching 1673 K (approx. 1400°C) or higher.
Resistance to Deformation
Unlike many other materials that soften or warp under sustained heat, high-purity alumina does not deform. It remains rigid and stable even when processing temperatures exceed 900°C, ensuring the physical geometry of the reaction chamber remains constant.
Handling Thermal Shock
The introduction of fuel, such as wood pellets, into a hot furnace creates immediate local thermal disturbances. Alumina is specifically selected for its thermal shock stability, allowing it to withstand these rapid temperature fluctuations without cracking or failing.
Ensuring Chemical and Data Purity
Chemical Inertness
A primary requirement for scientific analysis is that the equipment must not participate in the reaction. Alumina is chemically inert, meaning it prevents chemical reactions between the furnace wall materials and the combustion products or flue gases.
Eliminating Particulate Interference
This is a critical differentiator from metallic alternatives. Metal liners often degrade at high temperatures, producing flaking particles that mix with the sample.
Preserving Background Values
Because high-purity alumina does not flake or off-gas, it prevents interference with experimental background values. This ensures that any data collected is derived strictly from the sample being tested, guaranteeing high-purity experimental data.
Understanding the Alternatives: Why Not Metal?
The Limitation of Metal Alloys
While metal alloys are common in lower-temperature applications, they become a liability in high-precision Drop Tube Furnaces. The primary "trade-off" usually considered is durability vs. purity.
The Risk of Data Contamination
The supplementary data highlights that metal materials produce additional flaking particles at high temperatures. In a Drop Tube Furnace, these flakes introduce foreign contaminants that compromise the reliability of the entire experiment. Alumina is selected specifically to negate this risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your equipment delivers valid results, consider the following based on your experimental needs:
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: Alumina extends the service life of the furnace by resisting deformation and thermal shock at temperatures up to 1673 K.
- If your primary focus is Data Accuracy: High-purity alumina is non-negotiable to prevent chemical cross-reactivity and particulate flaking from skewing your background values.
Select alumina when the purity of your data is just as critical as the durability of your furnace.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Alumina Ceramic Tubing | Metal Alloy Alternatives |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Limit | Up to 1673 K (1400°C+) | Significant softening/warping at high temps |
| Chemical Inertness | High (No reaction with combustion gases) | Low (Prone to oxidation and reactivity) |
| Deformation Risk | Minimal (Maintains structural rigidity) | High (Prone to sagging and warping) |
| Data Integrity | High (No particulate flaking) | Low (Metallic flakes contaminate samples) |
| Thermal Shock | Excellent stability under rapid flux | Variable depending on specific alloy |
Elevate Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Don’t let equipment degradation compromise your experimental integrity. KINTEK’s high-purity alumina liners are engineered to withstand extreme thermal shocks and eliminate particulate contamination in your Drop Tube Furnace.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique scientific requirements.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Garikai T. Marangwanda, Daniel M. Madyira. Evaluating Combustion Ignition, Burnout, Stability, and Intensity of Coal–Biomass Blends Within a Drop Tube Furnace Through Modelling. DOI: 10.3390/en18061322
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What function does a tube furnace serve in metal nitride synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Nanoparticle Growth
- Why is the iodine source placed at the upstream end of the tube furnace? Optimizing I-NC Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What is the significance of cooling rate control in a high-precision tube furnace for h-ScFeO3? Prove Stability Now
- Why is a silicate glass fixed-bed reactor used instead of stainless steel? Ensure Pure Methanol Decomposition Data
- What is the significance of the calcination process using a high-temperature tube furnace? Enhance Bi2S3/BiOBr@In2S3 Performance
- Why is a secondary high-temperature activation process in a tube furnace necessary? Converting Biochar into CBAC
- Why are tubular furnaces important in material testing and research? Unlock Precision for Advanced Materials Development
- Why are the high-temperature carbonization and activation of sugarcane bagasse typically conducted in a tube furnace?



















