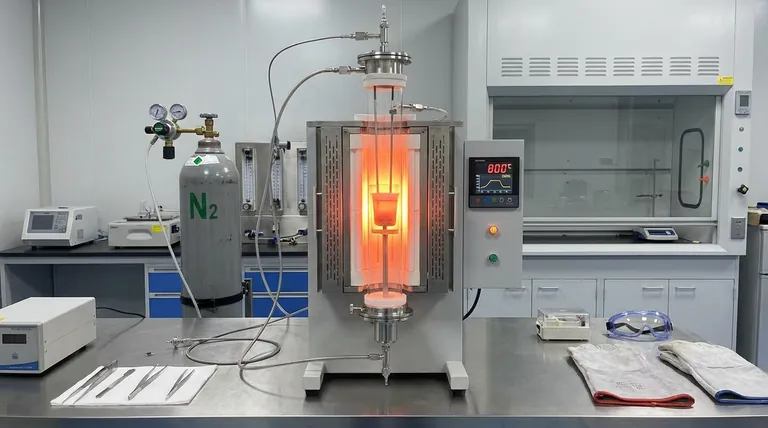
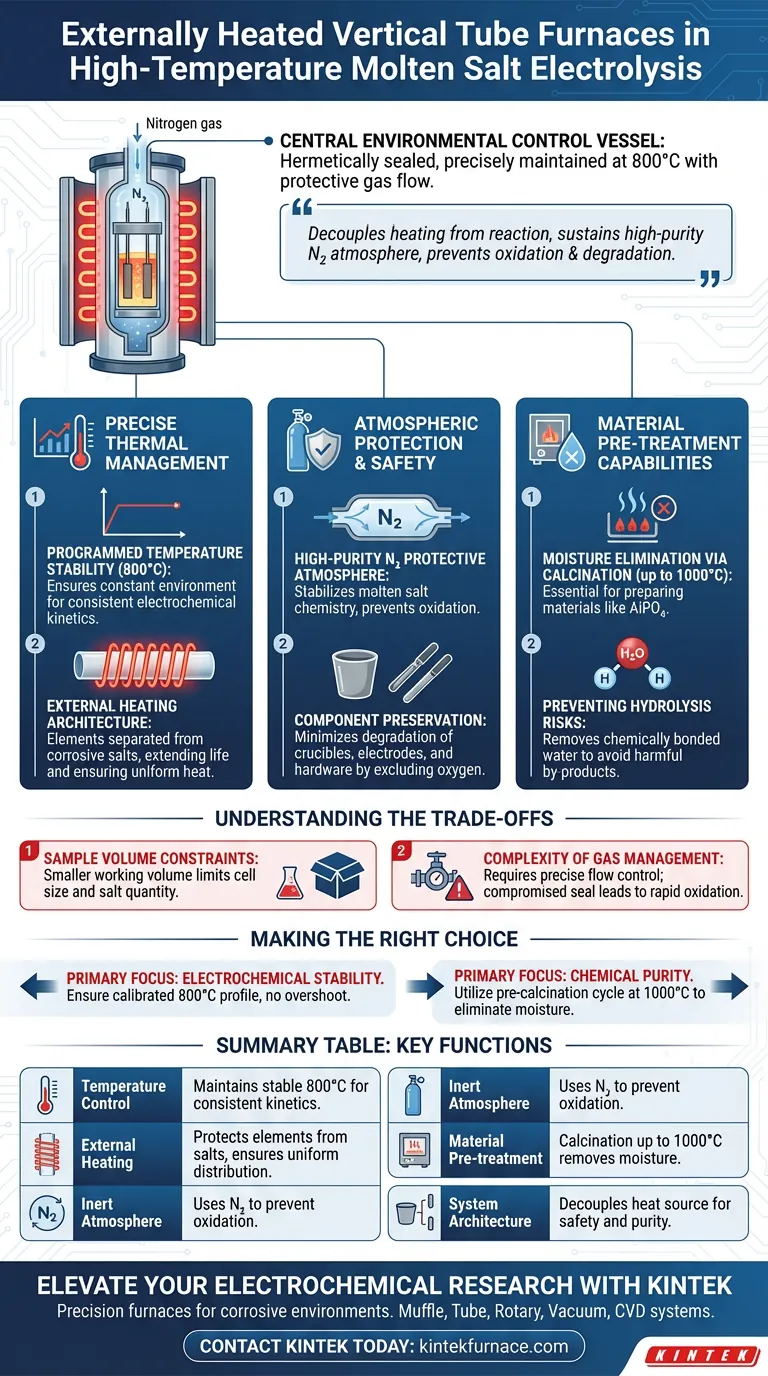
An externally heated Vertical Tube Furnace acts as the central environmental control vessel for high-temperature molten salt electrolysis systems. It functions by creating a hermetically sealed chamber that maintains the electrolysis cell at a precise, programmed temperature of 800°C while facilitating a protective gas flow.
The primary value of this equipment lies in its ability to decouple the heating source from the reaction environment. By sustaining a high-purity nitrogen atmosphere, it prevents the oxidation of sensitive molten salts and minimizes the degradation of internal experimental components.

Precise Thermal Management
Programmed Temperature Stability
In molten salt electrolysis, thermal fluctuations can disrupt electrochemical kinetics. The vertical tube furnace uses programmed temperature control to maintain a constant operating environment, typically around 800°C for these specific applications.
External Heating Architecture
By heating the tube externally, the furnace ensures that the heating elements do not come into direct contact with the corrosive molten salts. This separation prolongs equipment life and ensures uniform heat distribution around the electrolysis cell placed inside the tube.
Atmospheric Protection and Safety
Creating a Protective Environment
Molten salts are highly reactive and prone to oxidation at high temperatures. The furnace’s sealed structure allows for the continuous introduction of a high-purity nitrogen protective atmosphere.
Component Preservation
This inert atmosphere serves a dual purpose: it stabilizes the molten salt chemistry and protects the experimental hardware. By excluding oxygen, the system minimizes the high-temperature degradation of crucibles, electrodes, and other internal components.
Material Pre-treatment Capabilities
Moisture Elimination via Calcination
Beyond active electrolysis, these furnaces are essential for material preparation. They are often used to calcine materials, such as aluminum phosphate (AlPO4), at temperatures up to 1000°C.
Preventing Hydrolysis Risks
This pre-treatment thoroughly removes chemically bonded water and physically adsorbed moisture. Removing this moisture is critical because, in a high-temperature chloride salt system, any residual water causes the molten salt to hydrolyze, generating harmful by-products that compromise the experiment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sample Volume Constraints
Vertical tube furnaces generally have a smaller working volume compared to box furnaces. This limits the size of the electrolysis cell and the quantity of molten salt you can process in a single run.
Complexity of Gas Management
Unlike open-air systems, utilizing the protective atmosphere requires precise gas flow management. If the seal is compromised or the nitrogen purity is insufficient, the protective benefits are immediately lost, leading to rapid oxidation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a Vertical Tube Furnace in your research, align its usage with your specific experimental needs:
- If your primary focus is Electrochemical Stability: Ensure the programmed temperature profile is calibrated to maintain 800°C without overshooting, as thermal stability is key to consistent electrolysis.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Utilize the furnace for a pre-calcination cycle at 1000°C to eliminate all moisture before initiating the electrolysis process.
By strictly controlling both temperature and atmosphere, you transform the furnace from a simple heater into a precision instrument for high-fidelity electrochemical research.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Molten Salt Electrolysis |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Maintains stable 800°C to ensure consistent electrochemical kinetics. |
| External Heating | Protects heating elements from corrosive salts and ensures uniform distribution. |
| Inert Atmosphere | Uses high-purity nitrogen to prevent oxidation of salts and components. |
| Material Pre-treatment | Enables calcination up to 1000°C to eliminate moisture and prevent hydrolysis. |
| System Architecture | Decouples the heat source from the reaction environment for safety and purity. |
Elevate Your Electrochemical Research with KINTEK
Precision in molten salt electrolysis requires a furnace that can withstand corrosive environments while maintaining strict atmospheric integrity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a wide range of specialized lab high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems.
Whether you need an externally heated vertical tube furnace for precise thermal management or a custom-designed solution for unique chemical pre-treatments, our equipment is built to minimize degradation and maximize experimental fidelity.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature laboratory setup? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your customizable furnace needs
Visual Guide
References
- Kamaljeet Singh, Guðrún Sævarsdóttir. Overpotential on Oxygen-Evolving Platinum and Ni-Fe-Cu Anode for Low-Temperature Molten Fluoride Electrolytes. DOI: 10.1007/s11837-024-06425-5
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety features are included in an atmosphere tube furnace? Essential Systems for Secure High-Temp Operations
- Why is a programmable tube furnace required for the synthesis of bulk Cu13Se52Bi35 alloys? Essential Thermal Precision
- What is the function of a two-zone tube furnace in Borophene CVD? Achieve Precise Thermal Decoupling for 2D Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the performance of carbon nanowire networks? Enhance Electrode Performance
- What are the advantages of a dual-zone tube furnace for Ti3C2Tx MXene? Master Precise Sulfurization Kinetics
- How does a Tube Furnace ensure structural consistency in Fe/MWCNT synthesis? Expert Control for Composite Quality
- Why is heat treatment in a tube furnace or muffle furnace required after synthesizing magnesium hydroxide nano-precursors via electrochemical methods? Unlock the Full Potential of Your MgO Nanomaterials



















