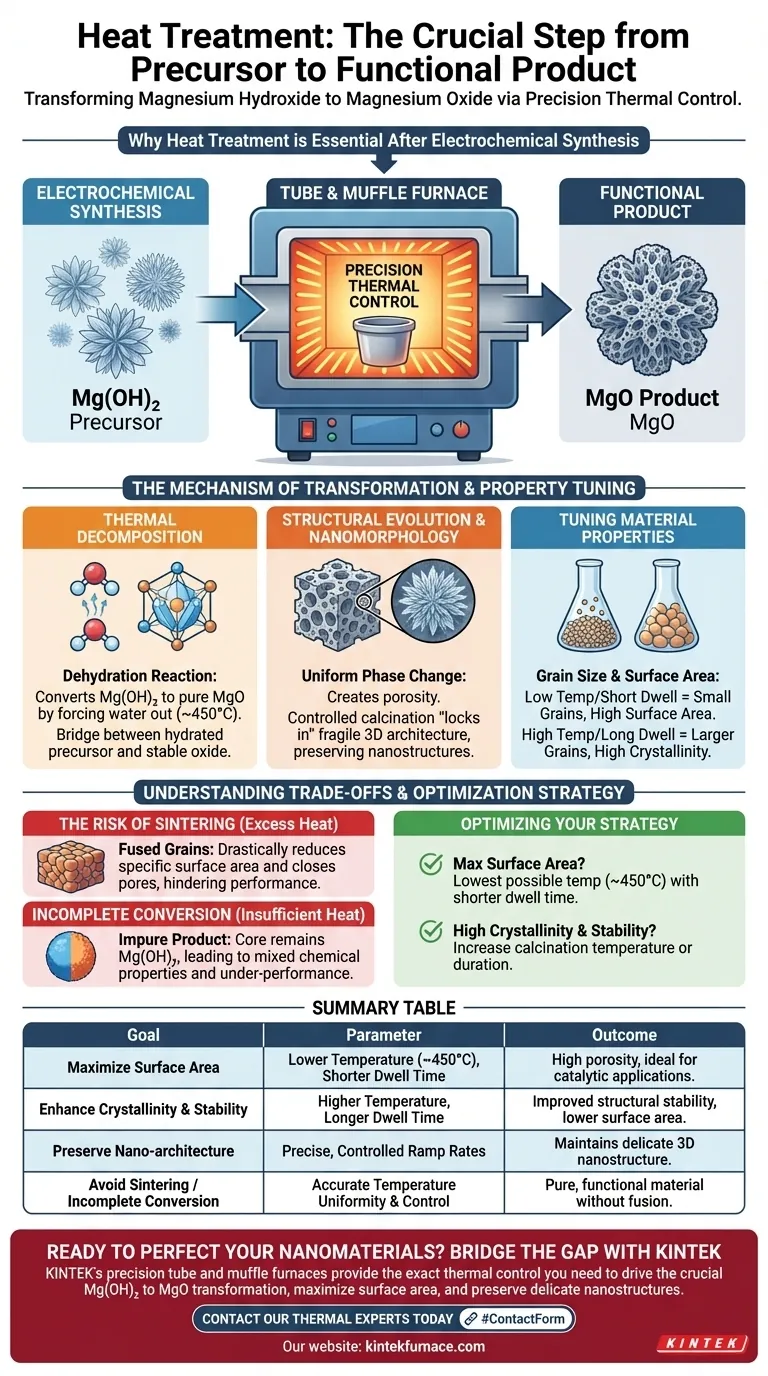
Heat treatment serves as the essential phase transformation step that converts your raw synthesized material into a functional product. The electrochemical process creates magnesium hydroxide ($Mg(OH)_2$), a precursor which must be thermally decomposed to become magnesium oxide ($MgO$). Using a tube or muffle furnace allows for the precise thermal control necessary to drive this chemical change while preserving the delicate nanostructures created during synthesis.
While the electrochemical deposition shapes the architecture of the material, the heat treatment defines its chemical identity and physical performance. It is the bridge between a hydrated precursor and a stable, high-surface-area oxide.
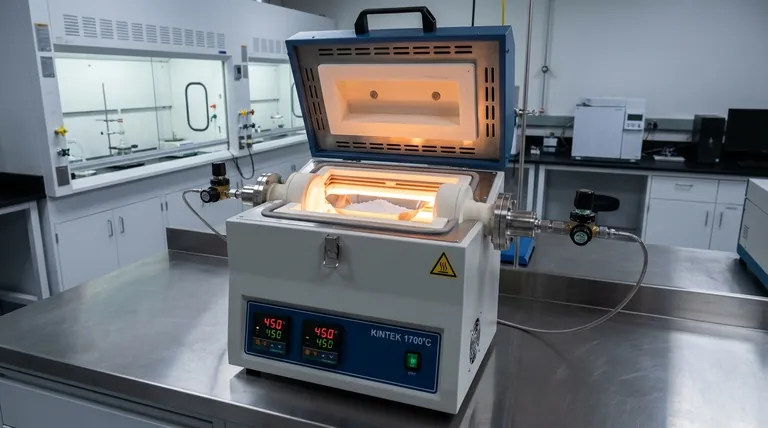

The Mechanism of Transformation
Thermal Decomposition
The primary function of the furnace is to execute a dehydration reaction. The electrochemical process takes place in an aqueous environment, naturally resulting in a hydroxide compound.
To achieve the desired magnesium oxide, the material must undergo calcination. This process physically forces water molecules out of the crystal lattice, typically around 450°C, leaving behind pure oxide.
Structural Evolution
This phase change is not merely chemical; it is structural. As water leaves the structure, it creates porosity within the material.
The furnace environment ensures this evolution happens uniformly. This uniformity is critical for preventing the material from cracking or collapsing unevenly during the transition.
Tuning Material Properties
Controlling Grain Size
The specific temperature and duration of the heat treatment act as control knobs for the material's final grain size.
Lower temperatures generally result in smaller grains. Conversely, higher temperatures or longer dwell times promote crystal growth, resulting in larger grains.
Defining Surface Area
There is a direct correlation between the heating profile and the specific surface area of the final $MgO$.
By carefully managing the heat, you maximize the porosity created during decomposition. This results in a material with a high surface area, which is often a critical metric for catalytic or reactive applications.
Retaining Nanomorphology
Electrochemical methods are often used to create complex shapes, such as "nanoflowers." These structures are fragile.
Controlled calcination is required to "lock in" these shapes. If done correctly, the chemical composition changes to $MgO$, but the valuable 3D architecture (the nanoflower shape) remains intact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Sintering
Applying too much heat or maintaining peak temperature for too long can have detrimental effects.
Excessive thermal energy causes the individual grains to fuse together, a process known as sintering. This drastically reduces the specific surface area and closes off the pores that make the material effective.
Incomplete Conversion
Conversely, insufficient heat treatment leads to under-performance.
If the temperature is too low or the duration too short, the core of the material may remain as magnesium hydroxide. This results in an impure product with mixed chemical properties that may not meet application standards.
Optimizing Your Heat Treatment Strategy
To achieve the best results, you must tailor your furnace parameters to your specific performance metrics.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface area: Utilize the lowest possible temperature that achieves full decomposition (e.g., near 450°C) with a shorter dwell time to prevent grain growth.
- If your primary focus is high crystallinity and stability: Increase the calcination temperature or duration to encourage grain alignment and remove all structural defects, accepting a lower surface area.
Success relies on viewing the furnace not as a drying oven, but as a precision instrument that finalizes the material's morphology.
Summary Table:
| Heat Treatment Goal | Key Furnace Parameter | Expected Outcome for MgO |
|---|---|---|
| Maximize Surface Area | Lower Temperature (~450°C), Shorter Dwell Time | High porosity, ideal for catalytic applications |
| Enhance Crystallinity & Stability | Higher Temperature, Longer Dwell Time | Improved structural stability, lower surface area |
| Preserve Nano-architecture (e.g., Nanoflowers) | Precise, Controlled Ramp Rates | Maintains delicate 3D nanostructure from synthesis |
| Avoid Sintering / Incomplete Conversion | Accurate Temperature Uniformity & Control | Pure, functional material without grain fusion or impurities |
Ready to perfect your magnesium oxide nanomaterials?
Your electrochemical synthesis creates the precursor, but the final material properties are defined in the furnace. KINTEK's precision tube and muffle furnaces provide the exact thermal control you need to drive the crucial Mg(OH)₂ to MgO transformation, maximize surface area, and preserve delicate nanostructures without sintering.
Let us help you bridge the gap between synthesis and a high-performance material.
🔗 Contact our thermal experts today to discuss customizing a furnace solution for your unique research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do tube furnaces work? Achieve Precise Thermal Processing for Your Materials
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Heat and Atmosphere Control
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















