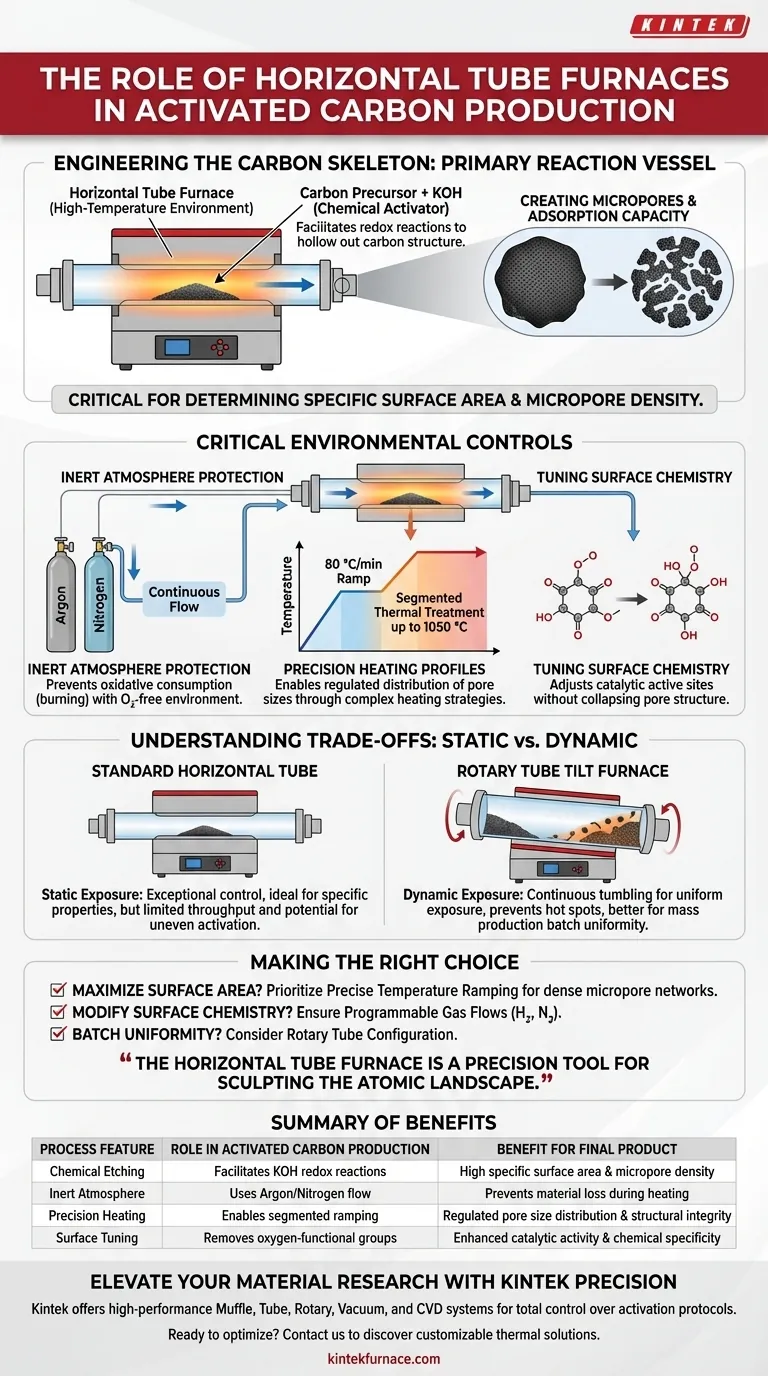
The horizontal tube furnace functions as the primary reaction vessel for engineering the internal structure of activated carbon. It provides a sealed, high-temperature environment that allows chemical agents (like Potassium Hydroxide) to physically etch the carbon skeleton while an inert gas flow prevents the material from burning away.
Core Takeaway The horizontal tube furnace is the critical instrument for determining the specific surface area and micropore density of the final product. It does not merely heat the material; it facilitates precise redox reactions that "hollow out" the carbon structure to create adsorption capacity.
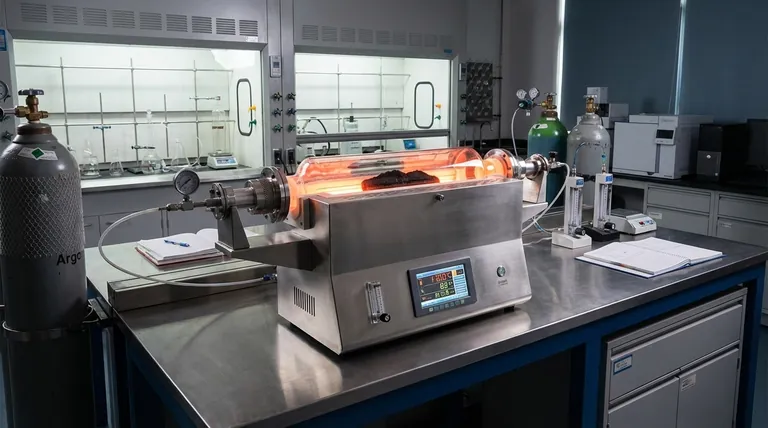

Engineering the Carbon Skeleton
The Role of Chemical Etching
The primary function of the horizontal tube furnace during activation is to facilitate a reaction between the carbon precursor and a chemical activator, most commonly Potassium Hydroxide (KOH).
Inside the tube, redox reactions occur between the KOH and the pre-carbonized materials. This process effectively "etches" the carbon skeleton, removing atoms to create a vast network of voids.
Determining Pore Structure
This etching process is what produces the large number of micropores that define high-quality activated carbon.
Consequently, the furnace acts as the core equipment for establishing the material's specific surface area. The precision of the furnace determines whether you create a highly absorbent filter or a chemically inert dust.
Critical Environmental Controls
Inert Atmosphere Protection
To prevent the carbon from simply turning into ash, the furnace must maintain a strictly controlled inert atmosphere.
By flowing gases like Argon or Nitrogen continuously, the system creates an oxygen-free environment. This prevents "oxidative consumption" (burning), ensuring that carbon atoms are removed only where chemically targeted to form pores.
Precision Heating Profiles
The horizontal tube furnace enables complex heating strategies, such as ramping at 80 °C/min up to temperatures of 800 °C.
This capability is essential for segmented thermal treatment. For example, a protocol might hold at 850 °C for initial activation and then push to 1050 °C for deep activation, allowing for the regulated distribution of pore sizes.
Tuning Surface Chemistry
Beyond physical pores, the furnace allows for the modification of the carbon's chemical properties.
By introducing specific reducing gases (like hydrogen mixtures) or maintaining specific temperatures, the process can remove oxygen-containing functional groups. This adjusts the material's catalytic active sites without collapsing the delicate pore structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Static vs. Dynamic Exposure
A standard horizontal tube furnace offers exceptional control over atmosphere and temperature, but the material inside often sits statically.
In contrast, a Rotary Tube Tilt Furnace continuously tumbles the raw material (such as coconut shells). This rotation ensures uniform exposure to both the heat and the activating agents, preventing "hot spots" or uneven activation that can occur in a static tube.
Throughput Limitations
Standard horizontal tube furnaces are ideal for precision and developing specific chemical properties, such as high electrocatalytic activity.
However, for mass production where uniformity across large volumes is paramount, the static nature of a standard tube may limit throughput compared to rotary or fluidized bed systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your carbonization and activation process, align your equipment usage with your specific end-goal:
- If your primary focus is maximizing specific surface area: Prioritize a furnace with precise temperature ramping to control the rate of KOH redox etching, creating dense micropore networks.
- If your primary focus is surface chemistry modification: Ensure your furnace supports programmable gas flows to introduce reducing agents (Hydrogen) or inert gases (Nitrogen) at specific thermal stages.
- If your primary focus is batch uniformity: Consider a rotary tube configuration to ensure consistent contact between the activation agent and the carbon material.
The horizontal tube furnace is not just a heat source; it is a precision tool for sculpting the atomic landscape of your carbon material.
Summary Table:
| Process Feature | Role in Activated Carbon Production | Benefit for Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Etching | Facilitates KOH redox reactions to hollow carbon skeletons | High specific surface area & micropore density |
| Inert Atmosphere | Uses Argon/Nitrogen flow to prevent oxidative consumption | Prevents material loss (burning) during heating |
| Precision Heating | Enables segmented ramping (e.g., 80°C/min up to 1050°C) | Regulated pore size distribution & structural integrity |
| Surface Tuning | Removes oxygen-functional groups via reducing gases | Enhanced catalytic activity & chemical specificity |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't leave your carbon structure to chance. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to give you total control over the activation process. Whether you need a standard horizontal tube furnace for precise chemical etching or a customizable rotary system for batch uniformity, our equipment is engineered to meet the unique needs of lab-scale and industrial high-temperature research.
Ready to optimize your activation protocols? Contact us today to discover how KINTEK’s customizable thermal solutions can help you sculpt the perfect atomic landscape for your materials.
Visual Guide
References
- Nokuthula Mekgoe, Kriveshini Pillay. Synergistic electrochemical detection of ciprofloxacin using bismuth vanadate nanocomposite-modified activated carbon derived from banana peel biomass. DOI: 10.1039/d5ma00168d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How is a tube furnace utilized to construct DTB sites for Co/Co0.85Se@NC? Mastering Phase Engineering
- What critical process conditions does a tube furnace provide for orange peel activated carbon synthesis?
- Why is a precision temperature control tube furnace necessary for CNT and AlN synthesis? Ensure Vertical Alignment
- How is an industrial tube furnace utilized to evaluate the thermal stability of modified diamond powders?
- What is a tube furnace and what are its primary uses? Essential for Controlled High-Temperature Processes
- What are the limitations of tube furnaces when cracking heavy materials? Overcome Coking and Boost Efficiency
- What design features make horizontal furnaces versatile? Achieve High-Volume, Uniform Thermal Processing
- What is the function of an industrial tube furnace during the secondary carbonization of biomass? Achieve Precision.



















