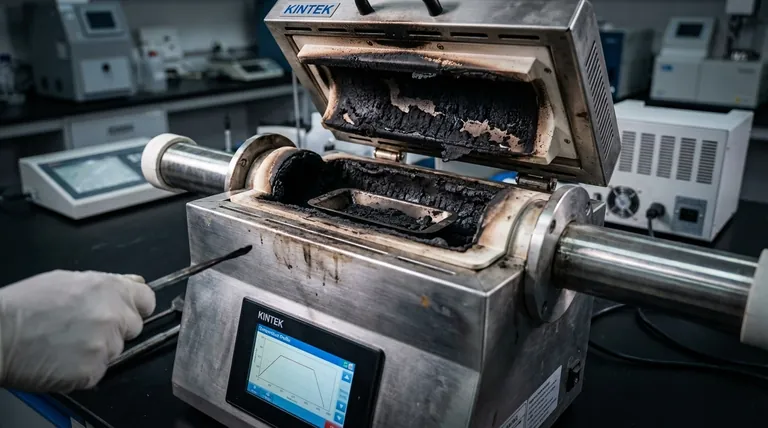
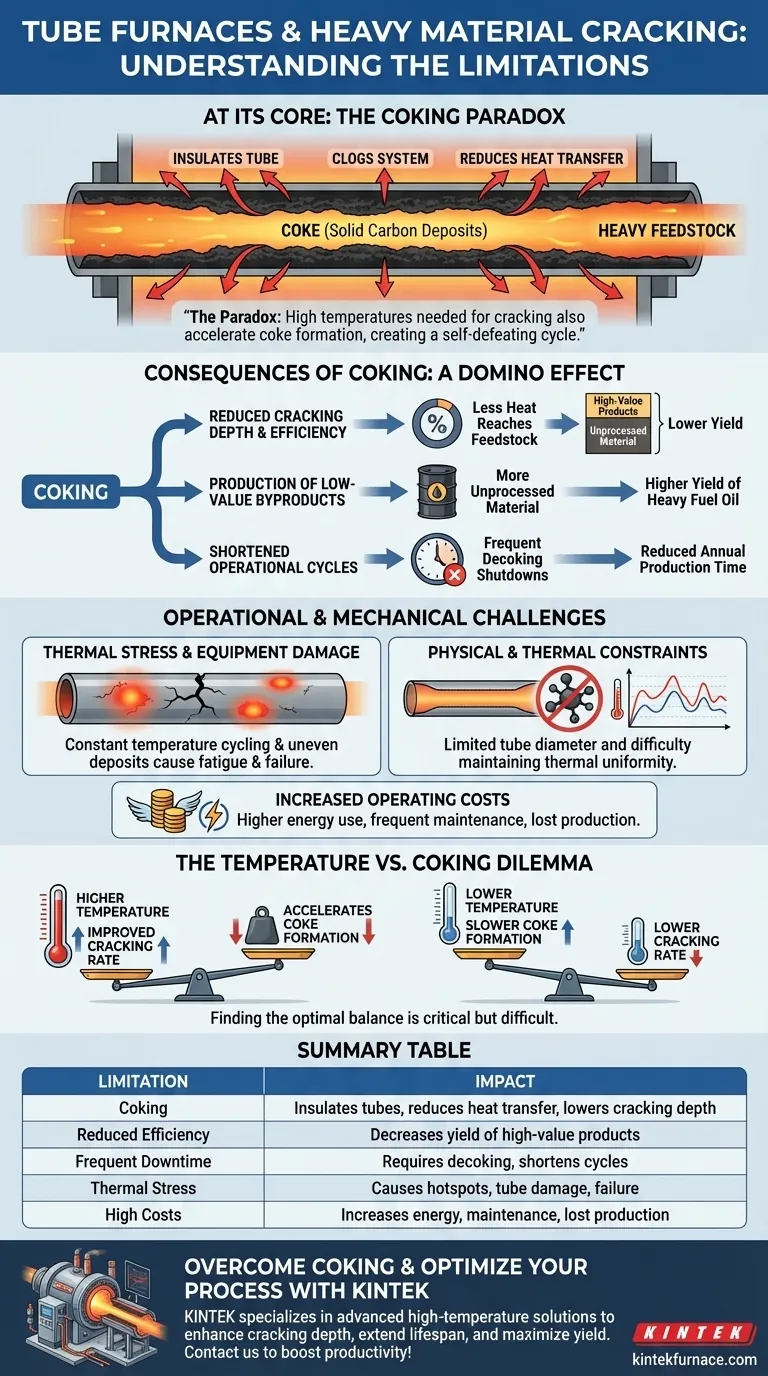
At its core, the primary limitation of using tube furnaces for cracking heavy materials is coking. This is the formation of solid carbon deposits inside the furnace tubes. Coking acts as an insulator, clogs the system, reduces the efficiency of the cracking process, and ultimately shortens the operational lifespan of the entire furnace assembly.
The fundamental challenge is a paradox: the high temperatures required to effectively crack heavy hydrocarbons are the very same conditions that accelerate the formation of coke, creating a self-defeating cycle of inefficiency and mechanical stress.

The Core Problem: Coking and Its Consequences
When heavy feedstocks like crude oil fractions are heated to extreme temperatures, they are meant to "crack" into smaller, more valuable molecules. However, a parallel and highly problematic reaction also occurs.
What is Coking?
Coking is a chemical process where heavy hydrocarbon molecules polymerize and dehydrogenate under high heat, forming a hard, solid layer of carbon residue on the interior surface of the furnace tubes.
Reduced Cracking Depth and Efficiency
The layer of coke acts as a thermal insulator. This barrier prevents heat from effectively reaching the feedstock flowing through the tube.
As a result, the cracking depth—the extent to which the heavy material is broken down—is significantly reduced. This means a lower percentage of the raw material is converted into the desired high-value products.
Production of Low-Value Byproducts
With a lower cracking depth, a larger portion of the feedstock passes through the furnace without being fully processed. This leads to a higher yield of low-value byproducts, such as heavy fuel oil, and a lower yield of valuable products like ethylene and propylene.
Shortened Operational Cycles
As the coke layer thickens, the furnace's efficiency drops to a point where it is no longer economical to run. The process must be shut down for decoking, a procedure to remove the carbon buildup.
This necessity for frequent decoking drastically shortens the furnace's operational work cycle, reducing the effective annual production time and overall throughput.
Compounding Operational and Mechanical Challenges
The issue of coking creates a domino effect, leading to a series of secondary problems that impact both the equipment and the bottom line.
Impact on Equipment Lifespan
The constant cycling between high-temperature operation and lower-temperature decoking cycles induces significant thermal stress on the furnace tubes, which can lead to fatigue and failure.
Furthermore, uneven coke deposits create hotspots on the tube walls. These localized areas of extreme temperature can weaken the metal and cause premature tube rupture, leading to costly and dangerous failures.
Physical and Thermal Constraints
Tube furnaces are inherently limited by the tube's diameter. This geometry is not ideal for processing large or bulky samples, which restricts the total volume and throughput of the operation.
Achieving perfect thermal uniformity along the entire length of a long tube is also a challenge. Coking exacerbates this issue, making it nearly impossible to maintain the precise temperature profile needed for optimal cracking.
Increased Operating Costs
Each of these limitations contributes to higher operational costs. Frequent downtime for decoking means lost production, while lower raw material utilization directly impacts profitability.
Adding the costs of higher energy consumption (to overcome the insulating coke layer) and frequent maintenance or replacement of expensive furnace tubes makes this a significant financial challenge.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or operating a tube furnace for heavy material cracking involves balancing several competing factors.
The Temperature vs. Coking Dilemma
Operators face a constant trade-off. Increasing the furnace temperature can improve the cracking rate, but it also dramatically accelerates coke formation. Finding the optimal balance is critical but difficult to maintain.
Material and Design Limitations
Specialty tubes made from advanced materials like corundum can withstand higher temperatures, but they come with their own drawbacks. They are extremely expensive, often opaque (preventing visual inspection of the process), and can be brittle or susceptible to thermal shock.
Contamination and Purity
For applications in materials science where purity is paramount, any interaction between the feedstock and the tube material, or flaking of coke deposits, can introduce contamination. This can ruin the properties of the final processed material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these limitations is the first step toward effective process design and technology selection. Your optimal strategy depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the yield of high-value products: You must prioritize technologies or advanced tube materials that aggressively manage coke formation, even if it requires a higher initial investment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs and downtime: You may need to accept a lower cracking depth by using more moderate temperatures or processing lighter feedstocks to extend cycle times between decoking.
- If your primary focus is achieving high throughput: The inherent physical and volume limitations of a standard tube furnace may mean you need to investigate alternative reactor designs better suited for large-scale continuous processing.
Ultimately, acknowledging the inherent conflict between cracking and coking is crucial for optimizing any high-temperature hydrocarbon process.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Impact |
|---|---|
| Coking | Insulates tubes, reduces heat transfer, lowers cracking depth |
| Reduced Efficiency | Decreases yield of high-value products like ethylene |
| Frequent Downtime | Requires decoking, shortens operational cycles |
| Thermal Stress | Causes hotspots, tube damage, and equipment failure |
| High Costs | Increases energy use, maintenance, and lost production |
Struggling with coking and inefficiency in your heavy material processing? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions to overcome coking, enhance cracking depth, and extend equipment lifespan—maximizing your yield and reducing downtime. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your process and boost productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















