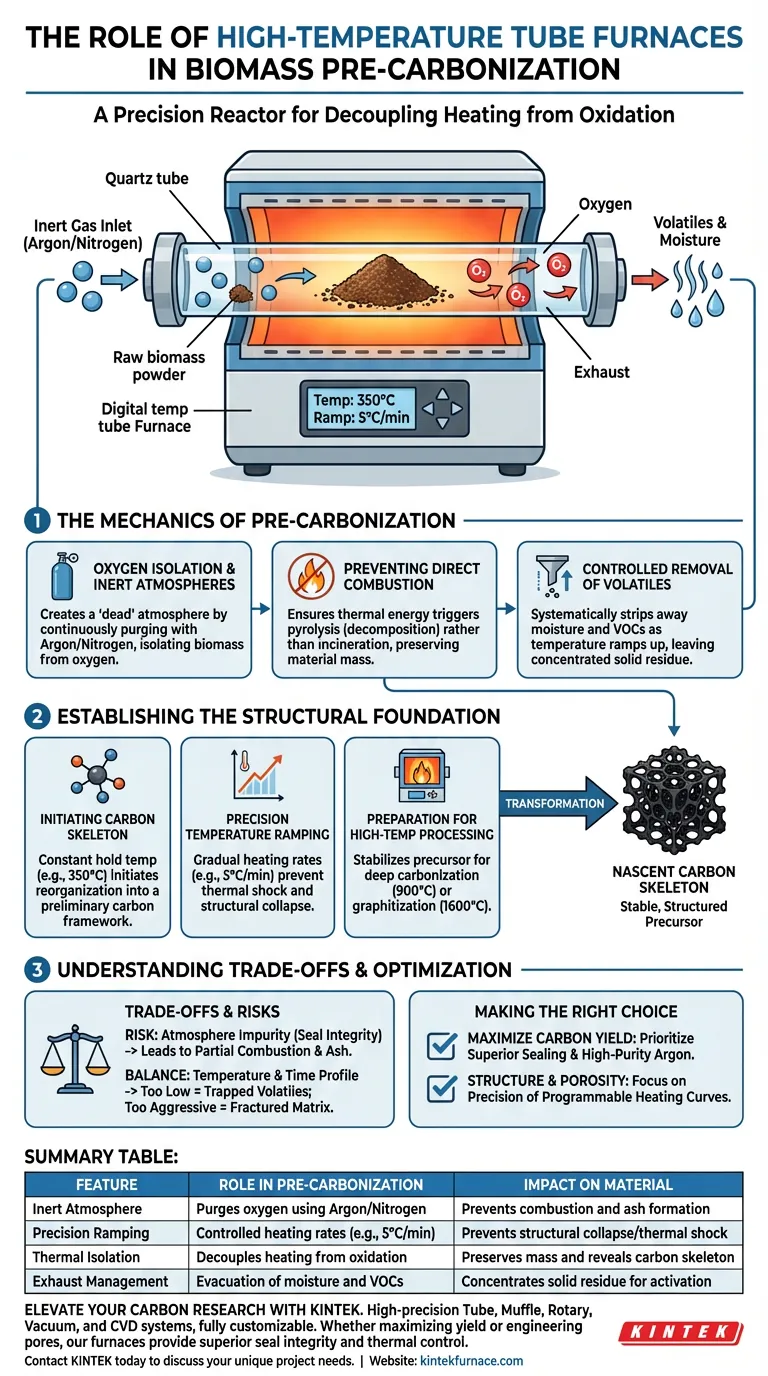
A high-temperature tube furnace acts as a precision reactor that isolates raw biomass to fundamentally alter its chemical structure without burning it. During pre-carbonization, the furnace utilizes a strictly controlled inert atmosphere (typically Argon) and precise temperature ramping to heat the material to moderate levels, such as 350°C. This specific environment facilitates pyrolysis, forcing the release of volatile components while preserving the solid material, preventing oxygen-fueled combustion.
The furnace’s primary role during pre-carbonization is to decouple heating from oxidation. By driving off volatile organic compounds in an oxygen-free zone, it reveals a nascent carbon skeleton, creating the essential structural foundation required for any subsequent high-temperature activation or graphitization.

The Mechanics of Pre-Carbonization
Oxygen Isolation and Inert Atmospheres
The most critical function of the tube furnace is the creation of a "dead" atmosphere. By continuously purging the chamber with inert gases like Argon or Nitrogen, the furnace effectively isolates the biomass powder from oxygen.
Preventing Direct Combustion
Without this isolation, heating biomass to hundreds of degrees would simply result in incineration (turning the material to ash). The tube furnace ensures that the thermal energy triggers chemical decomposition (pyrolysis) rather than oxidative burning, preserving the material's mass for conversion into carbon.
Controlled Removal of Volatiles
As the temperature ramps up, the furnace environment allows for the systematic release of non-carbon elements. This process strips away moisture and volatile organic compounds, which are evacuated from the tube, leaving behind a concentrated solid residue.
Establishing the Structural Foundation
Initiating the Carbon Skeleton
The pre-carbonization phase is where the material's architecture is defined. By maintaining a constant hold temperature, such as 350°C, the furnace initiates the reorganization of organic matter into a preliminary carbon skeleton.
Precision Temperature Ramping
Unlike uncontrolled heating methods, a tube furnace applies specific heating rates (e.g., 5°C/min). This gradual increase prevents thermal shock and ensures that the evolution of volatiles occurs uniformly throughout the biomass powder, preventing structural collapse.
Preparation for High-Temperature Processing
While pre-carbonization occurs at lower temperatures, it is the prerequisite for later stages. It stabilizes the precursor material, ensuring it can withstand subsequent heating to 900°C or 1600°C for deep carbonization or graphitization without losing its structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Atmosphere Impurity
The effectiveness of the process is entirely dependent on the seal integrity of the tube furnace. Even minor oxygen leaks during this phase can lead to partial combustion, significantly lowering the final carbon yield and introducing ash impurities into the carbon skeleton.
Balancing Temperature and Time
There is a delicate balance in the heating profile. If the temperature is too low or the holding time too short, volatile components remain trapped, which can disrupt pore structure during later activation steps. Conversely, aggressive ramping can cause rapid gas release that fractures the developing carbon matrix.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your biomass processing, you must align the furnace parameters with your desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is maximizing carbon yield: Prioritize a furnace with superior sealing and high-purity Argon flow to completely eliminate oxidative burnout during the heating phase.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity and porosity: Focus on the precision of the programmable heating curves to ensure a slow, steady release of volatiles that keeps the carbon skeleton intact.
By strictly controlling the atmosphere and thermal ramp, the tube furnace transforms volatile biomass into a stable, structured precursor ready for advanced material applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Pre-Carbonization | Impact on Material |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Purges oxygen using Argon/Nitrogen | Prevents combustion and ash formation |
| Precision Ramping | Controlled heating rates (e.g., 5°C/min) | Prevents structural collapse/thermal shock |
| Thermal Isolation | Decouples heating from oxidation | Preserves mass and reveals carbon skeleton |
| Exhaust Management | Evacuation of moisture and VOCs | Concentrates solid residue for activation |
Elevate Your Carbon Research with KINTEK
Precise pre-carbonization is the foundation of high-performance biomass materials. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific temperature and atmosphere requirements.
Whether you are maximizing carbon yield or engineering complex pore structures, our furnaces provide the seal integrity and thermal control necessary for superior results. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique project needs and let our engineers help you design the perfect thermal solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Rohit Yadav, Kusum Kumari. Synthesis and Electrochemical Characterization of Activated Porous Carbon Derived from Walnut Shells as an Electrode Material for Symmetric Supercapacitor Application. DOI: 10.3390/engproc2023059175
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of alumina tube furnaces? Unlock Precision in Materials Processing
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace used for AlPO4 calcination? Ensure Safety in Molten Salt Electrolysis
- What are the key capabilities of the 3-Zone tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Lab
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for the preparation of non-enzymatic glucose sensor electrodes?
- What are the steps involved in calibrating the temperature control system of a tube furnace? Ensure Precision and Repeatability
- What are the typical applications for tube furnaces? Master Precise Thermal Processing
- Why is it important to calibrate the temperature profile of a tube furnace? Ensure Accurate and Repeatable Results
- What environmental benefits do tube furnaces provide? Boost Efficiency and Drive Sustainable Innovation



















