At their core, tube furnaces provide significant environmental benefits by enabling exceptional process efficiency and serving as a critical tool for developing green technologies. Their design focuses on precise control over temperature and atmosphere, which directly translates to reduced energy consumption, minimized material waste, and the ability to conduct research into sustainable solutions like carbon capture and biofuels.
The primary environmental advantage of a tube furnace is not a single feature, but its fundamental design for containment and precision. This allows for highly efficient energy use, reduced waste, and the development of next-generation sustainable materials and energy technologies.
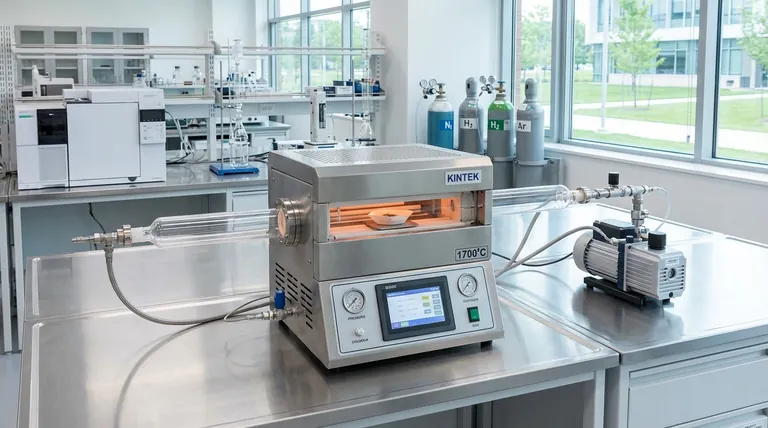

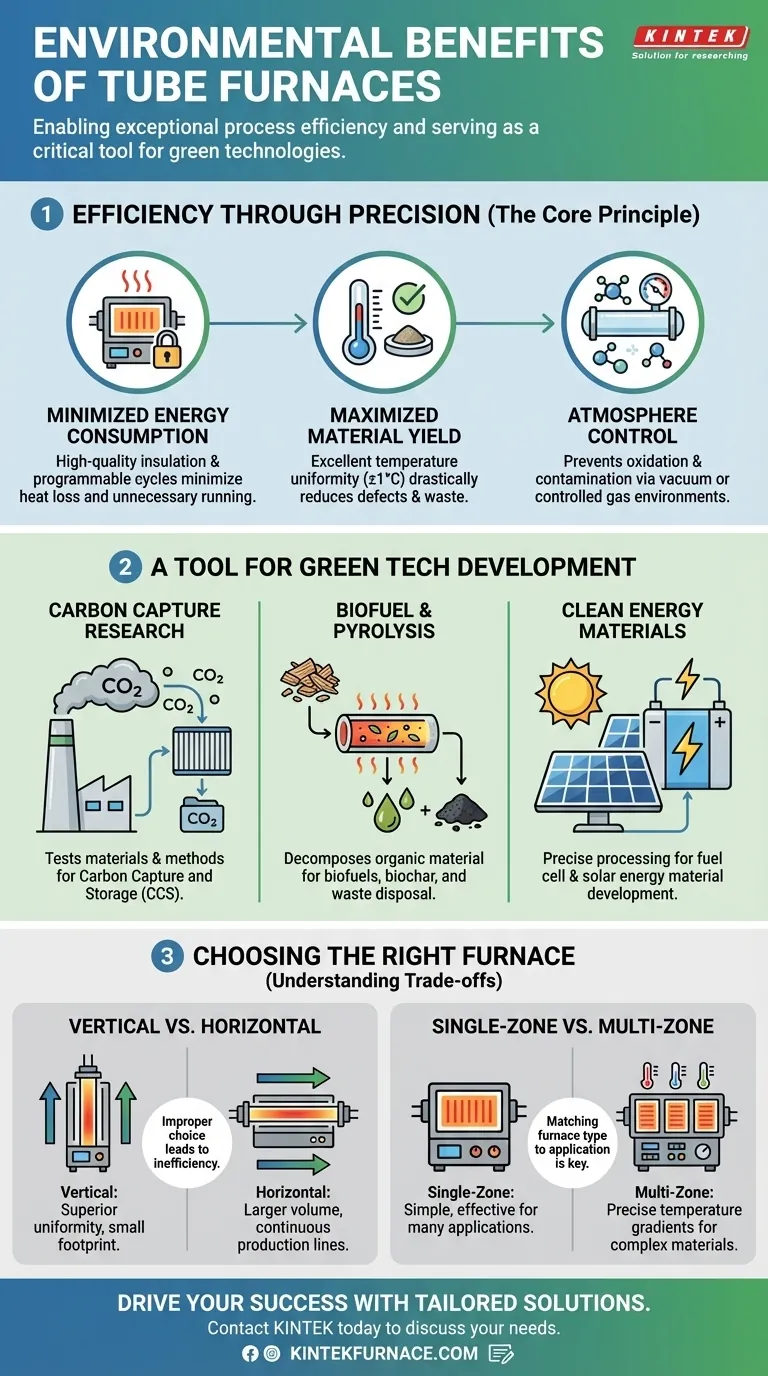
The Core Principle: Efficiency Through Precision
The most significant environmental impact of any high-temperature process is its energy consumption and material waste. A tube furnace's design directly addresses these challenges through unparalleled control.
Minimizing Energy Consumption
Modern tube furnaces are engineered for energy efficiency. They use high-quality insulation to minimize heat loss to the surrounding environment, ensuring the energy consumed is directed at the sample.
Furthermore, fully programmable controllers allow for optimized heating cycles. You can program precise ramp-up rates, hold times, and cool-down periods, eliminating the energy waste associated with overheating or running the furnace longer than necessary.
Maximizing Material Yield
In processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or annealing, temperature consistency is critical. Tube furnaces provide excellent temperature uniformity (often with a precision of ±1°C) along the entire heated zone.
This uniformity ensures that the entire sample is processed under identical conditions, drastically reducing defects, inconsistencies, and rejected parts. This higher yield means less raw material is wasted to produce the desired outcome.
Enabling Atmosphere Control
The enclosed tube design, combined with sealed end caps, allows for complete control over the internal atmosphere. Processes can be run under vacuum conditions (down to 10⁻⁵ torr) or within a specific, controlled gas environment.
This prevents unwanted oxidation and side reactions, ensuring the purity of the final product and eliminating the creation of contaminated waste materials that require further processing or disposal.
A Tool for Green Technology Development
Beyond process efficiency, tube furnaces are indispensable instruments in the research and development of future environmental solutions.
Advancing Carbon Capture Research
Scientists use tube furnaces to test new materials and methods for carbon capture and storage (CCS). The furnace's ability to simulate specific industrial gas conditions and temperatures is essential for this work.
Enabling Biofuel and Pyrolysis
Tube furnaces are ideal for biomass pyrolysis, a process that thermally decomposes organic material in the absence of oxygen to create biofuels and biochar. This is a cornerstone of renewable energy research.
They are also used for high-temperature incineration and pyrolysis for waste disposal, turning harmful waste into inert material and potentially recovering valuable resources.
Innovating Clean Energy Materials
The development of materials for fuel cells and solar energy production requires extremely precise thermal processing. Tube furnaces provide the controlled environment needed to create and test these advanced materials, directly supporting the growth of sustainable energy sources.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Choosing the Right Furnace
The environmental benefits of a tube furnace are only fully realized when the correct type is chosen for the application. An improper choice can lead to inefficiency.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Furnaces
A vertical tube furnace often provides superior temperature uniformity and has a smaller footprint, making it ideal for space-constrained labs and batch processes requiring high consistency.
A horizontal tube furnace typically offers a larger working volume, allowing for larger samples or continuous production lines. Choosing the wrong orientation can lead to wasted space, energy, or inefficient sample loading.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Control
A single-zone furnace is simple and effective for many applications. However, a multi-zone furnace provides multiple independent heating zones along the tube.
This allows for even greater temperature precision and the ability to create specific temperature gradients, which is critical for complex material synthesis. Using a multi-zone furnace for a simple task can be an unnecessary use of energy, while using a single-zone furnace for a complex task can result in a failed process and wasted material.
Applying This to Your Process
Your specific goal will determine which features provide the most significant environmental and operational advantage.
- If your primary focus is process optimization and cost reduction: Prioritize a furnace with high-quality insulation and a fully programmable controller to minimize energy consumption and maximize yield.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge materials research: Multi-zone control, high-vacuum capabilities, and gas mixing systems are the most critical features for enabling novel sustainable technologies.
- If your primary focus is direct waste treatment or biofuel production: Look for high-temperature capabilities (up to 1700°C or more) and a robust design suitable for pyrolysis applications.
By aligning the furnace's capabilities with your core objective, you ensure that your process is as efficient, clean, and environmentally responsible as possible.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Benefit | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Reduced Energy Consumption | High-quality insulation, programmable controllers |
| Minimized Material Waste | Excellent temperature uniformity, atmosphere control |
| Green Technology Development | Vacuum/gas control for carbon capture, biofuels, clean energy materials |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with a custom tube furnace? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on process optimization, materials research, or waste treatment, we can help you achieve superior efficiency and environmental benefits. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how our tailored solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















