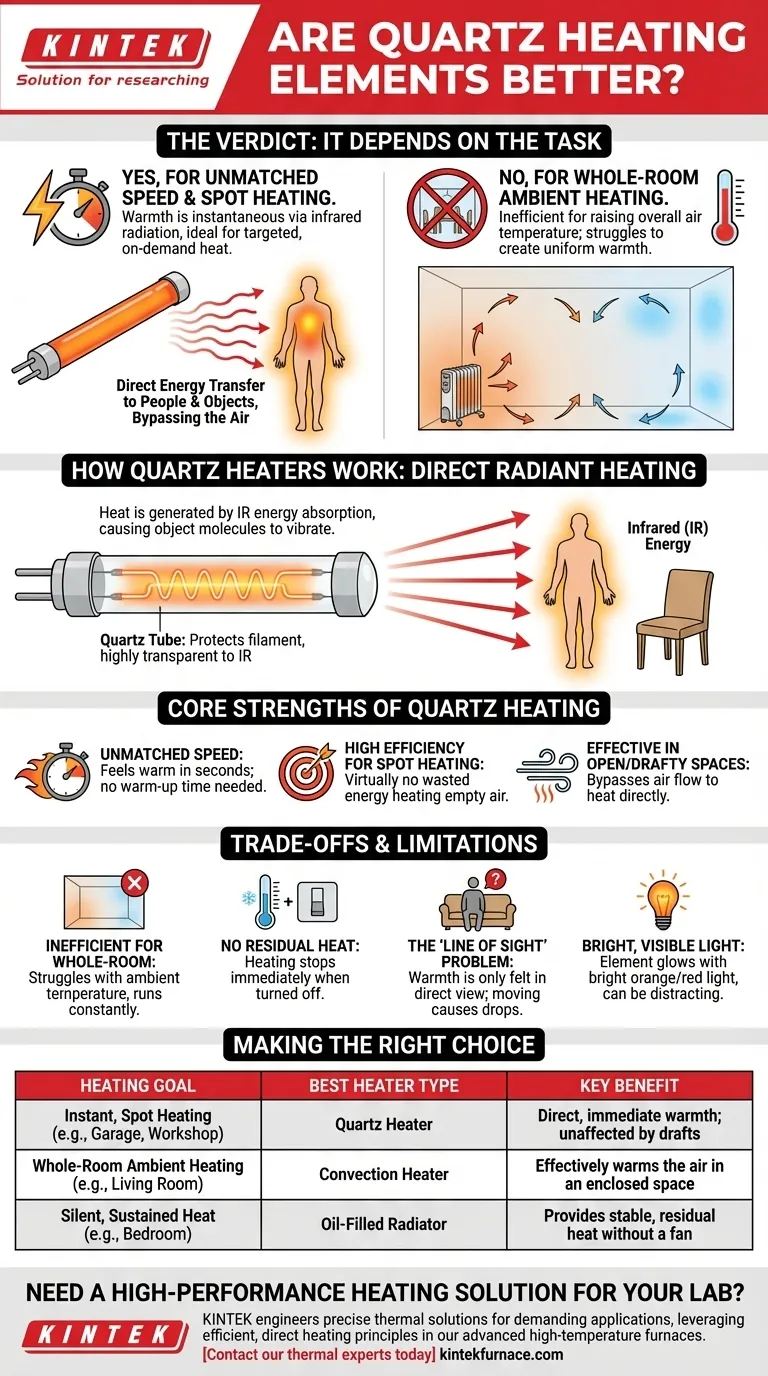
When it comes to speed, quartz heating elements are unequivocally better. They deliver warmth almost instantaneously by emitting infrared radiation, making them an excellent choice for targeted, on-demand heat. However, their superiority is entirely dependent on the task; they are not a universal solution for every heating need.
A quartz heater does not warm the air in a room. Instead, it directly heats the people and objects in its path, much like the sun's rays. This makes it highly efficient for spot heating but a poor choice for raising the ambient temperature of an entire space.

How Quartz Heaters Actually Work
The defining characteristic of a quartz heater is its mechanism: it is a form of radiant heater. Understanding this principle is crucial to using it effectively.
The Principle of Infrared Radiation
Quartz elements contain a heating filament enclosed in a quartz tube. When electricity passes through the filament, it heats up and emits infrared (IR) energy.
This IR energy travels in a straight line through the air until it hits an object, like a person or a piece of furniture. The energy is then absorbed, causing the object's molecules to vibrate and generate heat. This is a direct energy transfer.
The Role of the Quartz Tube
The quartz tube itself is not the primary source of heat. Its main purpose is to protect the hot filament inside from the air and physical contact.
Quartz is used because it is highly transparent to infrared radiation and can withstand very high temperatures. It allows the maximum amount of energy to radiate outwards efficiently.
The Core Strengths of Quartz Heating
In the right context, the advantages of quartz technology are significant. Its performance is rooted in its method of direct, radiant heating.
Unmatched Speed
Because they don't need to warm up the surrounding air via convection, quartz heaters provide a feeling of warmth within seconds of being turned on. This makes them ideal for applications where instant heat is the priority.
High Efficiency for Spot Heating
When you need to heat a specific zone, such as a desk area or a workbench, a quartz heater is extremely efficient. Virtually no energy is wasted heating the empty air between the unit and you.
Effectiveness in Open or Drafty Spaces
Conventional heaters that warm the air (convection heaters) are useless in drafty areas like garages, patios, or workshops. A quartz heater excels here because it bypasses the air and heats you directly, regardless of air movement.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The strengths of quartz heaters are also the source of their weaknesses. Their targeted nature makes them unsuitable for many common heating goals.
Inefficiency for Whole-Room Heating
If your goal is to raise the overall temperature of an insulated room, a quartz heater is the wrong tool. It will struggle to create a comfortable, uniform ambient temperature and will run constantly in an attempt to do so. A convection heater is far better for this task.
No Residual Heat
The moment you turn off a quartz heater, the heating effect stops completely. This is unlike oil-filled radiators, which continue to radiate heat long after they are powered down, providing a more stable thermal environment.
The "Line of Sight" Problem
You only feel the warmth from a quartz heater if you are in its direct line of sight. If you move behind a piece of furniture or even turn your back to it, you will feel a dramatic drop in temperature.
Bright, Visible Light
The heating element in a quartz heater typically glows with a bright orange or red light. While some may find this pleasant, it can be distracting or undesirable in environments like a bedroom at night.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a quartz element is "better," you must first define your heating objective.
- If your primary focus is instant, personal warmth for a workspace or garage: A quartz heater is an excellent and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is raising the ambient temperature of a closed, insulated room: A convection or ceramic fan heater will be far more effective.
- If your primary focus is silent, sustained, and even heating for a bedroom: An oil-filled radiator is likely the superior option.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between heating objects directly and heating the air around you is the key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Heating Goal | Best Heater Type | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Instant, Spot Heating (e.g., garage, workshop) | Quartz Heater | Direct, immediate warmth; unaffected by drafts |
| Whole-Room Ambient Heating (e.g., living room) | Convection Heater | Effectively warms the air in an enclosed space |
| Silent, Sustained Heat (e.g., bedroom) | Oil-Filled Radiator | Provides stable, residual heat without a fan |
Need a high-performance heating solution for your lab or industrial process?
At KINTEK, we don't just sell heaters; we engineer precise thermal solutions. Our advanced high-temperature furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces—leverage the same principles of efficient, direct heating for demanding applications.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss how we can develop a custom heating system to accelerate your research and improve your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Which heating element is more brittle, SiC or MoSi2? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- Can MoSi2 heating elements be customized for specific industrial needs? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Efficiency
- Which heating element is most effective? The definitive guide to choosing the right material for your application.
- What are the limitations of molybdenum disilicide as a structural material? Overcome Brittleness and High-Temperature Weakness
- What are the properties and handling requirements of ceramic sheath materials? Master High-Temp and Insulation Challenges
- What are the disadvantages of using silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements? Manage Aging, Cost, and Brittleness
- What are the key benefits of silicon carbide heating elements? Achieve High-Temp Efficiency and Durability
- How does a graphite heater work? Achieving Extreme Temperatures Beyond 2000°C



















