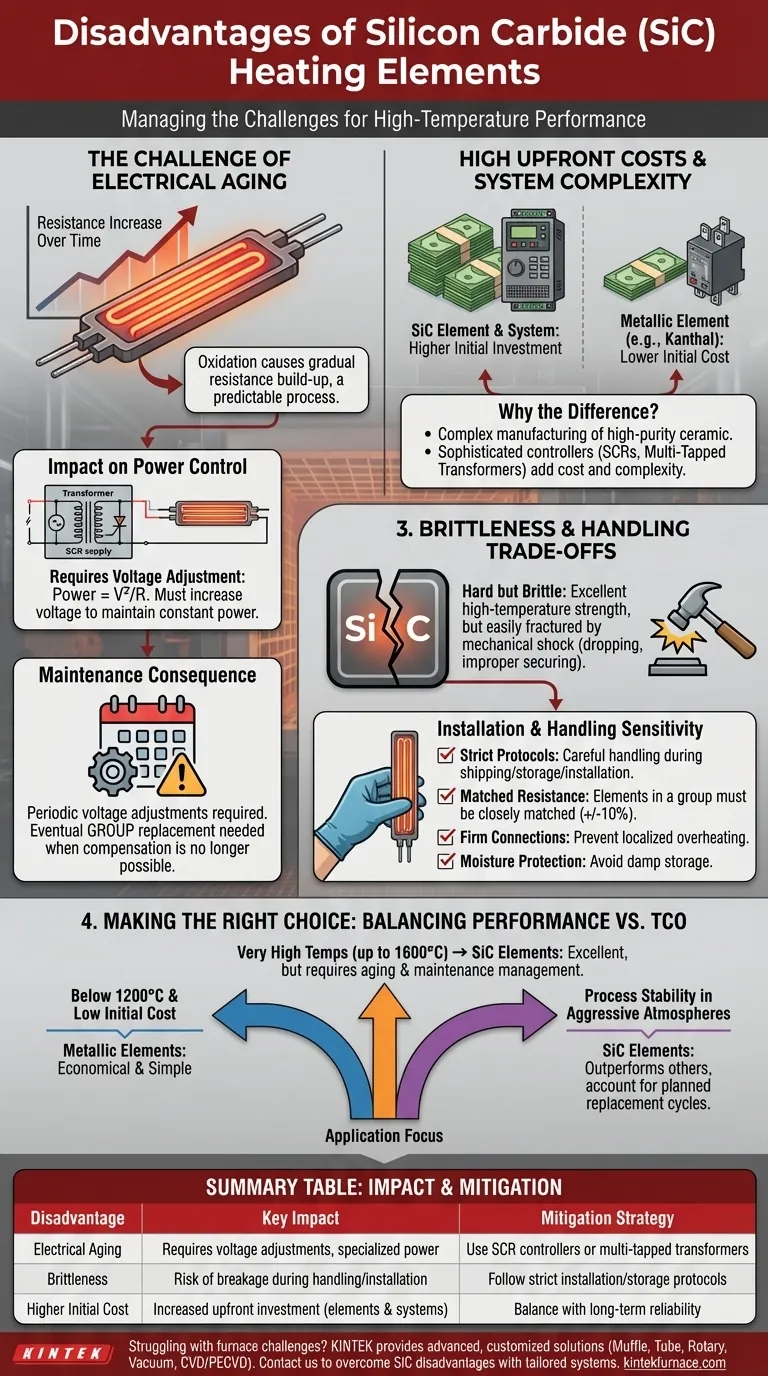
While powerful and versatile, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements possess distinct disadvantages that must be managed. The primary drawbacks are their tendency to increase in electrical resistance over time (a process known as aging), their inherent brittleness which demands careful handling, and a higher initial cost compared to common metallic elements. These factors introduce unique complexities related to power control, maintenance planning, and installation.
The core challenge of using SiC elements is not their performance, which is excellent at high temperatures, but the total cost of ownership. You are trading higher upfront investment and ongoing maintenance complexity for the ability to operate reliably in extreme thermal environments.
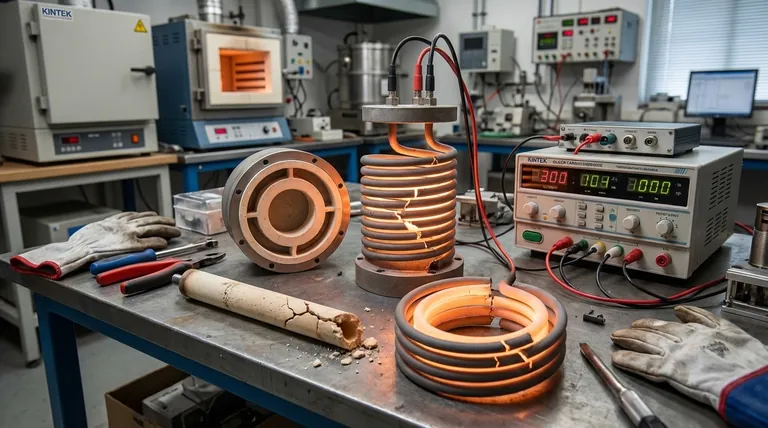

The Challenge of Electrical Aging
The most significant operational disadvantage of SiC is its gradual change in electrical properties over its service life. This "aging" process is a fundamental characteristic of the material.
Understanding Resistance Increase
As SiC elements operate at high temperatures, they slowly oxidize. This oxidation builds up within the material's structure, causing its electrical resistance to steadily increase.
This change is not a sign of imminent failure but a predictable aspect of the element's lifecycle. However, it directly impacts the power delivery system.
The Impact on Power Control
To maintain a constant power output (and therefore a stable temperature), the voltage supplied to the element must be increased to compensate for its rising resistance (Power = V²/R).
This means a simple on/off controller is insufficient. SiC systems require a specialized power supply, typically a multi-tapped transformer or a Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (SCR) phase-angle fired controller, to gradually step up the voltage over time.
The Consequence for Maintenance
The need to adjust voltage means maintenance is not optional. Technicians must periodically switch to a higher voltage tap on the transformer to keep the furnace at its setpoint.
Eventually, the resistance increases to a point where the power supply can no longer compensate. At this stage, the entire set of elements in a control zone must be replaced as a group to ensure uniform heating. This planned replacement cycle is a key operational cost.
Upfront Costs and System Complexity
Beyond the operational characteristics, the initial investment for a SiC heating system is typically higher than for alternatives designed for lower temperatures.
Higher Initial Element Cost
Individually, SiC heating elements are more expensive than standard metallic wire elements, such as those made from iron-chromium-aluminum alloys (e.g., Kanthal).
This cost difference is a direct result of the complex manufacturing process required to produce the high-purity, high-density ceramic material.
The Need for Specialized Power Supplies
As mentioned, the requirement for sophisticated power controllers like SCRs or multi-tapped transformers adds another layer of cost and complexity to the overall system design.
These components are more expensive and require more specialized knowledge to integrate and maintain than the simple relays or contactors used with many metallic elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brittleness and Handling
The physical nature of silicon carbide as a hard, dense ceramic introduces practical challenges that are not present with ductile metallic elements.
Fragility During Installation and Operation
SiC elements are hard but brittle. They have excellent strength at high temperatures but can be easily fractured by mechanical shock, such as being dropped or improperly secured.
Careful handling during shipping, storage, and installation is critical to prevent breakage and premature failure.
Sensitivity to Installation Details
For optimal performance and lifespan, strict installation protocols must be followed. Elements within a single control group must have closely matched resistance values (e.g., within +/-10%) to ensure uniform temperature.
Furthermore, electrical connections must be firm to prevent localized overheating, and the elements should be protected from damp conditions during storage to avoid potential issues.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element requires balancing performance needs against the total cost of ownership, including initial investment and long-term maintenance.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial cost for applications below 1200°C: Metallic elements are almost always the more economical and simpler choice.
- If your primary focus is reaching very high temperatures (up to 1600°C): SiC is an excellent choice, provided you can engineer a system to manage its aging and maintenance requirements.
- If your primary focus is process stability in aggressive atmospheres: SiC often outperforms other elements, but you must account for the planned replacement cycles in your operational budget and downtime planning.
Ultimately, understanding these disadvantages allows you to design a robust system that leverages the unique high-temperature capabilities of SiC while mitigating its operational challenges.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Aging (Resistance Increase) | Requires voltage adjustments and specialized power supplies | Use SCR controllers or multi-tapped transformers for stable power |
| Brittleness | Risk of breakage during handling and installation | Follow strict protocols for careful installation and storage |
| Higher Initial Cost | Increased upfront investment for elements and systems | Balance with long-term reliability in extreme temperatures |
| System Complexity | Needs advanced controllers and maintenance planning | Plan for periodic voltage adjustments and group replacements |
Struggling with high-temperature furnace challenges? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise fit for your unique experimental needs, helping you overcome SiC element disadvantages with reliable, tailored systems. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















