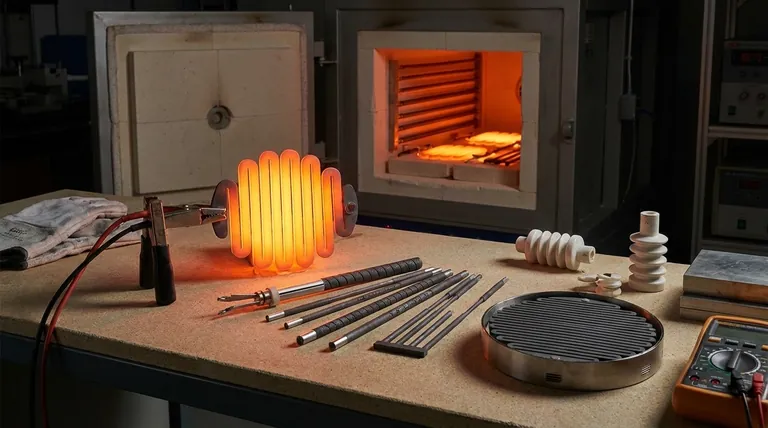
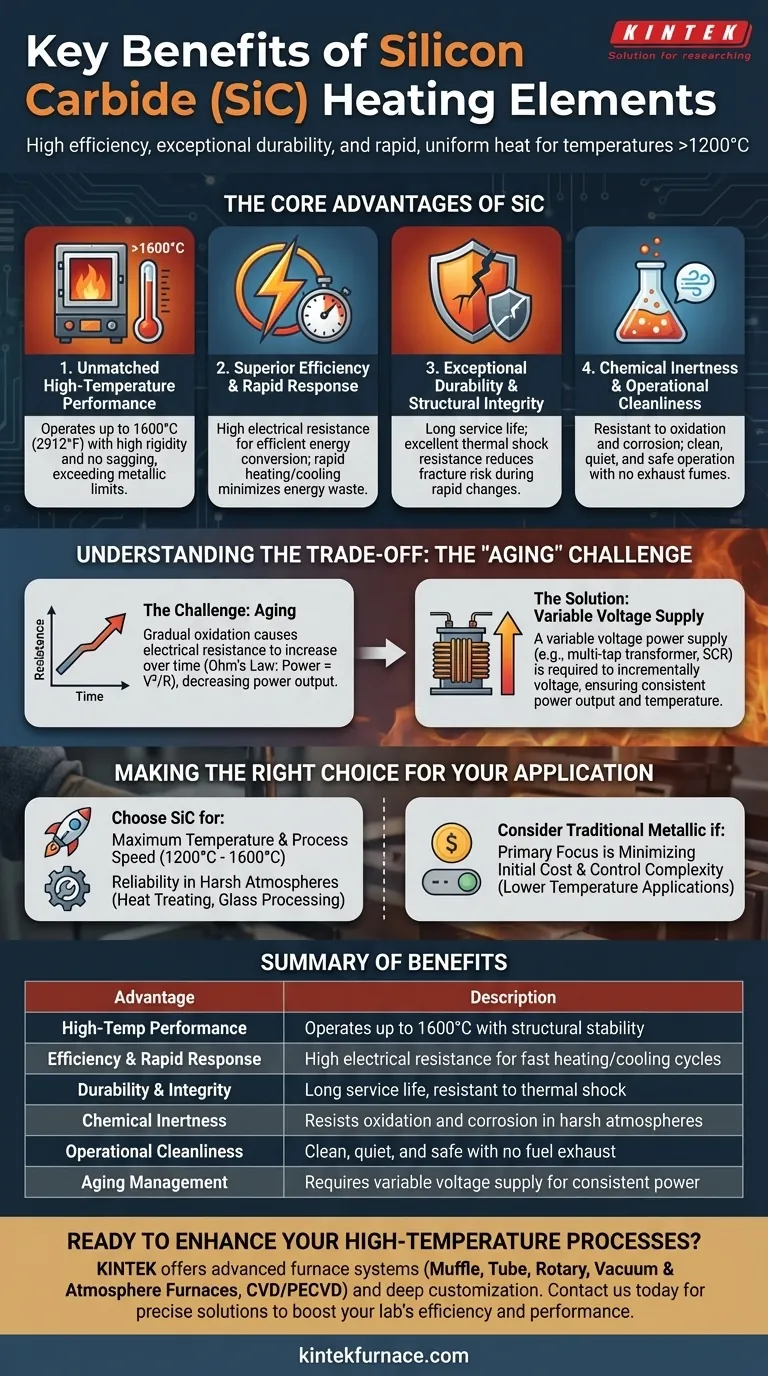
In essence, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are chosen for their unique ability to deliver high efficiency, exceptional durability, and rapid, uniform heat at extremely high temperatures. Their robust material properties make them a superior choice over traditional metallic elements for demanding industrial processes that operate well above 1200°C.
Silicon carbide elements provide a powerful combination of high-temperature performance and long-term reliability. However, their primary operational characteristic is a gradual "aging" process, which must be managed with a variable voltage power supply to ensure consistent output over their lifespan.

The Core Advantages of Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide's fundamental material properties translate directly into significant operational benefits for high-heat applications. These elements are not simply hotter; they are engineered for a different class of thermal processing.
Unmatched High-Temperature Performance
SiC elements can operate at surface temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F) and beyond, far exceeding the limits of most metallic heating elements.
This capability stems from the material's high rigidity and the absence of a liquid phase. Unlike metallic elements that can sag or creep under their own weight at high temperatures, SiC remains structurally stable.
Superior Efficiency and Rapid Response
These elements have a high electrical resistance, which allows them to convert electrical energy into heat with exceptional efficiency.
They are also known for their rapid heating and cooling capabilities. This fast thermal response is critical for processes requiring quick cycles, improving throughput and minimizing energy waste during furnace downtime.
Exceptional Durability and Structural Integrity
SiC elements are known for their long service life, even in continuous or cyclical operation.
Their low coefficient of thermal expansion provides excellent resistance to thermal shock, reducing the risk of fracture during rapid temperature changes. This physical strength contributes directly to their reputation for reliability.
Chemical Inertness and Operational Cleanliness
Silicon carbide is highly resistant to both oxidation and chemical corrosion, making it suitable for use in a wide range of controlled and aggressive industrial atmospheres.
As an electric heat source, SiC elements are inherently clean, quiet, and safe. They eliminate the complexities of fuel storage, piping, and the need to vent noxious exhaust fumes, simplifying furnace design and plant safety.
Understanding the Trade-off: The Challenge of "Aging"
The primary consideration when designing with SiC elements is managing a natural process known as aging. Understanding this characteristic is key to achieving their full performance potential and lifespan.
What is "Aging" in SiC Elements?
Over time, the surface of the SiC element gradually oxidizes, which causes its electrical resistance to slowly increase. This is a predictable and inherent property of the material.
This "aging" process is a function of the element's temperature and the furnace atmosphere. Hotter temperatures and certain atmospheric conditions will accelerate the rate of aging.
The Impact on Power Control
According to Ohm's Law (Power = Voltage² / Resistance), if the voltage remains constant while the resistance increases, the power output of the heating element will decrease.
This means that to maintain a consistent furnace temperature, the power delivered to the aging element must be actively managed.
The Requirement for Variable Voltage Supplies
To compensate for the steady increase in resistance, a variable voltage power supply is required. This is typically achieved using a multi-tap transformer or a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR).
As the element ages, the voltage is incrementally increased to maintain the target power output and temperature. This control strategy is a fundamental part of any SiC heating system design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a heating element technology requires balancing performance requirements with operational complexity. SiC elements occupy a critical space for high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and process speed: SiC is a premier choice for applications running between 1200°C and 1600°C, offering the rapid cycling that metallic elements cannot.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh environments: The chemical inertness and structural strength of SiC make it ideal for heat treating, glass processing, and other demanding industrial atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial cost and control complexity: Be aware that the mandatory variable voltage power supply adds cost and complexity compared to simple resistive systems used for lower-temperature metallic elements.
Ultimately, silicon carbide elements empower industries to achieve process temperatures and efficiencies that are otherwise unattainable, provided the system is designed to manage their unique operational needs.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Performance | Operates up to 1600°C with structural stability |
| Efficiency and Rapid Response | High electrical resistance for fast heating/cooling cycles |
| Durability and Integrity | Long service life, resistant to thermal shock |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists oxidation and corrosion in harsh atmospheres |
| Operational Cleanliness | Clean, quiet, and safe with no fuel exhaust |
| Aging Management | Requires variable voltage supply for consistent power |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable silicon carbide heating solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can boost your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















