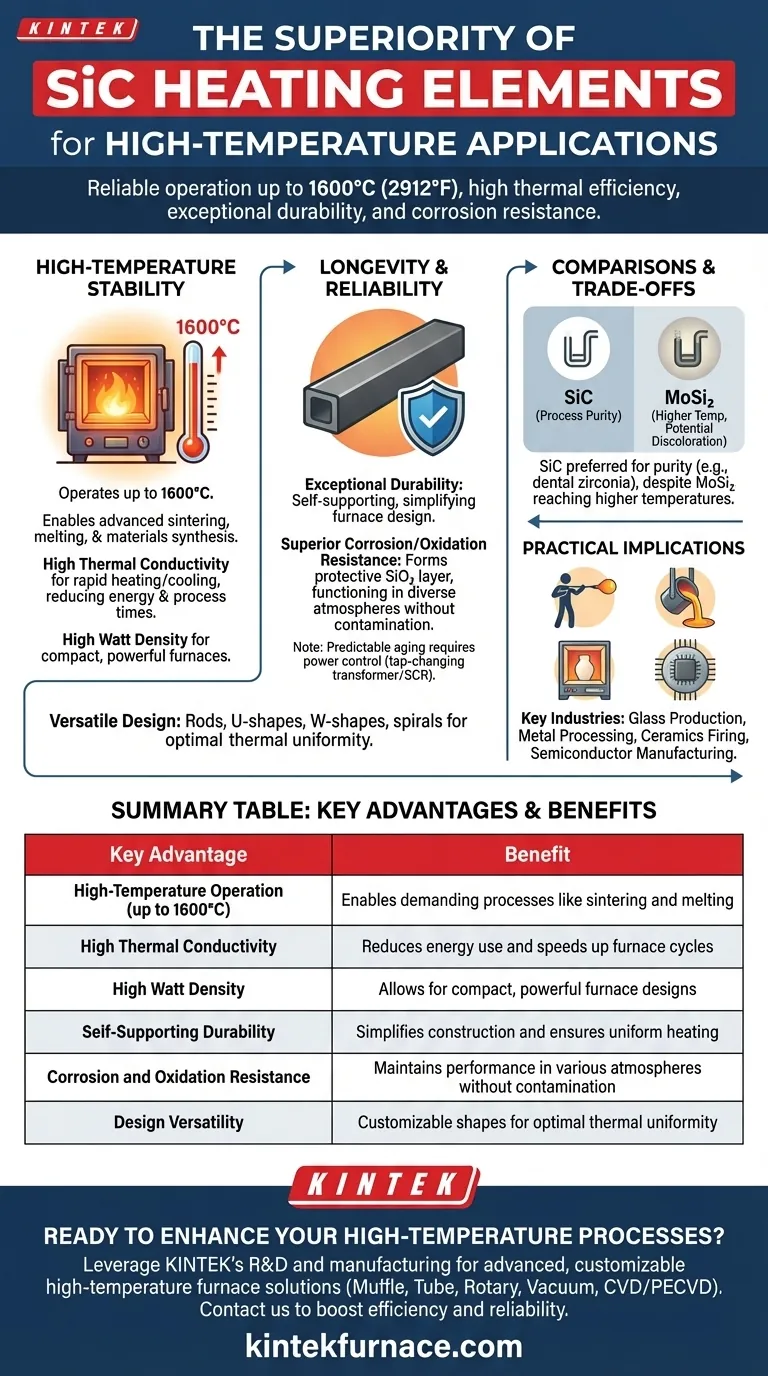
At their core, Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are superior for high-temperature applications due to a unique combination of physical and chemical properties. Their ability to operate reliably at extreme temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F), paired with high thermal efficiency, exceptional durability, and resistance to chemical corrosion, makes them uniquely suited for the most demanding industrial heating processes.
The true advantage of SiC elements is not merely their ability to get hot, but their capacity to deliver consistent, clean, and efficient heat under conditions that would cause metallic or other ceramic elements to fail. This translates directly to improved process control, longer service life, and lower operational costs in critical applications.

The Foundation: Unmatched High-Temperature Stability
The primary reason to select any heating element is its ability to reach and maintain a target temperature. This is where SiC elements first distinguish themselves.
Operating at Extreme Temperatures
Standard metallic heating elements typically falter above 1200-1300°C. SiC elements, however, operate comfortably up to 1600°C (2912°F), opening up a range of high-temperature processes like sintering, melting, and advanced materials synthesis.
High Thermal Conductivity
SiC possesses excellent thermal conductivity. This means it heats up and cools down very quickly, allowing for rapid furnace cycles. This efficiency directly reduces energy consumption and shortens process times, boosting productivity.
High Watt Density
SiC elements can handle high electrical power loads for their size. This high watt density allows for the design of compact, powerful furnaces, as you can generate a massive amount of heat within a smaller physical footprint.
Beyond Heat: The Keys to Longevity and Reliability
In an industrial environment, performance over time is just as important as peak performance. Durability and chemical stability are critical factors for operational success.
Exceptional Durability and Self-Support
SiC is a hard, rigid ceramic material. Unlike metallic wire elements that can sag and require complex supports, SiC elements are self-supporting. This simplifies furnace construction, eliminates a common point of failure, and ensures uniform heating over the element's life.
Superior Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
When heated, SiC forms a thin, protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). This passive layer makes the element highly resistant to oxidation and chemical attack, allowing it to function in a wide variety of process atmospheres without degrading or contaminating the product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Comparisons
No single solution is perfect for every scenario. Understanding the specific context where SiC shines, and its limitations, is key to making an informed decision.
SiC vs. MoSi2 Elements
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements can reach even higher temperatures than SiC. However, SiC is often preferred in applications where process purity is paramount. For example, in the sintering of dental zirconia, MoSi₂ can cause a slight discoloration, whereas SiC has a much cleaner effect.
The Consideration of Element Aging
A critical characteristic of SiC elements is that their electrical resistance gradually increases with use over time. This aging process is predictable but requires a power control system—such as a tap-changing transformer or a Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR)—that can adjust the voltage to maintain consistent power output.
Practical Implications: Where SiC Excels
The theoretical advantages of SiC translate into tangible benefits across numerous industries.
Versatility in Design
SiC elements can be manufactured in a wide array of shapes—including rods, U-shapes, W-shapes, and spirals. This versatility allows furnace designers to customize the heating configuration for optimal thermal uniformity in any specific application.
Impact on Industrial Processes
The unique properties of SiC make it the ideal choice for demanding processes. Its use is prevalent in glass production, metal processing, ceramics firing, and semiconductor manufacturing, where high temperatures, process cleanliness, and absolute reliability are non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element requires matching its properties to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is reaching temperatures above 1300°C with fast cycle times: SiC's combination of high-temperature stability and thermal conductivity is your ideal solution.
- If your primary focus is process purity and minimizing contamination: SiC's chemical inertness, especially compared to MoSi₂ in atmospherically sensitive applications, provides a significant advantage.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and simplified furnace design: The self-supporting nature and physical durability of SiC elements reduce maintenance requirements and structural complexity.
By understanding these core principles, you can design and operate more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective thermal processing systems.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Operation (up to 1600°C) | Enables demanding processes like sintering and melting |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Reduces energy use and speeds up furnace cycles |
| High Watt Density | Allows for compact, powerful furnace designs |
| Self-Supporting Durability | Simplifies construction and ensures uniform heating |
| Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance | Maintains performance in various atmospheres without contamination |
| Design Versatility | Customizable shapes for optimal thermal uniformity |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with reliable SiC heating solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can boost your efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















