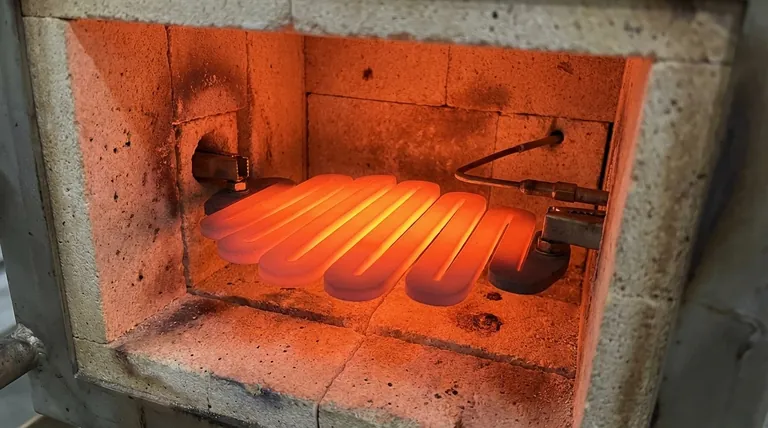
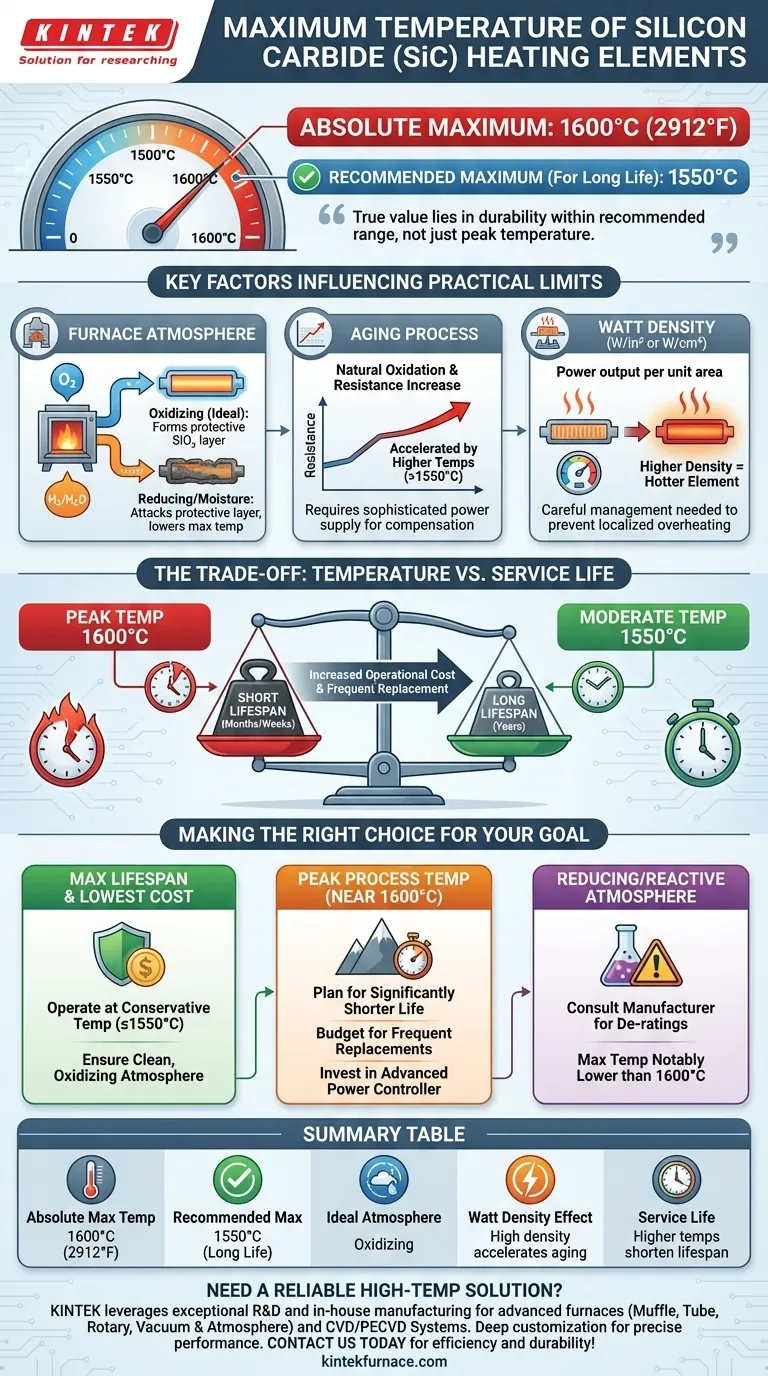
In most industrial applications, the absolute maximum element temperature for silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements is 1600°C (2912°F). However, the practical and recommended maximum temperature for ensuring a long service life is often lower, typically around 1550°C. This operational limit is heavily influenced by the furnace atmosphere and the power density applied to the element.
While SiC elements are capable of reaching 1600°C, their true value lies in their durability and performance within their recommended operating range. Pushing an element to its absolute thermal limit almost always involves a significant trade-off in its operational lifespan.

Why "Maximum Temperature" is More Than a Single Number
Simply knowing the 1600°C figure is insufficient for reliable system design. Several factors dictate the practical, sustainable operating temperature of a SiC element. Understanding these is key to avoiding premature failure and ensuring process stability.
The Critical Role of Furnace Atmosphere
The environment inside the furnace is the single most important factor affecting element life and performance at high temperatures.
An oxidizing atmosphere, such as air, is the ideal environment. It allows a protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) to form on the element's surface, which slows down further oxidation and degradation.
Reducing atmospheres (like hydrogen or cracked ammonia) or the presence of moisture (water vapor) can attack this protective layer, leading to accelerated aging and a lower effective maximum temperature.
The Process of "Aging"
All SiC elements "age," which means their electrical resistance gradually increases over time. This process is a natural result of oxidation.
This aging process is significantly accelerated by higher temperatures. Operating continuously near the 1600°C limit will cause resistance to increase much faster than operating at a more conservative 1500°C. A sophisticated power supply is required to compensate for this change by delivering more voltage to maintain the desired power output.
Element Loading (Watt Density)
Watt density is the measure of power output per unit of the element's surface area (W/in² or W/cm²).
Higher watt densities mean the element must run hotter to dissipate that energy into the furnace. Pushing an element to its maximum temperature requires careful management of watt density to prevent localized overheating and premature failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Temperature vs. Service Life
Choosing an operating temperature is an engineering decision that balances process requirements against operational cost and reliability. There is no single "right" answer, only the best choice for a specific goal.
The Cost of Operating at Peak Temperatures
Continuously running SiC elements at or near their 1600°C limit will drastically shorten their service life. The accelerated aging means they will need to be replaced far more frequently than elements run at a more moderate temperature.
For example, an element that might last for years at 1500°C could potentially fail in a matter of months, or even weeks, if held constantly at 1600°C.
Impact on Process Stability
As elements age and their resistance changes, maintaining a stable and uniform furnace temperature becomes more challenging.
Fast-aging elements require more frequent adjustments from the power control system. If the system cannot respond effectively, it can lead to temperature fluctuations that compromise the quality and repeatability of your thermal process.
Context: SiC vs. Other Elements
While SiC elements are robust and versatile, they are not the only option. For processes in an air atmosphere that require sustained temperatures above 1600°C, alternatives like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements are often the superior choice. Conversely, SiC elements generally exhibit better durability in certain reducing atmospheres compared to MoSi₂.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your target operating temperature based on a clear understanding of your primary objective. A lower temperature is not a sign of a less capable process, but often a mark of an efficient and reliable one.
- If your primary focus is maximum element lifespan and lowest operating cost: Operate at a conservative temperature, typically no higher than 1500°C - 1550°C, and ensure your furnace atmosphere is clean and oxidizing.
- If your primary focus is reaching a peak process temperature near 1600°C: Plan for a significantly shorter element life, budget for more frequent replacements, and invest in a power controller that can manage rapidly increasing resistance.
- If you are operating in a reducing or reactive atmosphere: Consult the element manufacturer directly for specific temperature de-ratings, as the maximum allowable temperature will be notably lower than 1600°C.
By balancing your temperature needs with these physical limitations, you can engineer a heating system that is powerful, reliable, and cost-effective over its entire lifecycle.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on SiC Element |
|---|---|
| Absolute Max Temperature | 1600°C (2912°F) |
| Recommended Max Temperature | 1550°C for long life |
| Furnace Atmosphere | Oxidizing ideal; reducing atmospheres lower max temp |
| Watt Density | High density accelerates aging |
| Aging Process | Resistance increases with temperature and time |
| Service Life | Higher temps shorten lifespan significantly |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced heating systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise performance for your specific experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and durability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















