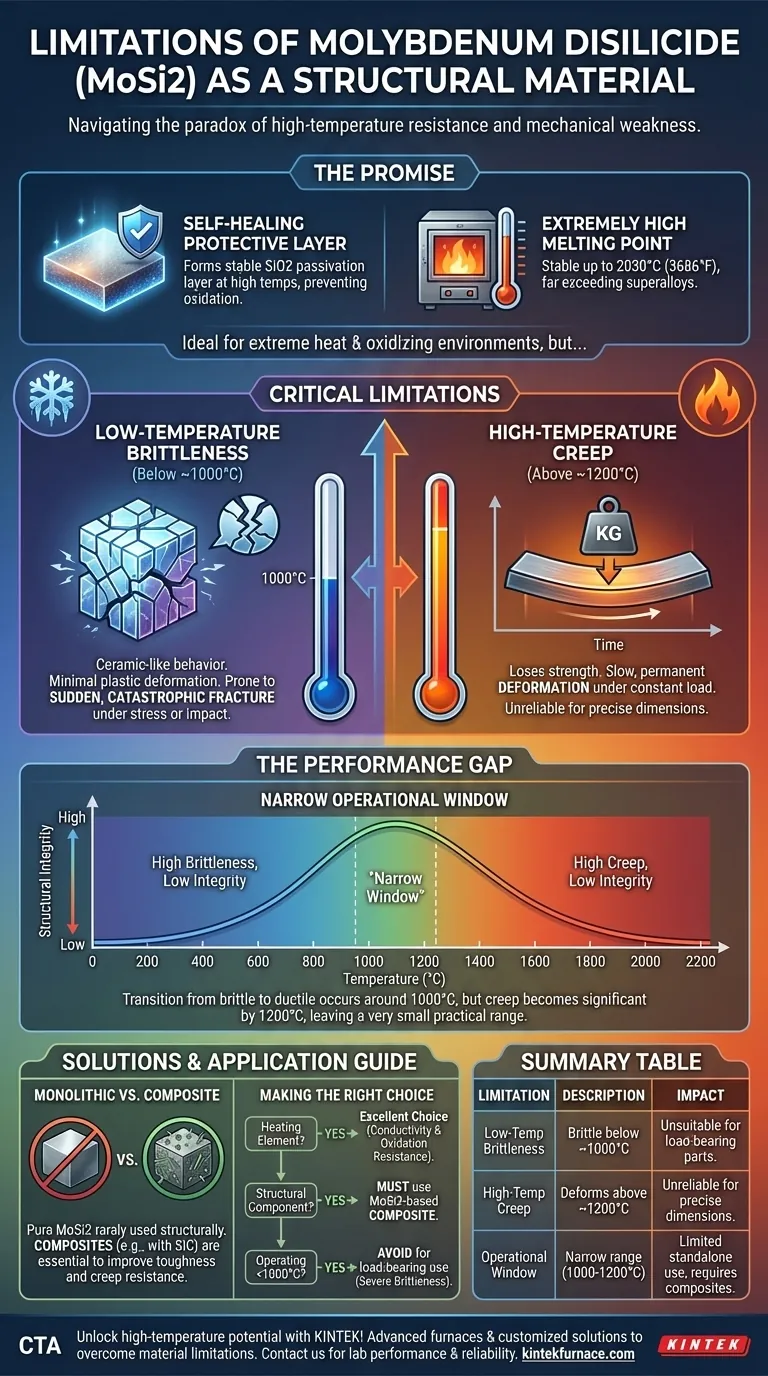
As a structural material, molybdenum disilicide's primary limitations are its profound brittleness at temperatures below approximately 1000°C and a significant loss of strength and creep resistance at temperatures above 1200°C. While it possesses an exceptionally high melting point and outstanding resistance to oxidation, these two specific weaknesses create a challenging performance gap for load-bearing applications.
Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) presents a paradox for engineers. Its ability to form a protective, self-healing glass layer makes it ideal for extreme heat, yet its ceramic-like brittleness and high-temperature weakness prevent its use as a pure, monolithic structural component.
The Promise: Why MoSi2 is Considered at All
To understand its limitations, we must first appreciate its primary strength: exceptional performance in oxidizing, high-temperature environments.
A Self-Healing Protective Layer
At high temperatures, MoSi2 reacts with oxygen to form a thin, stable passivation layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2) on its surface. This glassy layer acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying material from further oxidation and degradation.
Extremely High Melting Point
With a melting point of 2030°C (3686°F), MoSi2 is fundamentally stable at temperatures far exceeding those of most superalloys. This makes it a compelling candidate for next-generation turbines, furnaces, and aerospace components.
Critical Limitations for Structural Use
Despite its thermal stability, MoSi2 fails on two key mechanical fronts that are non-negotiable for structural integrity.
Low-Temperature Brittleness
Below approximately 1000°C, MoSi2 behaves like a ceramic. Its rigid tetragonal crystal structure allows for very little plastic deformation, meaning it will fracture suddenly and catastrophically under stress, rather than bending or yielding like a metal.
This brittleness makes it extremely difficult to fabricate and highly susceptible to damage from thermal shock or minor impacts during operation or maintenance.
High-Temperature Creep
The second limitation appears at the other end of the temperature spectrum. Despite its high melting point, MoSi2 begins to lose its strength and deform under a constant load (a phenomenon known as creep) at temperatures above 1200°C.
This slow deformation makes it unreliable for components that must maintain precise dimensions under stress, such as a turbine blade or support beam.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Performance Gap
The core challenge of using MoSi2 is that its strengths and weaknesses create a narrow and problematic operational window.
The Brittle-to-Ductile Transition
The material transitions from brittle to more ductile behavior around 1000°C. However, this is precisely where its creep resistance begins to degrade, peaking as a major issue by 1200°C.
This leaves a very small temperature range where the material is neither too brittle nor too weak, severely limiting its practical application as a standalone structure.
Monolithic vs. Composite Solutions
Because of these inherent flaws, monolithic (pure) MoSi2 is rarely used for structural parts. Its limitations are almost always addressed by using it as a matrix material in a composite.
By reinforcing the MoSi2 matrix with other materials like silicon carbide (SiC) fibers or other ceramic particles, engineers can dramatically improve both its low-temperature toughness and its high-temperature creep resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use MoSi2 depends entirely on whether the application is structural and how you intend to mitigate its weaknesses.
- If your primary focus is a heating element: MoSi2 is an excellent choice, as its electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance are paramount and structural loads are minimal.
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature structural component: Do not use pure MoSi2. You must specify an MoSi2-based composite to achieve the necessary toughness and creep resistance for a reliable design.
- If your application operates entirely below 1000°C: Avoid MoSi2 for any load-bearing purpose due to its severe and unreliable brittleness.
By understanding MoSi2 not as a flawed standalone material but as a high-performance base for advanced composites, you can effectively harness its remarkable properties for extreme environments.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Description | Impact on Structural Use |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Brittleness | Brittle below ~1000°C, prone to sudden fracture | Unsuitable for load-bearing parts, difficult fabrication |
| High-Temperature Creep | Loses strength and deforms above ~1200°C | Unreliable for precise dimensions under stress |
| Operational Window | Narrow range between brittleness and creep | Limited standalone use, requires composite solutions |
Unlock the full potential of high-temperature materials with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, overcoming material limitations like MoSi2 brittleness and creep. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's performance and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















