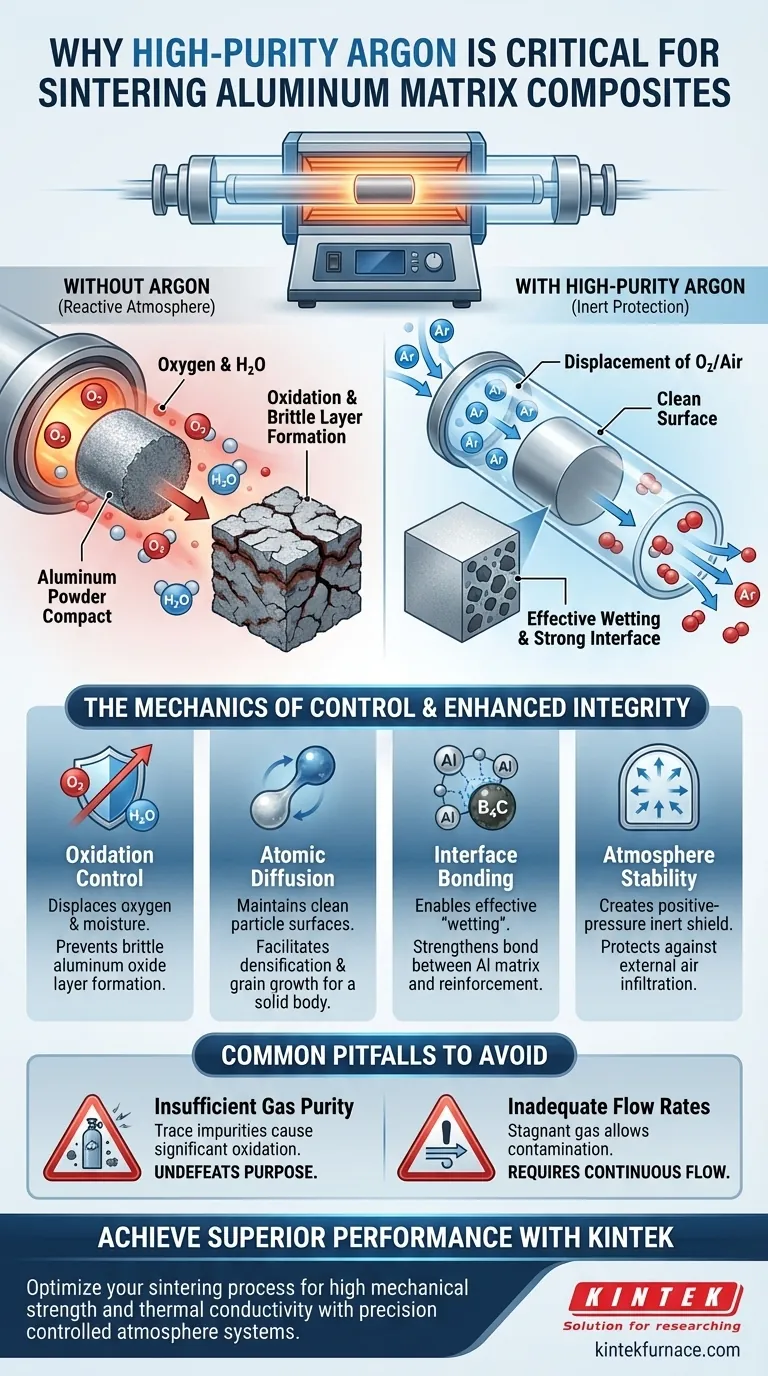
The introduction of high-purity argon gas is a critical preventative measure mandated by the high chemical reactivity of aluminum at elevated temperatures. Specifically, the argon serves as an inert protective atmosphere that physically displaces oxygen and air from the furnace chamber. Without this displacement, the aluminum powder would undergo severe oxidation during the sintering process, compromising the material's structural integrity.
Core Insight Aluminum has a natural affinity for oxygen, forming oxide barriers that inhibit particle interaction. High-purity argon neutralizes this threat by creating a strictly inert environment, ensuring the metal matrix remains clean enough to bond effectively with reinforcement particles like Boron Carbide ($\text{B}_4\text{C}$).

The Mechanics of Atmosphere Control
Displacing Reactive Elements
The primary function of high-purity argon is to evacuate the furnace chamber of ambient air.
Air contains oxygen and moisture, both of which are detrimental to the sintering process.
By flooding the system with argon, you replace a reactive atmosphere with a stable, inert one.
The Role of the Sealed Chamber
To maintain this atmosphere, the process typically utilizes a sealed quartz glass tube.
This tube acts as an independent reaction chamber.
When combined with the continuous flow of argon, it effectively isolates the material from the external environment, preventing the re-entry of oxygen.
Why Aluminum Demands an Inert Environment
Preventing Oxide Layer Formation
Aluminum alloy powder possesses high surface activity, meaning it reacts aggressively with oxygen at sintering temperatures.
If oxygen is present, a layer of aluminum oxide forms rapidly on the particle surfaces.
This oxide layer creates a high-thermal-resistance barrier that impedes heat transfer and physical contact between particles.
Facilitating Atomic Diffusion
Sintering relies on atomic diffusion and grain boundary migration to transform loose powder into a dense solid.
These mechanisms function best when metal-to-metal contact is unimpeded.
Surface oxidation acts as a physical contaminant, blocking the diffusion paths required for densification.
Enhancing Composite Integrity
Promoting Wetting
For a composite material to succeed, the metal matrix (aluminum) must "wet" the reinforcement particles ($\text{B}_4\text{C}$).
Wetting refers to how easily a liquid (or semi-solid) spreads over a solid surface.
An argon-protected, oxide-free aluminum surface flows and spreads much more effectively than an oxidized one.
Strengthening the Interface
The ultimate goal is a strong bond between the aluminum matrix and the $\text{B}_4\text{C}$ reinforcement.
By maintaining surface cleanliness, argon allows for direct chemical and mechanical bonding at the interface.
This results in a composite material with superior mechanical properties, rather than a loosely packed body held together by brittle oxides.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Insufficient Gas Purity
Standard industrial argon may still contain trace amounts of oxygen or moisture.
High-purity argon is specified because even small impurities can cause significant oxidation in aluminum powders.
Using lower-grade gas undermines the entire purpose of the controlled atmosphere.
Inadequate Flow Rates
Simply filling the tube is often insufficient; a continuous flow is typically required.
Stagnant gas allows impurities to accumulate or seep in through minor leaks.
A steady flow ensures positive pressure, constantly purging any potential contaminants away from the workload.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your aluminum matrix composites achieve their target specifications, consider the following priorities:
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Strength: Ensure the argon flow is established before heating begins to prevent the formation of oxide layers that inhibit the bonding of the $\text{B}_4\text{C}$ reinforcement.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Conductivity: strict adherence to high-purity gas is essential to avoid the formation of aluminum oxide interfaces, which possess high thermal resistance.
Successful sintering of aluminum composites is not just about temperature; it is defined by the purity of the environment in which that temperature is applied.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role of High-Purity Argon | Impact on Aluminum Composites |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Control | Displaces oxygen and moisture | Prevents brittle oxide layer formation |
| Atomic Diffusion | Maintains clean particle surfaces | Facilitates densification and grain growth |
| Interface Bonding | Enables effective 'wetting' | Strengthens bond between Al matrix and $B_4C$ |
| Atmosphere Stability | Creates a positive-pressure inert shield | Protects against external air infiltration |
Elevate Your Advanced Material Processing with KINTEK
Precision sintering of aluminum matrix composites requires more than just heat; it demands a perfectly controlled atmosphere. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to maintain high-purity environments for your most sensitive materials.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research or production needs. Don't let oxidation compromise your structural integrity—leverage our expertise to achieve superior mechanical properties and thermal conductivity.
Ready to optimize your sintering process? Contact KINTEK Experts Today
Visual Guide
References
- Ahmet Köken. INVESTIGATION OF THE INFLUENCE OF B4C REINFORCEMENT RATIO AND SINTERING TEMPERATURE ON MECHANICAL AND MICROSTRUCTURAL PROPERTIES OF Al6061-BASED METAL MATRIX COMPOSITES. DOI: 10.36306/konjes.1610106
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of using different sizes of steel working ampoules? Precision vs. Efficiency in Lab Research
- How does a temperature-programmed system influence molybdenum carbide formation? Expert Catalyst Synthesis Guide
- What is the importance of dynamic sealing in an InP crystal growth furnace? Ensure Pressure Integrity & Motion Control
- How does the secondary calcination process improve Na2WO4-loaded catalysts? Optimize Surface Performance Today
- What are the technical advantages of using an ALD system over PVD? Achieve Precise Ge:ZnO Thin Film Fabrication
- How does an infrared rapid thermal annealing belt furnace affect battery performance? Maximize Efficiency Today
- What is a horizontal furnace? A space-saving heating solution for attics and crawl spaces
- Why is a forced-air drying oven necessary for impregnated kaolin catalysts? Achieve Uniform Component Immobilization



















