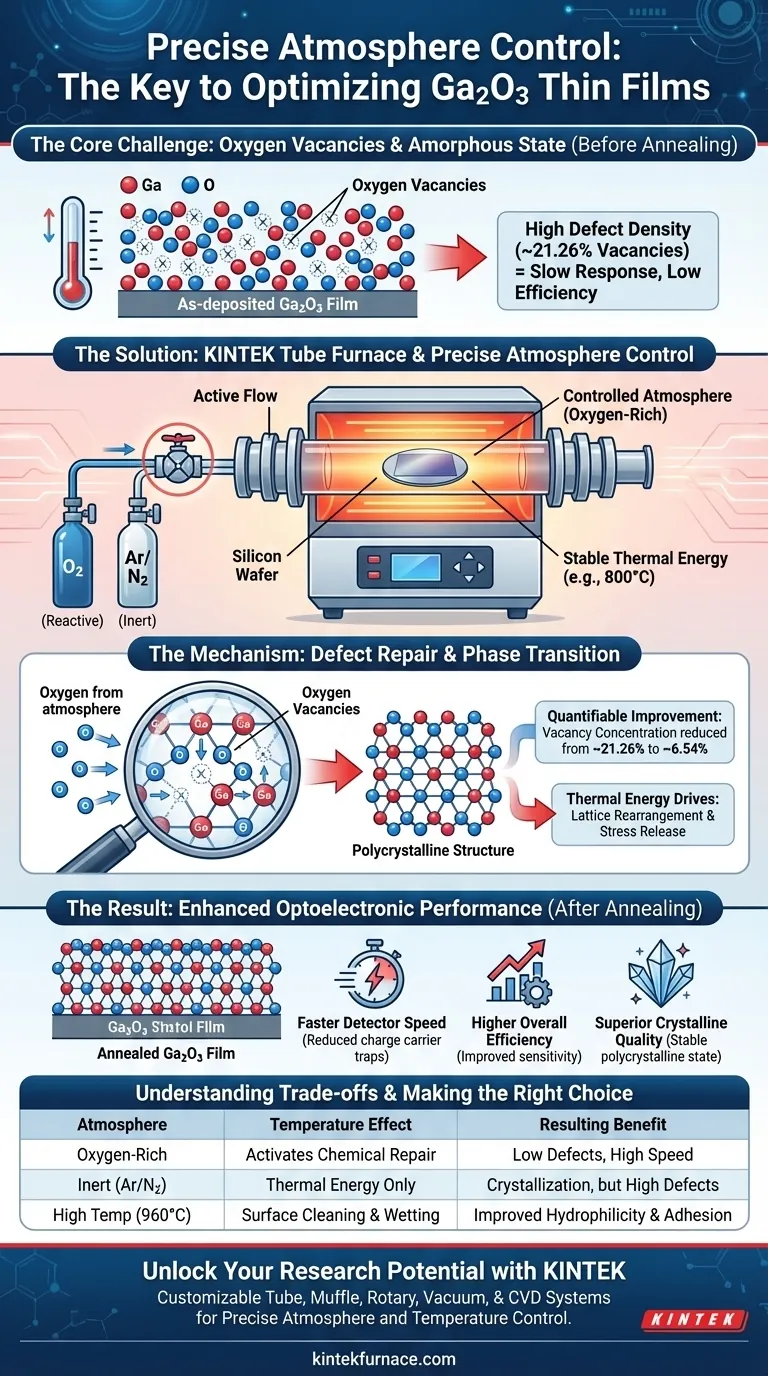
Precise atmosphere control is the defining factor in optimizing the electrical properties of Gallium Oxide (Ga2O3) thin films. In a tube furnace, this capability allows for the introduction of specific reactive gases, such as oxygen, rather than simply heating the material in a vacuum or inert air. By annealing the film in an oxygen-rich environment, the atmosphere actively participates in the chemical reconstruction of the material.
The core value of atmosphere control lies in "defect engineering." By supplying an external source of oxygen atoms, the furnace enables the repair of atomic deficiencies within the film, significantly lowering defect concentrations to enhance the final device's sensitivity and speed.
The Mechanism of Defect Repair
The Role of Reactive Gases
Standard heating supplies energy, but atmosphere control supplies the necessary chemical components. When annealing Ga2O3, introducing oxygen gas creates a reactive environment around the thin film.
Filling Oxygen Vacancies
As-deposited Ga2O3 films often suffer from a high concentration of oxygen vacancies—sites in the crystal lattice where oxygen atoms are missing. During the annealing process, oxygen atoms from the controlled atmosphere migrate into the film.
Quantifiable Improvements
This interaction effectively fills the vacancy defects. For example, annealing in an oxygen atmosphere can reduce the oxygen vacancy concentration from approximately 21.26% down to 6.54%.
Impact on Optoelectronic Performance
Enhancing Detector Speed
Oxygen vacancies act as "traps" for charge carriers, which can slow down the electrical response of a material. By significantly reducing these defects, the material facilitates faster electron movement.
Boosting Overall Efficiency
The reduction in defects leads to a direct improvement in the performance of optoelectronic detectors. Devices fabricated from these optimized films exhibit sharper response times and higher overall efficiency.
The Role of Thermal Energy
While atmosphere controls the chemistry, temperature controls the structure.
Phase Transition
The tube furnace provides the stable thermal environment (e.g., 800°C) necessary to convert the film from an amorphous state to a polycrystalline state.
Lattice Rearrangement
Constant high temperatures provide the kinetic energy required for gallium and oxygen atoms to migrate. This allows them to rearrange into proper lattice positions, releasing internal stress and improving crystalline quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Inert Atmospheres
If you strictly use inert gases like argon or nitrogen without oxygen, you provide thermal energy for crystallization but fail to repair the oxygen deficiencies. This may result in a crystalline film that still possesses poor electrical properties due to high defect density.
Balancing Thermal and Atmospheric Needs
It is critical to balance temperature with gas flow. High temperatures (e.g., 960°C for LAO substrates) are excellent for surface cleaning and wetting, but the specific atmosphere must be tailored to the material's chemical needs to prevent unwanted decomposition or surface reactions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure you are utilizing your tube furnace effectively, align your settings with your specific material objectives:
- If your primary focus is improving detector response speed: Prioritize an oxygen-rich atmosphere to aggressively reduce oxygen vacancy defects from the crystal lattice.
- If your primary focus is crystalline structure: Focus on maintaining a stable, constant temperature (e.g., 800°C) to ensure a complete phase transition from amorphous to polycrystalline.
- If your primary focus is substrate preparation: Utilize higher temperatures (e.g., 960°C) to improve hydrophilicity and adhesion, ensuring the precursor solution wets the surface uniformly.
Mastering the interplay between reactive atmosphere and thermal stability is the only way to unlock the full potential of gallium oxide thin films.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Influence on Ga2O3 Film | Resulting Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Atmosphere | Reduces vacancies from ~21.26% to 6.54% | Faster electron movement & higher sensitivity |
| Thermal Stability (800°C) | Phase transition (Amorphous to Polycrystalline) | Improved crystalline quality & stress release |
| Inert Atmosphere | Provides thermal energy only | Fails to repair chemical oxygen deficiencies |
| High Temperature (960°C) | Surface wetting and cleaning | Improved hydrophilicity and film adhesion |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Thin Film Research
Precise control over your thermal environment is the difference between a failed sample and a breakthrough. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific atmosphere and temperature requirements.
Whether you are engineering defects in Ga2O3 or optimizing complex polycrystalline structures, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the stability and reactive gas precision your project demands. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace needs and see how our expertise can accelerate your material science innovations.
Visual Guide
References
- Wen-Jie Chen, Qing‐Chun Zhang. Influence of annealing pretreatment in different atmospheres on crystallization quality and UV photosensitivity of gallium oxide films. DOI: 10.1039/d3ra07568k
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature tube furnace with a steam generator for LOCA simulation?
- What are the main differences in appearance between tube furnaces and box furnaces? Compare Shapes and Uses for Your Lab
- How does an alumina-lined vertical tube furnace provide a stable environment for corrosion experiments? Get Expert Data
- What is the purpose of purging a tube furnace with argon for tellurium reduction? Ensuring Safety and Purity
- How does a laboratory tube annealing furnace contribute to the final formation of CNT-Al2O3-Ag-TiO2 composite materials?
- What are the technical advantages of using an oscillating tube furnace for tellurium dioxide recovery?
- Why are horizontal tube furnaces ideal for small scale materials tests? Unlock Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What are the main applications of a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Thermal Processing



















