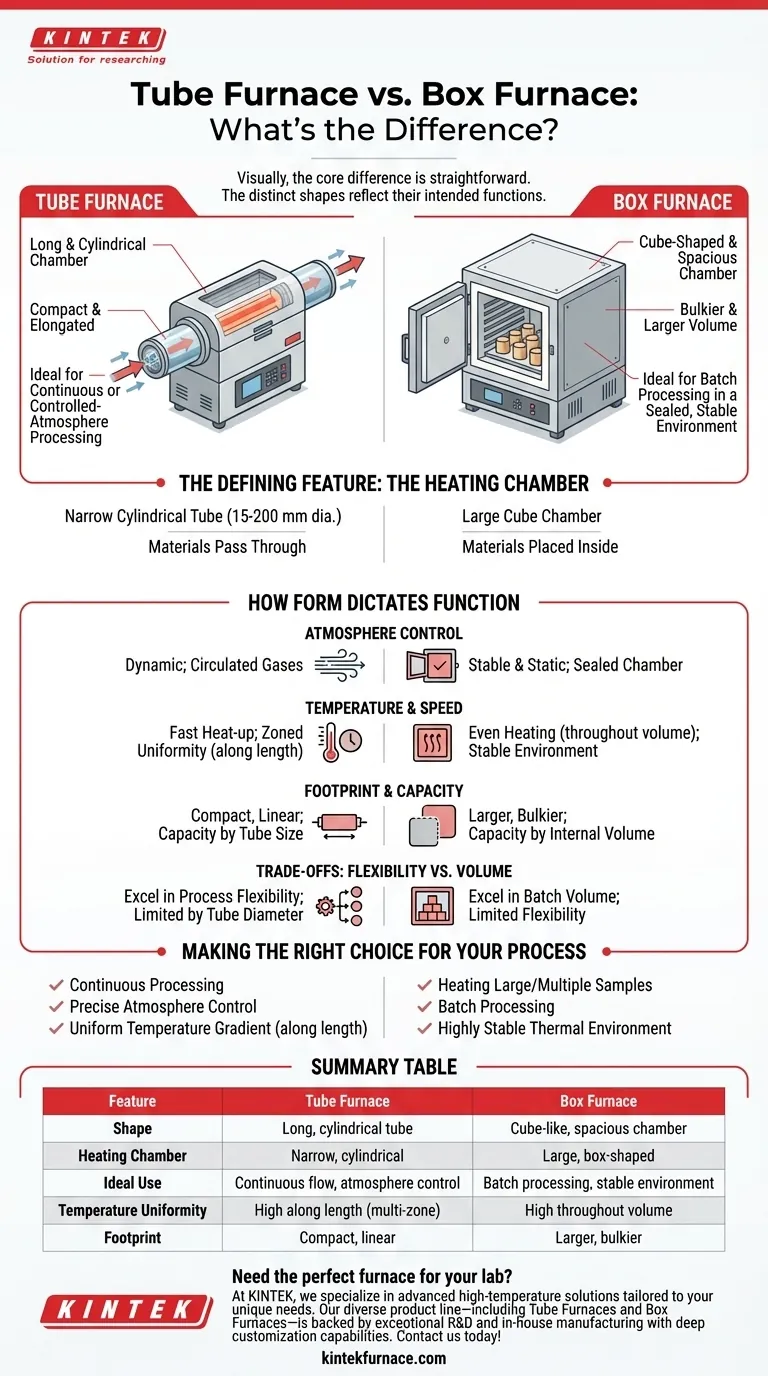
Visually, the core difference is straightforward. A tube furnace is built around a long, cylindrical chamber, making it appear compact and elongated. In contrast, a box furnace (or muffle furnace) is larger and cube-shaped, designed around a spacious internal chamber.
The distinct shapes of tube and box furnaces are not merely aesthetic; they are a direct reflection of their intended function. One is a conduit designed for continuous or controlled-atmosphere processing, while the other is a sealed chamber optimized for heating larger batches in a stable environment.

The Defining Feature: The Heating Chamber
The primary visual and functional difference between these furnaces is the design of the space where heating occurs. This fundamental design choice dictates their size, shape, and ideal application.
The Tube Furnace: A Conduit for Processing
A tube furnace is defined by its long, typically narrow, cylindrical heating chamber. These tubes can range in diameter from 15 mm to over 200 mm.
This design is ideal for processes where materials pass through the heat source. The furnace body can be oriented horizontally or vertically, and its elongated shape allows for multiple heating zones (often up to three) to create a highly uniform temperature profile along its length.
The Box Furnace: A Chamber for Batch Work
A box furnace, as its name implies, features a cube-like chamber. Its appearance is bulkier and more spacious than a tube furnace.
The entire purpose of a box furnace is to heat materials placed inside its sealed chamber. This design is optimized for batch processing—placing one or more items inside, heating them for a set duration, and then removing them.
How Form Dictates Function
The visual differences in shape and size have direct consequences for how each furnace performs in a lab or industrial setting.
Atmosphere Control
In a tube furnace, the atmosphere can be dynamic. Gases are often circulated through the tube as materials are processed, making it ideal for experiments that require specific or changing atmospheric conditions, such as work with oxygen-sensitive materials.
In a box furnace, the atmosphere is generally stable and static. The chamber is sealed to isolate the contents from the external environment, providing a consistent thermal environment.
Temperature Uniformity and Speed
Tube furnaces often provide superior temperature uniformity along their heated length, especially three-zone models. Their smaller thermal mass also allows for faster heat-up times.
Box furnaces are designed to provide excellent temperature uniformity throughout their entire internal volume, ensuring a large batch of material is heated evenly.
Physical Footprint and Capacity
The compact, linear shape of a tube furnace generally gives it a smaller footprint. Its capacity is defined by the tube's diameter and heated length.
A box furnace is physically larger and requires more space. Its capacity is measured by the internal volume of its chamber, which is designed to hold larger or more numerous samples than a typical tube furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these furnaces involves balancing processing style against capacity and environmental control.
Flexibility vs. Volume
The primary trade-off is between the tube furnace's process flexibility and the box furnace's batch volume.
A tube furnace excels at continuous flow, controlled atmospheres, and creating specific temperature gradients. However, it is limited by the small diameter of its tube.
A box furnace excels at heating large, bulky items or large quantities of smaller items simultaneously in a stable environment.
Speed vs. Stability
A tube furnace generally heats up faster due to its lower thermal mass, which can increase throughput for certain processes.
A box furnace provides a highly stable and isolated thermal environment, which is critical for processes like annealing, where slow, even heating and cooling are paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be guided entirely by the nature of your material and the requirements of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is continuous processing or precise atmosphere control: A tube furnace is the superior choice due to its flow-through design and ability to manage gas environments.
- If your primary focus is heating large or multiple samples in a single batch: A box furnace provides the volume and stable thermal environment necessary for this type of work.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly uniform temperature gradient: A multi-zone tube furnace offers unmatched control over the temperature profile along a specific length.
Ultimately, the furnace's appearance is a direct consequence of its specific engineering purpose.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Box Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Long, cylindrical tube | Cube-like, spacious chamber |
| Heating Chamber | Narrow, cylindrical | Large, box-shaped |
| Ideal Use | Continuous flow, atmosphere control | Batch processing, stable environment |
| Temperature Uniformity | High along length (multi-zone) | High throughout volume |
| Footprint | Compact, linear | Larger, bulkier |
Need the perfect furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our diverse product line—including Tube Furnaces for precise atmosphere control and Box Furnaces for efficient batch processing—is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our furnaces meet your exact experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your thermal processing efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















