In short, horizontal tube furnaces are ideal for small-scale materials testing because their design offers an exceptional balance of precise temperature and atmosphere control, ease of sample access, and a compact footprint suitable for any lab. This combination allows for rapid, repeatable, and reliable experimentation.
The true value of a horizontal tube furnace isn't just its size, but how its accessible, linear design empowers researchers to meticulously control experimental variables, making it a cornerstone for fundamental materials science.
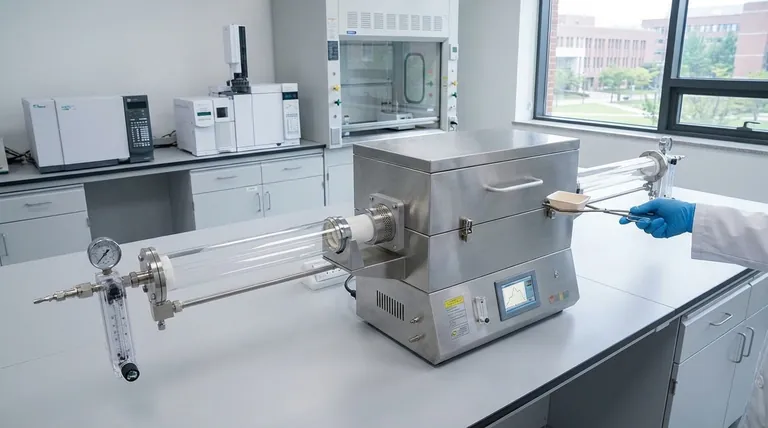

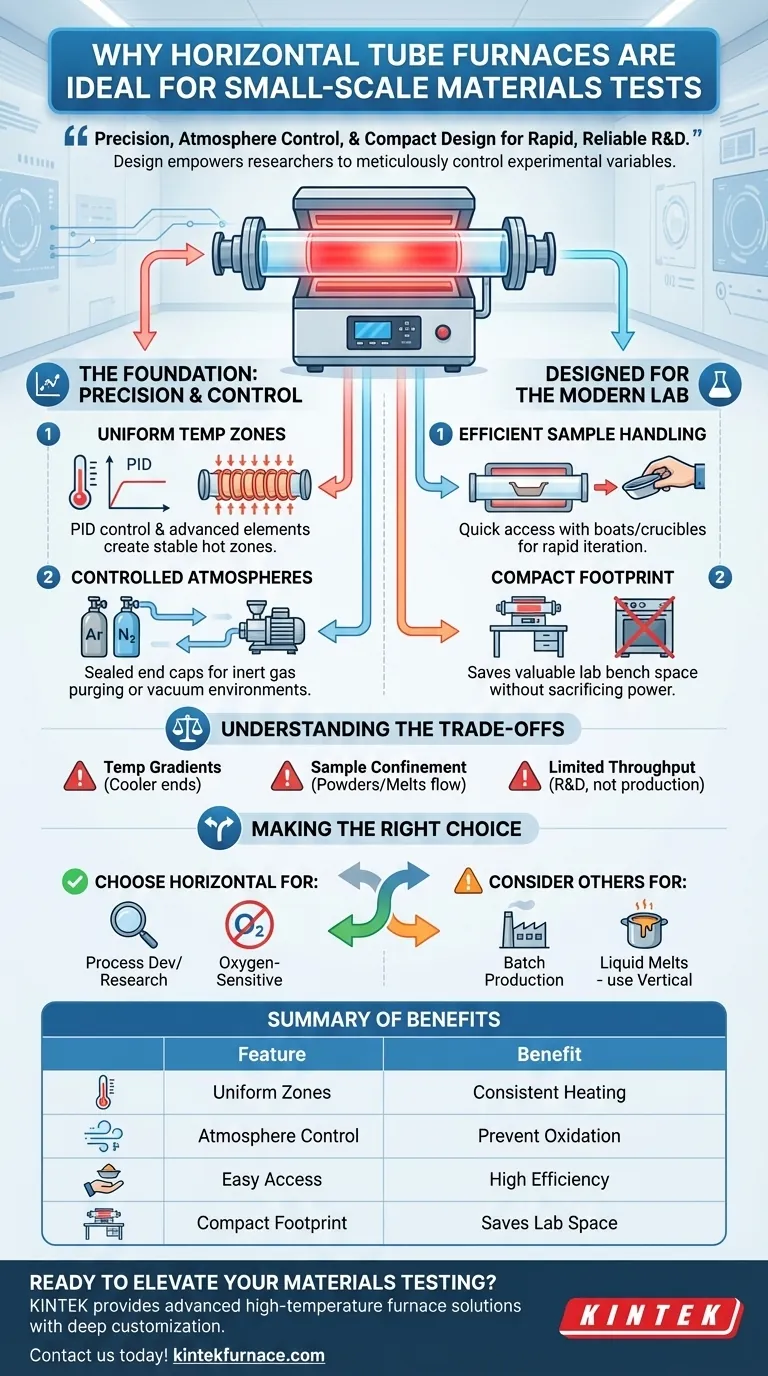
The Foundation: Precision and Control
For any materials test to be valid, the experimental conditions must be exact and repeatable. The architecture of a horizontal tube furnace is fundamentally built to deliver this control on a small scale.
Achieving Uniform Temperature Zones
A high-quality horizontal tube furnace uses advanced heating elements that encircle the process tube. Paired with a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, the system can achieve and hold a target temperature with remarkable stability.
This creates a well-defined uniform hot zone in the center of the tube, ensuring your sample is subjected to the intended thermal conditions and nothing else.
Controlled Atmospheres Made Simple
The most significant advantage is the ability to easily control the gaseous environment. The tube's ends are sealed with removable end caps or flanges.
These access points make it simple to connect gas lines for purging with inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation. They also allow for the connection of a vacuum pump to conduct tests in a low-pressure or vacuum environment.
Designed for the Modern Lab
Beyond thermal precision, the physical design addresses the practical realities of a research and development setting.
Efficiency in Sample Handling
The "easily accessible end caps" are critical for workflow. Researchers can quickly insert and retrieve samples, which are typically held in ceramic or quartz boats or crucibles.
This rapid turnaround is essential when screening multiple material compositions or iterating on a process parameter, maximizing laboratory efficiency.
A Compact Footprint
Lab bench space is always a premium asset. Horizontal tube furnaces are self-contained and have a minimal footprint compared to larger batch ovens or more complex vertical furnace systems.
This allows even small labs to possess powerful thermal processing capabilities without dedicating significant infrastructure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the horizontal orientation presents specific limitations that every user must understand to ensure valid results.
Potential for Temperature Gradients
While a central uniform zone exists, the temperature will naturally drop off toward the cooler ends of the tube. For very long samples or processes demanding exceptional uniformity over a large area, a multi-zone furnace with independent controllers for each section may be necessary.
Sample Confinement and Gravity
Gravity is a factor in a horizontal setup. Fine powders can be difficult to contain, and processes involving melting can be problematic if the sample flows. For these applications, a vertical tube furnace, where gravity helps contain the sample at the bottom of a sealed tube, is often a better choice.
Limited Sample Throughput
By their very nature, these furnaces are designed for small, individual samples. They are instruments for research and development, not for production. They are unsuited for processing large quantities or high-volume batches of material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your experimental objective.
- If your primary focus is process development or academic research: The horizontal tube furnace's ease of use, rapid sample cycling, and precise atmospheric control make it an unparalleled tool.
- If your primary focus is testing materials sensitive to oxygen: The simple and effective purging and vacuum capabilities are a primary reason to choose this design.
- If your primary focus is batch production or handling liquid melts: You should consider a larger batch oven or a vertical tube furnace to better suit your throughput and sample containment needs.
Ultimately, the horizontal tube furnace is a powerful and versatile instrument that enables precise scientific inquiry when aligned with the proper application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Uniform Temperature Zones | Ensures consistent heating for accurate experiments |
| Controlled Atmospheres | Allows inert gas or vacuum use to prevent oxidation |
| Easy Sample Access | Facilitates quick insertion and retrieval for high efficiency |
| Compact Footprint | Saves lab space while offering powerful thermal processing |
| Limitations | Not ideal for large batches or liquid melts; consider alternatives for high throughput |
Ready to elevate your materials testing with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Horizontal Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're in research, development, or small-scale processing, our furnaces deliver unmatched control and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your lab's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















