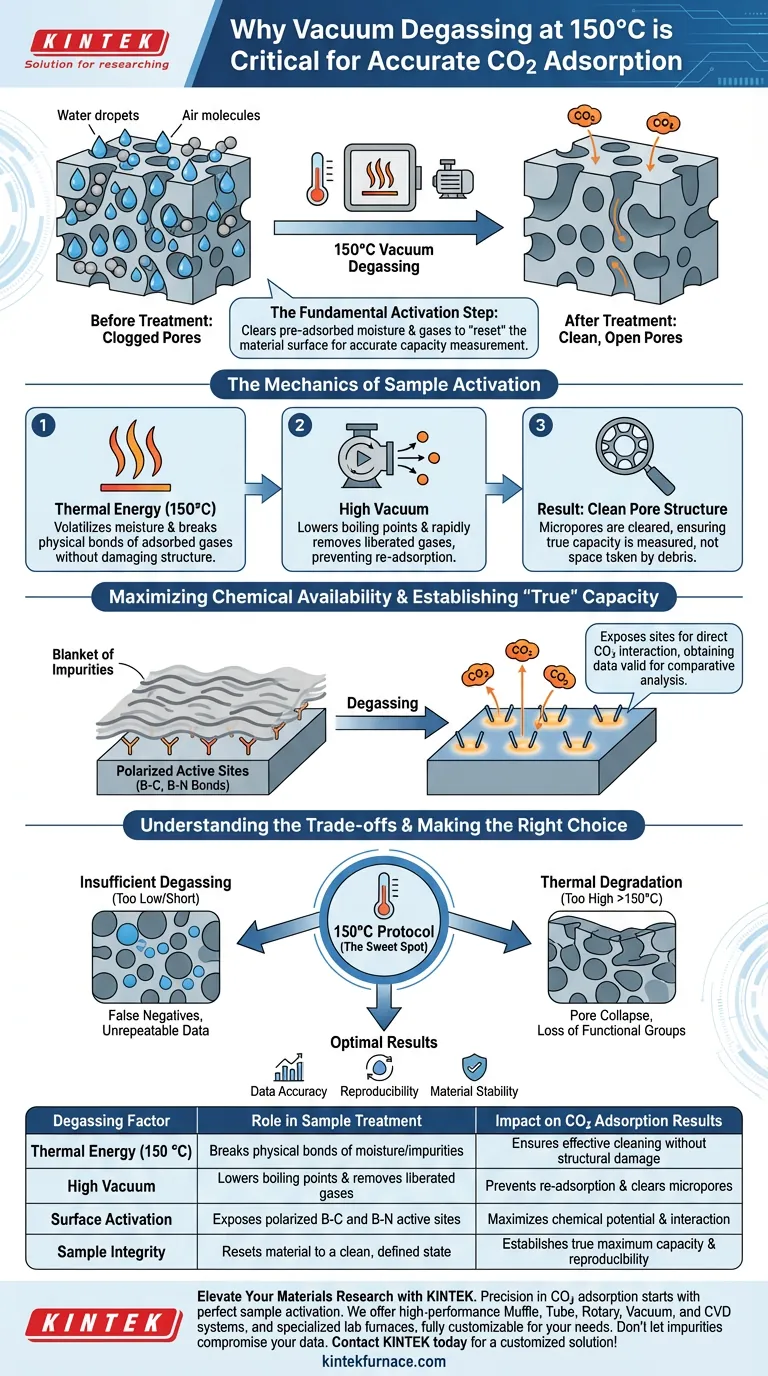
Vacuum degassing at 150 °C is the fundamental activation step required to prepare a sample for accurate CO2 adsorption analysis. This process utilizes a combination of thermal energy and low pressure to forcefully strip away pre-adsorbed moisture, air molecules, and other volatile impurities that clog the material's porous structure. By clearing these contaminants, you ensure that subsequent measurements reflect the material's true capacity rather than the limited space left over by environmental debris.
The core purpose of this treatment is to "reset" the material's surface to a clean, defined state. Without thorough degassing, impurities occupy critical adsorption sites, leading to artificially low capacity readings and unrepeatable scientific data.

The Mechanics of Sample Activation
Clearing the Pore Structure
Porous materials, such as BN@C composites, act like sponges that naturally absorb moisture and gases from the atmosphere.
Before any experiment begins, these "guest" molecules—including water vapor and air—must be evacuated. If they remain, they physically block the micropores, preventing the CO2 molecules from entering during the actual test.
The Role of Thermal Energy (150 °C)
Heat provides the kinetic energy necessary to break the weak physical bonds holding impurities to the material's surface.
At 150 °C, the energy is sufficient to volatilize moisture and physically adsorbed gases without damaging the underlying structure of the composite. This temperature strikes a balance between effective cleaning and material safety.
The Function of High Vacuum
While heat loosens the impurities, the vacuum pump is responsible for removing them entirely from the system.
By lowering the pressure surrounding the sample, the vacuum lowers the boiling point of adsorbed liquids and ensures that liberated gas molecules are immediately drawn away from the sample surface. This prevents re-adsorption and drives the cleaning process to completion.
Maximizing Chemical Availability
Exposing Polarized Active Sites
For materials designed to capture CO2, specific chemical sites drive the performance. In the case of BN@C composites, these are often polarized B-C (Boron-Carbon) and B-N (Boron-Nitrogen) bonds.
Degassing removes the "blanket" of impurities covering these bonds. This exposure allows these polarized sites to interact directly with CO2 molecules, maximizing the chemical potential of the sorbent.
Establishing the "True" Maximum Capacity
Scientific accuracy requires that you measure the material, not the material plus its contaminants.
By removing residual gases and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), the degassing process ensures that the adsorption value you record represents the material's true maximum capacity. This is the only way to obtain data that is valid for comparative analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Insufficient Degassing
If the temperature is too low or the vacuum is not maintained long enough, the activation will be incomplete.
This leaves a fraction of the pores blocked, resulting in "false negatives" where a high-performance material appears mediocre because its active sites were never fully accessible.
The Danger of Thermal Degradation
While higher temperatures might clean a surface faster, they pose a risk to the material's structural integrity.
For carbon-based composites or functionalized nanomaterials, exceeding the recommended 150 °C can cause the collapse of pore structures or the loss of surface functional groups. Strict adherence to the specific temperature profile ensures the material is cleaned, not destroyed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your adsorption experiments yield publication-quality data, apply the following guidelines:
- If your primary focus is Data Accuracy: Ensure the vacuum level is stable and the temperature is held until the pressure rise is negligible, guaranteeing a fully "clean" surface.
- If your primary focus is Reproducibility: Standardize the 150 °C pretreatment protocol across all samples to eliminate variable initial states as a source of error.
- If your primary focus is Material Stability: Do not exceed the 150 °C threshold to preserve the delicate B-C and B-N bond structures essential for CO2 interaction.
Treat the degassing phase not as a preliminary chore, but as the calibration step that defines the validity of your entire experiment.
Summary Table:
| Degassing Factor | Role in Sample Treatment | Impact on CO2 Adsorption Results |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Energy (150 °C) | Breaks physical bonds of moisture/impurities | Ensures effective cleaning without structural damage |
| High Vacuum | Lowers boiling points and removes liberated gases | Prevents re-adsorption and clears micropores |
| Surface Activation | Exposes polarized B-C and B-N active sites | Maximizes chemical potential and interaction |
| Sample Integrity | Resets material to a clean, defined state | Establishes true maximum capacity and reproducibility |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision in CO2 adsorption starts with perfect sample activation. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as specialized lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique degassing and treatment needs.
Don't let impurities compromise your scientific data. Ensure your porous materials and composites reach their true potential with our reliable thermal solutions.
Ready to optimize your lab's efficiency? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Carlos A. Castilla-Martinez, Umit B. Demirci. A boron nitride–carbon composite derived from ammonia borane and ZIF-8 with promises for the adsorption of carbon dioxide. DOI: 10.1039/d4nj00643g
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazing and what materials does it primarily join? Discover High-Purity Joining for Superior Bonds
- How do inert gas technology, airflow, and air pressure work together in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- Why is long-duration temperature stability in a sintering furnace essential for Bi-2223? Master Phase Purity
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- How does a diffusion annealing furnace enhance magnet coercivity? Boost Performance with Grain Boundary Diffusion
- What are the technical challenges of SEM in-situ furnaces? Optimize High-Temperature Dynamic Observation
- What industries commonly use high vacuum furnaces? Unlock Purity and Strength for Critical Applications
- What types of quenching can be performed in a vacuum furnace? Explore High-Pressure Gas and Oil Quenching



















