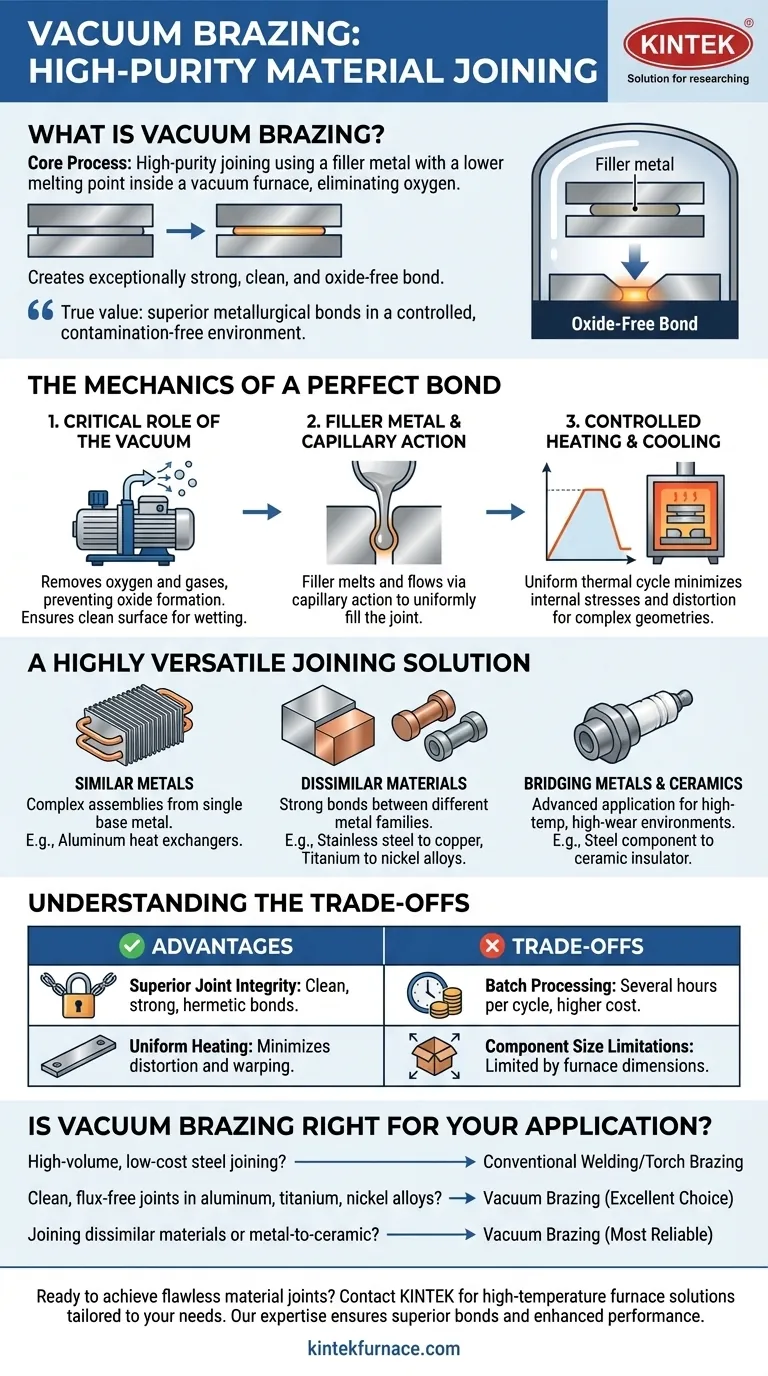
At its core, vacuum brazing is a high-purity material joining process. It uses a filler metal with a lower melting point to join two or more components inside a vacuum furnace. By heating the assembly in the absence of oxygen, the filler metal melts and flows between the parts, creating an exceptionally strong, clean, and oxide-free bond upon cooling. This method is highly versatile, used to join not only common metals like aluminum but also dissimilar materials such as stainless steel, titanium, nickel alloys, and even metal-to-ceramic combinations.
The true value of vacuum brazing lies in its ability to create superior metallurgical bonds in a controlled, contamination-free environment. This makes it the definitive choice for high-performance applications where joint integrity and material purity are non-negotiable.

The Mechanics of a Perfect Bond
To understand why vacuum brazing is so effective, we must look at the principles that govern the process. It's a precise sequence of environmental control, thermal management, and material science.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The defining feature of this process is the vacuum. By removing oxygen and other reactive gases from the furnace chamber, it completely prevents the formation of oxides on the surface of the parent materials.
This clean, oxide-free surface is essential. It allows the molten filler metal to properly "wet" and bond with the base materials, ensuring a seamless, high-integrity joint without the need for corrosive chemical fluxes.
The Filler Metal and Capillary Action
A filler metal, often an alloy designed for a specific application (like an aluminum-silicon alloy for aluminum parts), is placed at or near the joint. The entire assembly is heated to a temperature above the filler's melting point but below that of the components being joined.
Once molten, the filler metal is drawn into the tight gap between the components through a physical phenomenon called capillary action. This ensures the joint is filled completely and uniformly.
Controlled Heating and Cooling
The entire assembly is heated and cooled slowly and uniformly within the furnace. This controlled thermal cycle minimizes internal stresses and distortion, which is a significant advantage when joining complex or delicate geometries.
Upon cooling, the filler metal solidifies, forming a strong, permanent metallurgical bond between the parts. The result is a single, integrated assembly.
A Highly Versatile Joining Solution
While sometimes associated with a single material like aluminum, the true strength of vacuum brazing is its remarkable versatility across a wide range of advanced materials.
Joining Similar Metals
The process is widely used for creating complex assemblies from a single base metal. A classic example is the manufacturing of aluminum heat exchangers, where intricate fins and tubes are joined to form a single, leak-proof unit.
The Power of Joining Dissimilar Materials
Vacuum brazing excels where other methods fail: joining materials with different properties. It is a proven method for creating robust bonds between different families of metals.
This includes combinations such as stainless steel to copper, titanium to nickel alloys, and other pairings that are critical for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications.
Bridging Metals and Ceramics
Perhaps its most advanced application is the ability to join metals to ceramics. This capability is essential for producing components used in high-temperature, high-wear, or electrically insulating environments, such as bonding a steel component to a ceramic insulator.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect for every situation. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging the limitations and practical considerations of vacuum brazing.
Advantage: Superior Joint Integrity
The flux-free, oxide-free nature of the process results in exceptionally clean and strong joints. These bonds are often hermetically sealed and exhibit strength that can rival the parent materials themselves.
Advantage: Uniform Heating Minimizes Distortion
Because the entire part is heated evenly in the furnace, there are no localized "hot spots" like those created by welding or torch brazing. This dramatically reduces the risk of warping and distortion in the final assembly.
Trade-off: Batch Processing Time and Cost
Vacuum brazing is a batch process. Loading the furnace, pumping down to a vacuum, running the thermal cycle, and cooling can take several hours. This, combined with the high cost of the equipment, makes it less suitable for high-volume, low-cost production compared to automated welding.
Trade-off: Component Size Limitations
The size of the components that can be brazed is strictly limited by the internal dimensions of the vacuum furnace chamber. This is a practical constraint for very large structures.
Is Vacuum Brazing Right for Your Application?
The decision to use vacuum brazing depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for material compatibility, performance, and production scale.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost joining of standard steels: Conventional welding or torch brazing will likely be more economical and faster.
- If your primary focus is creating clean, flux-free joints in sensitive materials like aluminum, titanium, or nickel alloys: Vacuum brazing is an excellent and often necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials, especially metal-to-ceramic assemblies: Vacuum brazing is one of the most reliable and effective methods available.
By controlling the joining environment at a molecular level, vacuum brazing delivers a level of quality and material integrity that few other processes can match.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | High-purity joining using filler metal in a vacuum furnace without oxygen |
| Key Materials Joined | Aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, nickel alloys, metal-to-ceramic combinations |
| Primary Advantages | Oxide-free bonds, uniform heating, minimal distortion, high joint integrity |
| Limitations | Batch processing time, higher cost, size constraints based on furnace dimensions |
| Best For | High-performance applications requiring clean, strong joints in sensitive or dissimilar materials |
Ready to achieve flawless material joints with vacuum brazing? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or dissimilar materials, our expertise ensures superior bonds and enhanced performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-purity joining projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering



















