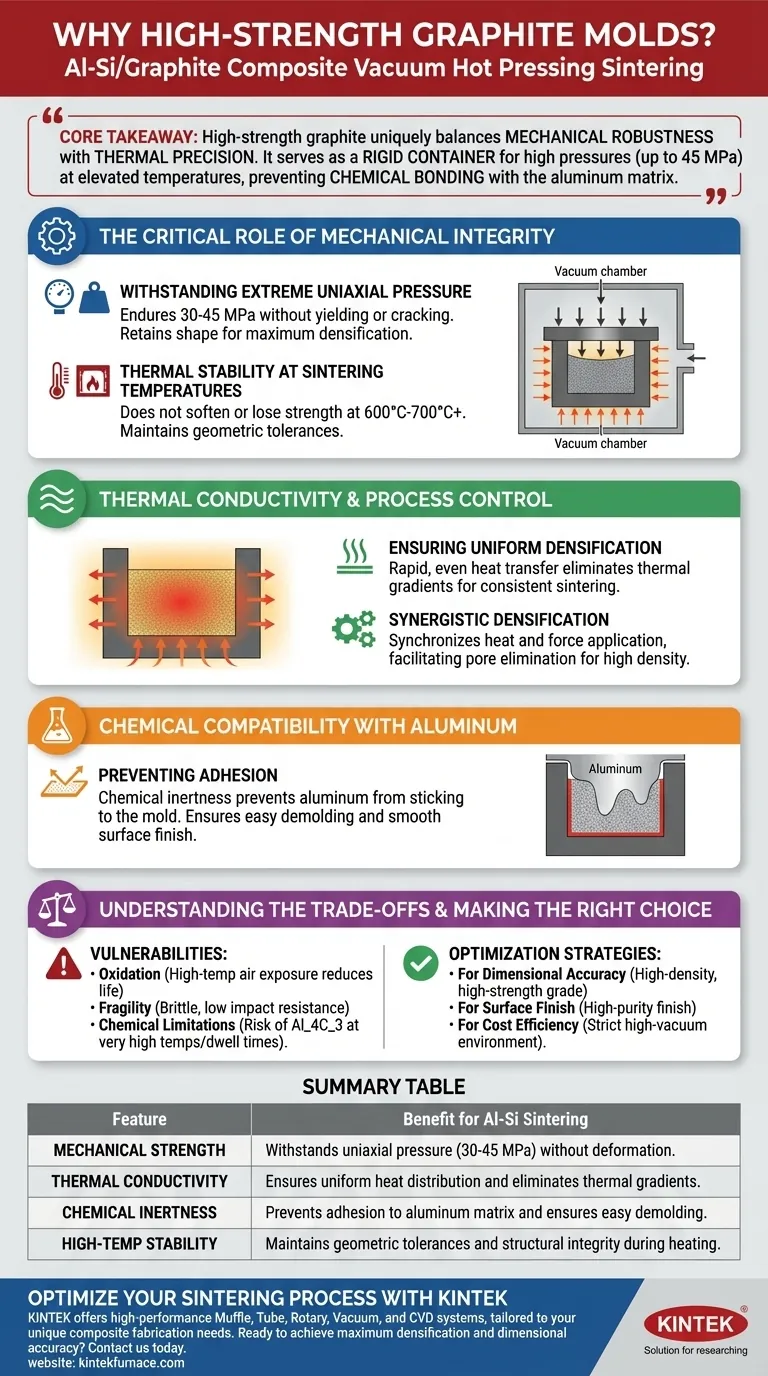
High-strength graphite is the definitive material choice for this application because it uniquely balances mechanical robustness with thermal precision. It serves as a rigid container capable of withstanding significant mechanical pressures (up to 45 MPa) at elevated temperatures without deforming, while simultaneously preventing chemical bonding with the aluminum matrix.
Core Takeaway The preference for high-strength graphite lies in its ability to maintain structural integrity under high heat and uniaxial pressure while ensuring the composite sinters evenly. Its resistance to adhering to the aluminum matrix is critical for ensuring the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the final Al-Si/graphite composite.

The Critical Role of Mechanical Integrity
Withstanding Extreme Uniaxial Pressure
In vacuum hot pressing, the mold does not just hold powder; it acts as a pressure vessel. High-strength graphite is essential because it must endure uniaxial mechanical pressures—often between 30 and 45 MPa—without yielding or cracking.
Standard materials would deform (creep) under this specific combination of force and heat, compromising the dimensions of the final part. High-strength graphite retains its shape, ensuring the applied force is effectively transmitted to the powder for maximum densification.
Thermal Stability at Sintering Temperatures
The sintering process for Al-Si composites requires elevated temperatures to promote particle rearrangement and plastic deformation. Graphite exhibits exceptional thermal stability, meaning it does not soften or lose strength when heated to these processing ranges (typically 600°C–700°C for Aluminum alloys, though graphite can withstand much higher).
This stability ensures that the geometric tolerances of the "green body" (the compressed powder) are maintained throughout the entire heating cycle.
Thermal Conductivity and Process Control
Ensuring Uniform Densification
One of the most critical challenges in sintering is uneven heating, which leads to internal stress and warping. Graphite possesses excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to transfer heat from the furnace environment (or induction coils) to the powder core rapidly and evenly.
By eliminating thermal gradients, the mold ensures that the aluminum-silicon alloy particles and graphite reinforcements sinter at the same rate throughout the sample volume.
Synergistic Densification
The vacuum hot press relies on the simultaneous application of heat and force. The graphite mold acts as the medium that synchronizes these two forces.
It transfers the hydraulic pressure while conducting the heat, facilitating the elimination of microscopic pores and resulting in a high-density composite material.
Chemical Compatibility with Aluminum
Preventing Adhesion
Aluminum is a highly reactive metal, particularly in its liquid or semi-solid state, and tends to stick to mold walls. A key advantage of graphite is its chemical inertness relative to the aluminum matrix.
It does not easily adhere to or react severely with the aluminum at sintering temperatures. This "non-stick" characteristic allows for easier demolding and ensures the surface of the final composite remains smooth and defect-free.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vulnerability to Oxidation
While graphite is robust in a vacuum, it is highly susceptible to oxidation if exposed to air at high temperatures. The service life of a graphite mold drops precipitously (e.g., from 30+ uses to 4-5 uses) if the vacuum integrity is compromised or if used in an oxygen-rich atmosphere.
Fragility and Handling
Despite its high compressive strength, graphite is a brittle ceramic-like material. It has low impact resistance. Accidental drops or misalignment of the press rams can easily fracture the mold, leading to sudden failure under load.
Chemical Limitations
While graphite is generally inert with aluminum, at very high temperatures or extended dwell times, there is a risk of forming Aluminum Carbide ($Al_4C_3$), a brittle and unwanted phase. Process parameters must be strictly controlled to prevent this reaction at the interface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting mold materials for Al-Si composites, your priorities dictate your process parameters.
- If your primary focus is Dimensional Accuracy: Prioritize high-density, high-strength graphite grades to minimize mold deformation under the 45 MPa pressure limit.
- If your primary focus is Surface Finish: Ensure the graphite mold has a high-purity finish to prevent minor chemical interactions and sticking at the interface.
- If your primary focus is Cost Efficiency: Strictly maintain a high-vacuum environment to prevent oxidation, extending the reusable life of the mold from single-digits to over 30 cycles.
Ultimately, high-strength graphite is the industry standard because it is the only material that acts as both a thermal conductor and a high-pressure structural container without chemically contaminating the aluminum alloy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Al-Si Sintering |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Withstands uniaxial pressure (30-45 MPa) without deformation |
| Thermal Conductivity | Ensures uniform heat distribution and eliminates thermal gradients |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents adhesion to aluminum matrix and ensures easy demolding |
| High-Temp Stability | Maintains geometric tolerances and structural integrity during heating |
Optimize Your Sintering Process with KINTEK
Precision material processing requires the right equipment and expertise. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable lab high-temp furnaces tailored to your unique composite fabrication needs.
Ready to achieve maximum densification and dimensional accuracy in your lab? Contact us today to discover how our specialized heating solutions can elevate your research and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Ultra High Vacuum Stainless Steel KF ISO CF Flange Pipe Straight Pipe Tee Cross Fitting
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision laboratory press used for TiB2-based composite ceramics? Ensure Flawless Green Body Preparation
- What are the technical advantages of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) for maraging steel? Achieve Rapid Densification
- What is a vacuum hot press and what is its primary function? Unlock Advanced Materials Processing
- What are the core functions of a vacuum hot pressing furnace in the densification of Cr2AlC ceramics?
- How does the vacuum system in these furnaces work? Achieve Purity and Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- How does the application of mechanical pressure contribute to the vacuum hot pressing formation of TiAl/Ti6Al4V? Expert Analysis
- What advantages does a Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system offer over traditional hot pressing? Boost SnSe Efficiency
- What are the technical advantages of using an SPS sintering furnace? Elevate Al2O3-TiC Material Performance



















