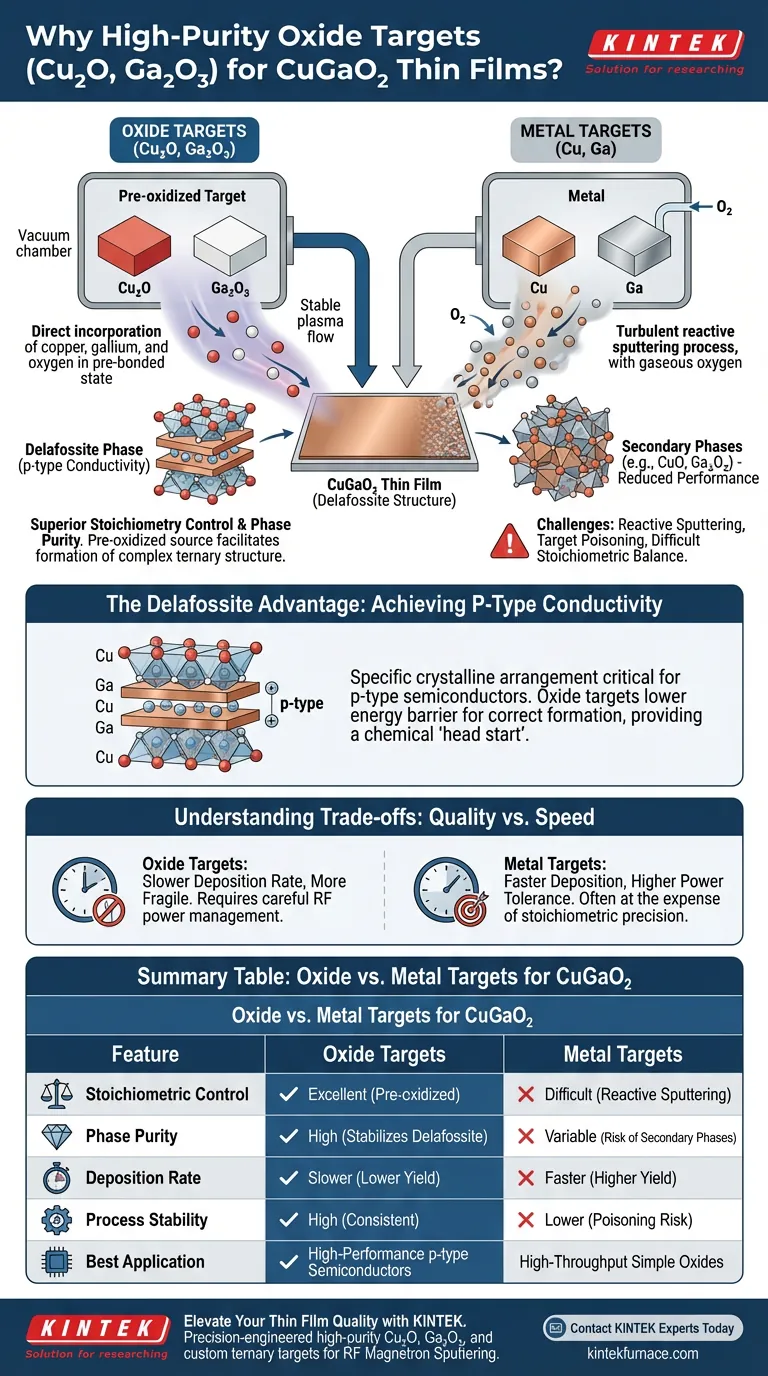
The fundamental reason for choosing high-purity oxide targets like Cu2O and Ga2O3 is the superior control they offer over the chemical stoichiometry and phase purity of the resulting thin films. Unlike metal targets, oxide targets allow for the direct incorporation of oxygen into the sputtering process, which is critical for forming the specific delafossite structure required for p-type semiconductor performance.
Using oxide targets simplifies the deposition of complex ternary compounds by providing a pre-oxidized source material. This ensures that the ratio of copper, gallium, and oxygen remains consistent, facilitating the growth of high-quality CuGaO2 films with predictable electronic properties.

The Challenge of Stoichiometric Precision
The Complexity of Ternary Oxides
Creating CuGaO2 is more difficult than simple binary oxides because it requires a precise 1:1 ratio of Copper to Gallium within an oxygen-rich lattice.
When using metallic targets, the process relies on reactive sputtering, where oxygen gas is introduced into the chamber to react with the metal atoms.
This reactive process is notoriously difficult to balance, often leading to "target poisoning" or films that are either metal-rich or oxygen-deficient.
Advantages of Pre-Oxidized Sources
High-purity oxide targets (Cu2O and Ga2O3) provide a stable source where the metal-to-oxygen bonds already exist.
This minimizes the reliance on the gaseous oxygen environment during the RF magnetron sputtering process.
The result is a more repeatable deposition process that accurately mirrors the chemical composition of the target material in the final thin film.
Facilitating the Delafossite Phase
Achieving P-Type Conductivity
The delafossite phase is a specific crystalline arrangement that enables p-type conductivity in wide-bandgap semiconductors.
Small deviations in oxygen content or metal ratios can easily lead to the formation of secondary phases, such as CuO or Ga2O3, which destroy the desired electrical properties.
By using oxide targets, researchers can more easily tune the process parameters to stabilize the CuGaO2 phase.
Thermodynamics of Phase Formation
Sputtering from oxide targets lowers the energy barrier for forming the correct ternary crystal structure.
Because the components arrive at the substrate in an oxidized state, they are more likely to organize into the delafossite lattice during growth or subsequent annealing.
This chemical "head start" is often the difference between a functional semiconductor and a high-resistance amorphous film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sputtering Yield and Deposition Rate
One significant trade-off is that oxide targets typically have lower sputtering yields than pure metal targets.
This results in slower deposition rates, which can increase the time required to grow films of a specific thickness.
However, for high-performance electronics, the gain in film quality and electrical consistency far outweighs the loss in production speed.
Target Fragility and Thermal Stress
Oxide ceramics are more brittle than metals and are prone to cracking under high thermal loads.
This requires careful management of the RF power applied to the magnetron to prevent target failure.
Using metal targets might allow for higher power densities, but the resulting films often lack the stoichiometric precision needed for advanced applications.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is phase purity and p-type performance: Use high-purity Cu2O and Ga2O3 targets to ensure the correct delafossite structure is achieved.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production of simple oxides: Metal targets with reactive sputtering may be viable, though they are rarely recommended for complex ternary materials like CuGaO2.
- If your primary focus is researching defect chemistry: Oxide targets allow you to precisely vary the oxygen flow rate to study how small stoichiometric changes affect hole mobility.
By prioritizing stoichiometric control through the use of oxide targets, you ensure the technical integrity and functional performance of your CuGaO2 thin films.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Oxide Targets (Cu2O/Ga2O3) | Metal Targets (Cu/Ga) |
|---|---|---|
| Stoichiometric Control | Excellent (Pre-oxidized source) | Difficult (Requires reactive sputtering) |
| Phase Purity | High (Stabilizes delafossite structure) | Variable (Risk of secondary phases) |
| Deposition Rate | Slower (Lower sputtering yield) | Faster (Higher sputtering yield) |
| Process Stability | High (Consistent chemical ratios) | Lower (Prone to target poisoning) |
| Best Application | High-performance p-type semiconductors | High-throughput simple oxides |
Elevate Your Thin Film Quality with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when developing advanced delafossite semiconductors. At KINTEK, we understand that the integrity of your CuGaO2 thin films depends on the purity and reliability of your source materials.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-purity Cu2O, Ga2O3, and custom ternary targets specifically designed for RF Magnetron Sputtering. Whether you need Muffle, Tube, or Vacuum systems, our lab solutions are fully customizable to meet your unique research requirements.
Ready to achieve superior phase purity and electrical consistency?
Contact KINTEK Experts Today to source your high-performance materials and equipment.
Visual Guide
References
- Akash Hari Bharath, Kalpathy B. Sundaram. Deposition and Optical Characterization of Sputter Deposited p-Type Delafossite CuGaO2 Thin Films Using Cu2O and Ga2O3 Targets. DOI: 10.3390/ma17071609
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a lab furnace? Find Your Perfect Match
- What are the main advantages of crucible furnaces? Unmatched Flexibility for Small-Scale Melting
- How does increasing the soaking zone temperature in a walking-beam furnace affect Titanium/Steel clad plates?
- What is the function of a ball mill in the raw material pretreatment stage for the szaibelyite vacuum thermal reduction process?
- What is the role of industrial drying ovens equipped with fan systems in the convective hot air drying of fruit materials? Boost Quality & Preserve Nutrients
- Why is a forced convection drying oven required for concrete moisture experiments? Achieve Precise Baseline Accuracy
- Why is SF6 gas utilized as the primary inhibitor in AS-ALD on ZrO2? Master Defect-Based Passivation Strategy
- Why is determining the hypercooling limit necessary when measuring the heat of fusion? Optimize Your Material Research



















