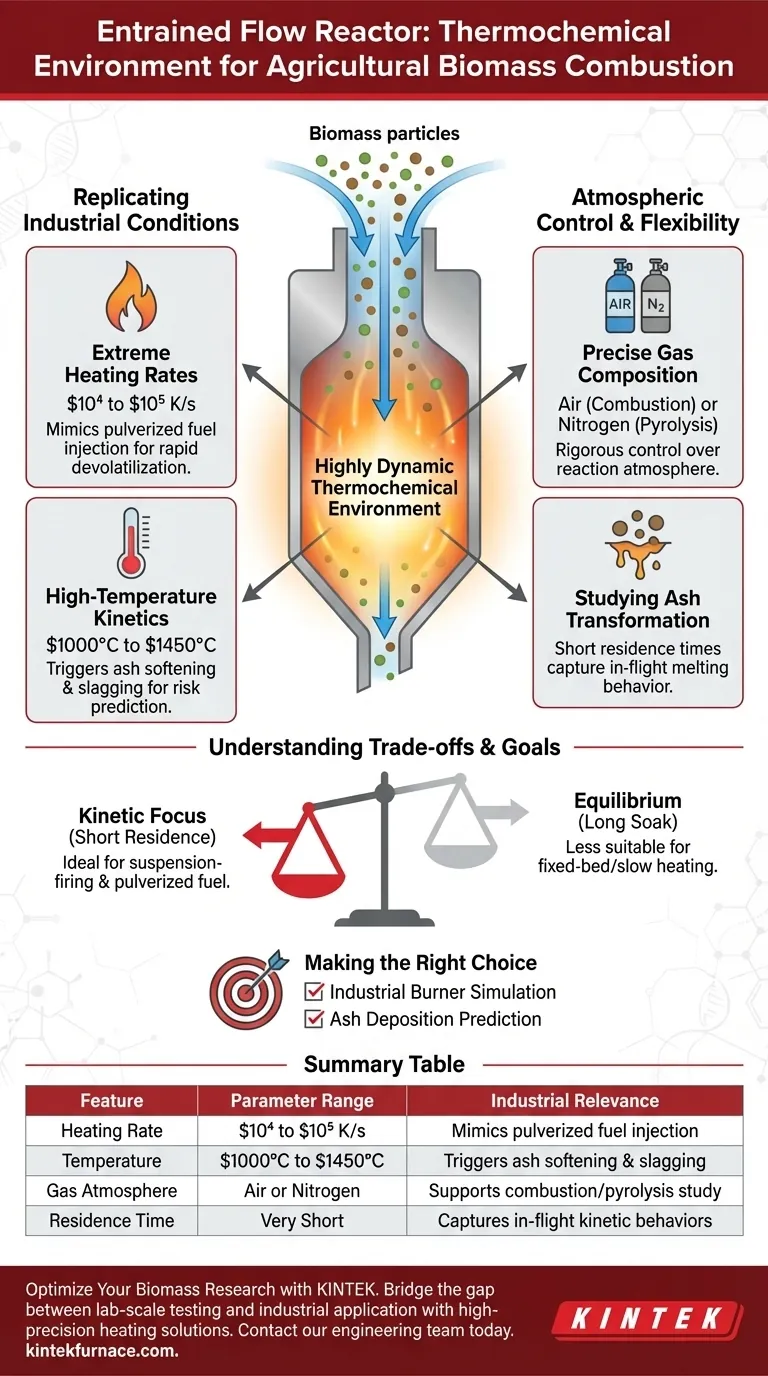
An entrained flow reactor provides a highly dynamic thermochemical environment designed to replicate the aggressive conditions found in industrial-scale burners. Specifically, it subjects agricultural biomass to ultra-rapid heating rates of $10^4$ to $10^5$ K/s and high temperatures ranging from $1000^\circ$C to $1450^\circ$C. This setup combines these thermal extremes with short residence times to isolate rapid kinetic behaviors.
By simulating the extreme kinetic conditions of industrial furnaces, entrained flow reactors allow researchers to isolate and observe ash transformation and melting behaviors that are impossible to replicate in static or slow-heating environments.

Replicating Industrial Conditions
Extreme Heating Rates
The defining characteristic of this reactor is its ability to achieve heating rates between $10^4$ and $10^5$ K/s.
This rapid thermal shock mimics the injection of pulverized fuel into a commercial burner. It ensures that the biomass undergoes devolatilization and combustion on a timescale relevant to actual power generation.
High-Temperature Kinetics
The reactor operates within a strictly controlled temperature window of $1000^\circ$C to $1450^\circ$C.
This range is critical for agricultural biomass research. It deliberately pushes the fuel into the thermal zone where inorganic matter (ash) begins to soften, melt, or transform, allowing for the prediction of slagging and fouling risks.
Atmospheric Control and Flexibility
Precise Gas Composition
The equipment allows for rigorous control over the reaction atmosphere.
Researchers can introduce air to simulate standard combustion conditions. Alternatively, the environment can be switched to nitrogen to study pyrolysis (thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen).
Studying Ash Transformation
The combination of specific gas environments and high temperatures is utilized to study ash transformation.
Because the residence time is short, the reactor captures the specific melting behavior of ash particles while they are in flight. This provides data on how agricultural residues will behave physically before they settle or deposit on boiler surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Kinetic Focus vs. Equilibrium
The environment provided is specialized for extreme kinetic conditions and short residence times.
Consequently, this setup is less suitable for studying processes that require long thermal "soak" times or slow heating profiles, such as fixed-bed combustion or charcoal production. The data derived is specific to suspension-firing or pulverized fuel applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if the data from an entrained flow reactor applies to your specific biomass project, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is Industrial Burner Simulation: This environment is ideal as it accurately replicates the rapid heating rates and short flight times of commercial suspension firing.
- If your primary focus is Ash Deposition Prediction: The ability to control temperatures up to $1450^\circ$C makes this the correct tool for analyzing melting behavior and slagging potential.
This reactor connects laboratory-scale experiments with industrial reality by prioritizing the time-temperature history of the fuel particle.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Parameter Range | Industrial Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | $10^4$ to $10^5$ K/s | Mimics pulverized fuel injection |
| Temperature | $1000^\circ$C to $1450^\circ$C | Triggers ash softening & slagging |
| Gas Atmosphere | Air or Nitrogen | Supports combustion or pyrolysis study |
| Residence Time | Very Short | Captures in-flight kinetic behaviors |
Optimize Your Biomass Research with KINTEK
Bridge the gap between lab-scale testing and industrial application. KINTEK provides high-precision heating solutions and customizable furnace systems tailored to your specific biomass and kinetic research needs. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to withstand extreme temperatures and specialized atmospheric requirements.
Ready to elevate your material testing? Contact our engineering team today to discuss your unique experimental parameters and discover how our customizable high-temp furnaces can deliver the precise thermal control your research demands.
Visual Guide
References
- Samarthkumar Pachchigar, Marcus Öhman. Ash Transformation during Combustion of Agricultural Biomass in Entrained Flow Conditions with a Focus on Phosphorus. DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.4c05064
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a laboratory electric drying oven in sample prep? Ensure Pure, Grinder-Ready Powders
- Why are graphite molds preheated to 800 °C for Invar 36 casting? Unlock High-Quality Ingot Production
- How do high-temp furnaces influence LTO sintering? Optimize Lithium Titanate Performance via Precision Control
- How does the analysis of optimized process paths assist in lab equipment selection? Expert Guide for Research Success
- Why is a laboratory oven used for constant temperature treatment of celadon? Ensure Peak Measurement Accuracy
- Why is a stainless steel high-pressure autoclave essential for starch hydrogenation? Unlock Peak Reaction Efficiency
- What is the function of a heated tundish in a metal powder production system? Optimize Flow and Thermal Consistency
- What is the function of a laboratory hot air drying oven in TiO2 treatment? Ensure Uniform Nanoparticle Quality



















