Analyzing optimized process paths provides a blueprint for successful laboratory equipment selection by grounding purchasing decisions in proven methodologies. By examining the specific workflows of successful research in complex fields like catalysis and energy materials, you can identify the exact equipment specifications—such as thermal limits or pressure tolerances—required to replicate or improve upon those results.
By comparing the technical specifications of critical equipment used in established, high-performing research, you can eliminate guesswork and build a laboratory infrastructure explicitly designed to support your experimental goals.
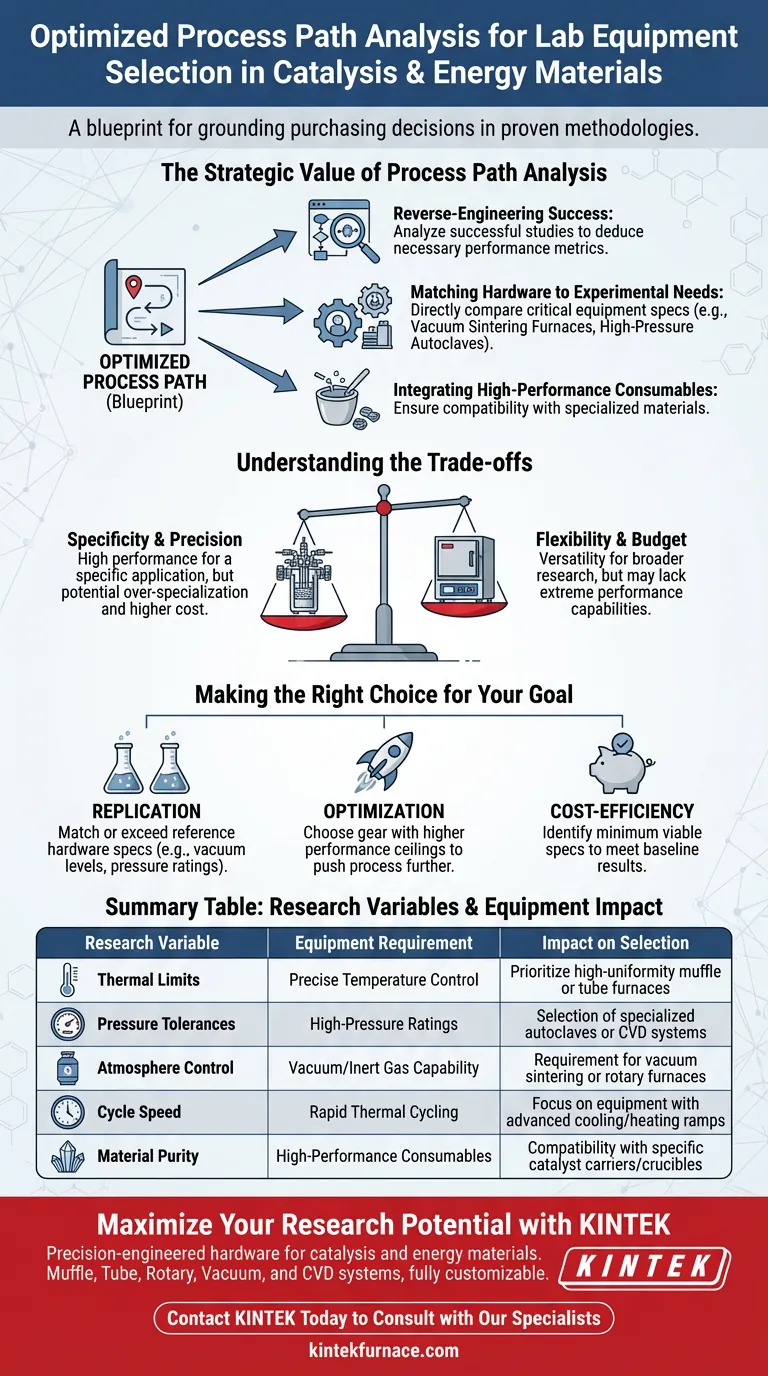
The Strategic Value of Process Path Analysis
Reverse-Engineering Success
In fields like catalysis, the difference between success and failure often lies in the precise control of environmental variables. Analyzing an optimized process path allows you to reverse-engineer these variables.
If a successful study utilized a specific method, you can deduce the necessary performance metrics for your hardware. This moves equipment selection from a general search to a targeted pursuit of specific capabilities.
Matching Hardware to Experimental Needs
Once the method is understood, you can directly compare specifications of critical equipment types, such as vacuum sintering furnaces or high-pressure autoclaves.
For example, if the optimized path requires rapid thermal cycling, a standard furnace will be insufficient. You would instead prioritize a vacuum sintering furnace known for precise temperature uniformity and control.
Integrating High-Performance Consumables
Equipment selection is not limited to heavy machinery; it extends to the consumables that interact with your samples.
Successful process paths often rely on high-performance consumables, such as specific catalyst carriers. Recognizing the role these components play ensures you select compatible equipment that can accommodate these specialized materials without degradation or interference.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Specificity vs. Flexibility
Optimizing your lab based on a specific process path ensures high performance for that specific application. However, this can lead to over-specialization. Equipment perfectly tuned for one type of energy material synthesis may lack the versatility required for broader, exploratory research.
The Cost of Precision
Equipment capable of meeting the rigorous specifications of an optimized process path—such as autoclaves with extreme pressure ratings—often comes at a premium.
You must balance the need for these high-end specifications against your budget. Ask yourself if the "optimized" path is the only path, or if a slightly less rigorous specification can still yield acceptable results for your specific objectives.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this analysis effectively, categorize your primary objective:
- If your primary focus is Replication: Select equipment that matches or exceeds the specifications of the hardware used in the reference research, specifically focusing on critical variables like vacuum levels or autoclave pressure ratings.
- If your primary focus is Optimization: Analyze where the reference equipment may have been a limiting factor and choose new gear that offers higher performance ceilings to push the process further.
- If your primary focus is Cost-Efficiency: Identify the minimum viable specifications in the successful process path and select the most affordable equipment that meets that baseline, avoiding unnecessary features.
Leveraging proven process paths transforms equipment selection from a gamble into a calculated strategic investment.
Summary Table:
| Research Variable | Equipment Requirement | Impact on Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Limits | Precise Temperature Control | Prioritize high-uniformity muffle or tube furnaces |
| Pressure Tolerances | High-Pressure Ratings | Selection of specialized autoclaves or CVD systems |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum/Inert Gas Capability | Requirement for vacuum sintering or rotary furnaces |
| Cycle Speed | Rapid Thermal Cycling | Focus on equipment with advanced cooling/heating ramps |
| Material Purity | High-Performance Consumables | Compatibility with specific catalyst carriers/crucibles |
Maximize Your Research Potential with KINTEK
Don't leave your experimental outcomes to chance. KINTEK empowers researchers in catalysis and energy materials by providing the precision-engineered hardware required to execute optimized process paths.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique thermal and pressure specifications. Whether you are replicating established studies or pushing the boundaries of material science, our team ensures your laboratory infrastructure is a catalyst for innovation, not a limitation.
Ready to bridge the gap between process design and performance?
Contact KINTEK Today to Consult with Our Specialists
Visual Guide
References
- Enhanced Methanol Production Through Photo‐Assisted CO<sub>2</sub> Hydrogenation Using Au@In<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> Core‐Shell Structures. DOI: 10.1002/cnma.202500129
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory vacuum oven required for GO slurry? Preserving Chemical Integrity in Graphene Oxide Dehydration
- Why is a glove box necessary for aluminum foil pre-lithiation? Ensure Purity in Anode Development
- What are the three types of dental ceramics? A Guide to Material Selection
- Why use a hydraulic press for szaibelyite briquetting? Boost Vacuum Reduction Efficiency & Throughput
- How does a solvothermal reactor contribute to silver nanowires synthesis? Precision Growth for High-Aspect-Ratio AgNWs
- Why is a high-precision furnace required for Li22Sn5 synthesis? Ensure Pure-Phase Alloy Stability
- Why is Copper (Cu) introduced as a flux in AlN single crystal growth? Enhance Source Stability and Yield
- What is the core function of a drying furnace in mold preparation? Build High-Strength Inorganic Silicate Molds



















